Calculating Ohm's Law Resistance
 Examples of solving simple electrical problems are shown. Almost every calculation is illustrated with a circuit diagram, a sketch of the relevant equipment. With the help of articles from this new section of the site, you can easily solve practical problems from the basics of electrical engineering, even without having a special education in electrical engineering.
Examples of solving simple electrical problems are shown. Almost every calculation is illustrated with a circuit diagram, a sketch of the relevant equipment. With the help of articles from this new section of the site, you can easily solve practical problems from the basics of electrical engineering, even without having a special education in electrical engineering.
The practical calculations presented in the article show how deeply electrical engineering has penetrated into our lives and what invaluable and irreplaceable services electricity provides us. Electrical engineering surrounds us everywhere and we encounter it every day.
This article discusses calculations of simple DC circuits, namely calculations of Ohm's resistance... Ohm's law expresses the relationship between the electric current I, voltage U and resistance r: I = U / r For more information on Ohm's law for a section of a circuit, see here.
Examples. 1. An ammeter is connected in series with the lamp. The voltage of the lamp is 220 V, its power is unknown. The ammeter shows current Az = 276 mA.What is the resistance of the filament of the lamp (the connection diagram is shown in Fig. 1)?
Let's calculate the resistance according to Ohm's law:
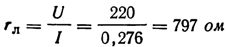
Bulb power P = UI = 220 x 0.276=60 watts
2. The current flows through the coil of the boiler Az = 0.5 A at a voltage U = 220 V. What is the resistance of the coil?
Payment:
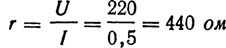
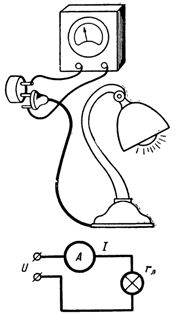
Rice. 1. Sketch and diagram for example 2.
3. An electric heating pad with a power of 60 W and a voltage of 220 V has three degrees of heating. At maximum heating, a maximum current of 0.273 A passes through the pillow. What is the resistance of the heating pad in this case?
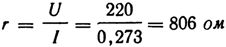
Of the three resistance steps, the smallest one is calculated here.
4. The heating element of an electric furnace is connected to a 220 V network through an ammeter that shows a current of 2.47 A. What is the resistance of the heating element (Fig. 2)?
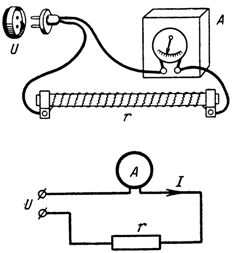
Rice. 2. Sketch and diagram for the calculation of Example 4
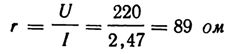
5. Calculate the resistance r1 of the entire rheostat if, when turning on stage 1, current Az = 1.2 A flows through the circuit, and at the last stage 6, current I2 =4.2 A at generator voltage U =110 V (Fig. 3). If the rheostat motor is in stage 7, the current Az flows through the entire rheostat and payload r2.
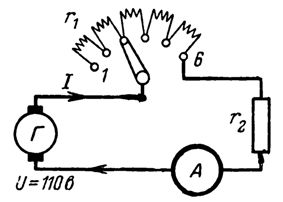
Rice. 3. Calculation scheme from example 5
The current is the smallest and the circuit resistance is the largest:
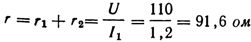
When the motor is positioned at stage 6, the rheostat is disconnected from the circuit and current flows through the payload only.
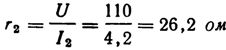
The resistance of the rheostat is equal to the difference between the total resistance of the circuit r and the resistance of the users r2:
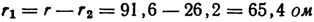
6. What is the resistance of the current circuit if it is broken? In fig. 4 shows a break in one wire of the iron cable.
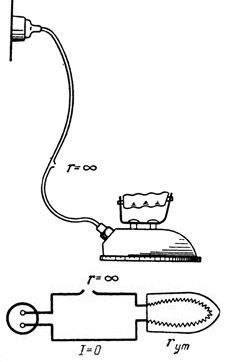
Rice. 4. Sketch and diagram for example 6
An iron with a power of 300 W and a voltage of 220 V has a resistance rut = 162 ohms. The current passing through the iron in working condition
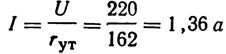
An open circuit is a resistance that approaches an infinitely large value, denoted by the sign ∞… There is a huge resistance in the circuit and the current is zero:
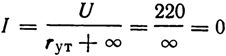
The circuit can be de-energized only in the case of an open circuit. (The same result will be if the spiral breaks.)
7. How is Ohm's law expressed in a short circuit?
The diagram in fig. 5 shows a board with resistance rpl connected via the cable to the socket and wiring with fuses P. When connecting two wires of the wiring (due to poor insulation) or connecting them through an object K (knife, screwdriver) that has practically no resistance, a short circuit occurs. This generates a large current through connection K, which, in the absence of P fuses, can lead to dangerous heating of the wiring.
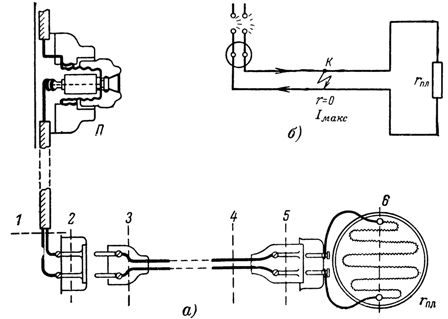
Rice. 5. Sketch and diagram of connecting tiles to a socket
A short circuit can occur in points 1 - 6 and many other places. In normal operating condition, the current I = U / rpl cannot be more than the permissible current for this wiring. With more current (less resistance rpl) fuses fuses burn. In a short circuit, the current increases to an enormous value as the resistance r tends to zero:
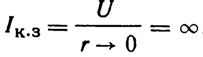
In practice, however, this condition does not occur, as blown fuses interrupt the electrical circuit.
