What is reactive power compensation for?
 Reactive power and energy, reactive current, reactive power compensation
Reactive power and energy, reactive current, reactive power compensation
Reactive power is needed to create alternating magnetic fields in inductive electrical receivers and does no direct useful work. At the same time, reactive power has a significant impact on such parameters of the power supply system as power and electricity losses, throughput levels and voltage at the nodes of the power network.
Reactive power and energy worsen the operation of the power system, that is, charging power plant generators with reactive currents increases fuel consumption, increases losses in power networks and receivers, and increases the voltage drop in networks.
Reactive current additionally loads power lines, which leads to an increase in the cross-sections of wires and cables and, accordingly, to an increase in capital costs for external and local networks.
Reactive power compensation is currently an important factor that allows you to solve the issue of energy saving in almost any enterprise.
According to estimates by local and leading foreign experts, the share of energy resources, and in particular electricity, is about 30-40% of the cost of production. This is a strong enough argument for the manager to take seriously the analysis and audit of energy consumption and the development of reactive power compensation methods. Reactive power compensation is the key to energy savings.
Reactive energy users
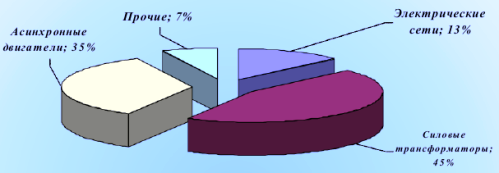
Major users of reactive power — asynchronous motorswhich consume 40% of the total power together with household and own needs; electric ovens 8%; converters 10%; transformers of all stages of transformation 35%; power lines 7%.
In electrical machines, the alternating magnetic flux is connected to the coils. As a result, a reactive emf is induced in the coils when alternating current flows. causing a phase shift (fi) between voltage and current. This phase shift usually increases and cosine phi decreases at low load. For example, if the cos phi of AC motors at full load is 0.75-0.80, then at low load it will decrease to 0.20-0.40.
 Low load transformers also have a low level Power factor (cosine phi). Therefore, applying reactive power compensation, the resulting cosine phi of the power system will be low, and the electric load current, without reactive power compensation, will increase with the same active power consumed by the network.Accordingly, when compensating the reactive power (using automatic capacitor blocks KRM), the current consumed by the network decreases, depending on the cosine phi, by 30-50%, respectively, the heating of the conductive wires and the aging of the insulation decrease.
Low load transformers also have a low level Power factor (cosine phi). Therefore, applying reactive power compensation, the resulting cosine phi of the power system will be low, and the electric load current, without reactive power compensation, will increase with the same active power consumed by the network.Accordingly, when compensating the reactive power (using automatic capacitor blocks KRM), the current consumed by the network decreases, depending on the cosine phi, by 30-50%, respectively, the heating of the conductive wires and the aging of the insulation decrease.
Moreover, the reactive power along with the active power is taken into account by the electricity supplier and is therefore paid according to the prevailing tariffs, hence it forms a significant part of the electricity bill.
The structure of reactive energy users in power systems (by installed active power):
Other converters: AC to DC, industrial frequency current to high frequency or low frequency current, furnace loading (induction furnaces, steel arc furnaces), welding (welding transformers, units, rectifiers, spot, contact).
The total absolute and relative losses of reactive power in the elements of the supply network are very large and reach 50% of the power supplied to the network. Approximately 70 - 75% of all reactive power losses are losses in transformers.
So, in a TDTN-40000/220 three-winding transformer with a load factor of 0.8, reactive power losses are about 12%. On the way from the power plant, at least three voltage transformations occur, and therefore reactive power losses in transformers and autotransformers reach large values.
Ways to reduce reactive power consumption. Reactive power compensation
The most effective and efficient way to reduce the reactive power consumed by the network is the use of reactive power compensation units (condensing units).
The use of capacitor units for reactive power compensation allows:
- unload power lines, transformers and switchgear;
- reducing electricity bills
- when using a certain type of installation, reduce the level of higher harmonics;
- suppress network noise, reduce phase imbalance;
- to make distribution networks more reliable and economical.
Reactive power compensation ensures compliance with the reactive power balance condition, reduces power and electricity losses in the network, and also allows voltage regulation through the use of compensating devices.
A significant economic effect of reactive power compensation can be achieved with the right combination of different measures, which must be technically and economically justified.
