Technical diagnostics and methods of technical diagnostics
 Technical diagnostics — the field of knowledge covering the theory, methods and means of determining the technical condition of the object. The purpose of technical diagnostics in the general maintenance system is to reduce the volume of costs at the operational stage due to targeted repairs.
Technical diagnostics — the field of knowledge covering the theory, methods and means of determining the technical condition of the object. The purpose of technical diagnostics in the general maintenance system is to reduce the volume of costs at the operational stage due to targeted repairs.
Technical diagnostics — the process of determining the technical condition of the object. It is subdivided into test, functional and express diagnostics.
Periodic and planned technical diagnostics allows:
-
carries out incoming control of aggregates and spare units when purchasing them;
-
to minimize sudden unplanned shutdowns of technical equipment;
-
managing equipment aging.
The comprehensive diagnosis of the technical condition of the equipment makes it possible to solve the following tasks:
-
to carry out repairs according to the actual condition;
-
increase the average time between repairs;
-
reducing the consumption of parts during the operation of various equipment;
-
reducing the amount of spare parts;
-
reduction of repair duration;
-
improving the quality of repairs and eliminating secondary damage;
-
extend the life of operational equipment on a rigorous scientific basis;
-
to increase safety in the operation of energy equipment:
-
reducing the consumption of fuel and energy resources.

Test technical diagnostics — this is diagnostics in which test influences are applied to the object (for example, determining the degree of insulation wear of electrical machines by changing the tangent of the angle of dielectric losses when voltage is applied to the winding of the motor from the alternating current bridge ) .
Functional technical diagnostics — this is diagnostics in which the parameters of an object are measured and analyzed during its operation, but for its intended purpose or in a special mode, for example, determining the technical condition of rolling bearings by changing vibrations during operation of electrical machines.
Express diagnostics — this is diagnostics based on a limited number of parameters in a predetermined time.
Object of technical diagnostics — a product or its constituent parts to be (subjected to) diagnostics (control).
Technical condition — this is a condition that is characterized at a certain point in time under certain environmental conditions by the values of the diagnostic parameters established by the technical documentation for the object.
Tools for technical diagnostics — equipment and programs with the help of which diagnostics (control) are carried out.
Built-in technical diagnostics — these are diagnostic tools that are an integral part of the site (for example, gas relays in transformers for voltage 100 kV).
External devices for technical diagnostics — these are diagnostic devices made structurally separate from the site (for example, a vibration control system of oil transfer pumps).
System of technical diagnostics — a set of tools, objects and contractors necessary to carry out diagnostics according to the rules established by the technical documentation.
Technical diagnostics — the result of the diagnosis.
Forecasting the technical condition is the determination of the technical condition of the object with a given probability for the upcoming time interval during which the working (non-working) state of the object will remain.
Algorithm for technical diagnostics — a set of prescriptions that determine the sequence of actions when performing diagnostics.
Diagnostic model — a formal description of the object that is needed to solve the diagnostic problems. The diagnostic model can be represented as a set of graphs, tables or standards in the diagnostic space.

There are different methods of technical diagnostics:
Visual-optical method filled with magnifying glass, endoscope, caliper and other simple devices. This method is used, as a rule, constantly, conducting external inspections of the equipment during its preparation for work or in the process of technical inspections.
Vibroacoustic method performed with various instruments for measuring vibrations. Vibration is assessed by vibration displacement, vibration velocity, or vibration acceleration.The evaluation of the technical condition by this method is carried out by the general level of vibrations in the frequency range 10 — 1000 Hz or by frequency analysis in the range 0 — 20 000 Hz.
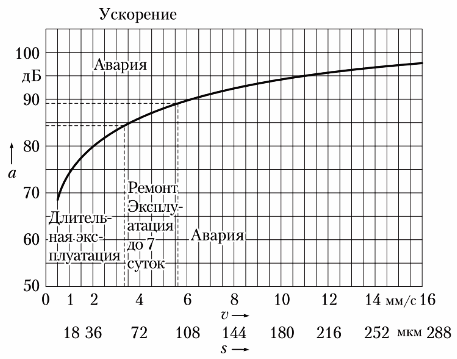
Relationship of vibration parameters
Thermal imaging (thermographic) method realized with pyrometers and thermal imagers… Pyrometers measure the temperature in a non-contact way at any specific point, i.e. to get zero temperature information, you need to scan an object with this device. Thermal insulators allow you to determine the temperature field in a certain part of the surface of the diagnosed object, which increases the efficiency in detecting emerging defects.

Method of acoustic emissions based on the registration of high-frequency signals in metals and ceramics when microcracks occur. The frequency of the sound signal varies in the range 5 — 600 kHz. The signal appears at the moment of microcracking. At the end of the development of the crack, it disappears. As a result, when this method is used, different object loading methods are used in the diagnostic process.
Magnetic method It is used to detect defects: microcracks, corrosion and breaks of steel wires in ropes, stress concentration in metal structures. The stress concentration is detected using special devices that are based on the principles of Barkhaussen and Villari.
Partial discharge method Used to detect defects in the insulation of high-voltage equipment (transformers, electrical machines).The physical basis of partial discharges is that local charges of different polarity are formed in the insulation of electrical equipment. A spark (discharge) occurs with charges of different polarity. The frequency of these discharges varies in the range 5 — 600 kHz, they have different power and duration.
There are different methods of registering partial discharges:
-
method of potentials (partial discharge probe Lemke-5);
-
acoustic (high-frequency sensors are used);
-
electromagnetic (partial discharge probe);
-
capacitive.
To detect defects in the insulation of station synchronous generators with hydrogen cooling and defects in transformers for voltage 3 — 330 kV, gas chromatographic analysis is used... When various defects occur in transformers, various gases are released into the oil: methane, acetylene, hydrogen, etc. . The proportion of these gases dissolved in the oil is extremely small, but nevertheless there are devices (chromatograms) with the help of which these gases are detected in transformer oil and the degree of development of certain defects is determined.
To measure the tangent of the angle of dielectric losses in insulation in high voltage electrical equipment (transformers, cables, electrical machines) a special device is used — AC bridge… This parameter is measured at a power supply with a voltage from nominal to 1.25 nominal. If the insulation is in good technical condition, the dielectric loss tangent should not change in this voltage range.
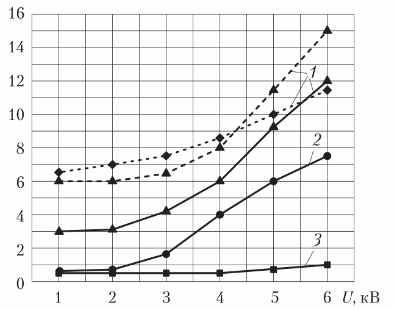
Graphs of changes in the tangent of the angle of dielectric losses: 1 — unsatisfactory; 2 — satisfactory; 3 — good technical condition of the insulation
In addition, the following methods can be used for technical diagnostics of shafts of electrical machines, transformer housings: ultrasound, ultrasonic thickness measurement, radiographic, capillary (color), eddy currents, mechanical testing (hardness, tension, bending), X-ray ray detection of defects, metallographic analysis.
Gruntovich N.V.
