Ultrasonic cutting of materials
 The principle of ultrasonic cutting is completely different from traditional material cutting technologies. In the first case we use ultrasonic energywhich does not require sharpening the cutting edges of the tool and applying large forces.
The principle of ultrasonic cutting is completely different from traditional material cutting technologies. In the first case we use ultrasonic energywhich does not require sharpening the cutting edges of the tool and applying large forces.
Unlike mechanical cutting, ultrasonic cutting has no chips, no noise, no burnt edges like laser or other heat treatment, no fumes or gases. Compared to water jet cutting, there is no moisture penetration into the material. In terms of cutting costs, ultrasonic cutting is an alternative to laser and water cutting.
The cutting tip vibrates ultrasonically, which causes very little friction and the cutting material does not stick, which is especially important for viscous and elastic materials, frozen foods, rubber and other materials that cannot be cut under pressure.
Ultrasound waves cannot be heard by humans. The ultrasonic cutting knife vibrates with an amplitude of 10 — 70 µm in the longitudinal direction. The vibration is microscopic, so it cannot be seen. The movement is repeated 20,000 — 40,000 times per second (frequency 20 — 40 kHz).
Ultrasound devices with a lower frequency have more weight and more power output. Higher amplitudes can also be achieved at lower frequencies. Machines with a frequency of 20 kHz are more suitable for cutting thick and strong materials.
The disadvantage of such devices is that the ultrasonic frequency is close to the audible range, and noise reduction measures may be necessary during operation.
35 kHz devices are more suitable for thinner materials such as foil, imitation leather and textiles, as well as for processing complex shapes. At the same time, the machines are silent in operation.

Application examples for ultrasonic cutting
Ultrasonic cutting devices consist of an ultrasonic transducer, a hub tip, a knife and a power supply. An ultrasonic transducer is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical (ultrasonic) energy.
Currently, electrostriction is used almost universally — the effect is the opposite piezoelectric… This means that an alternating electrical voltage is applied to the transducer on a ceramic or quartz plate that generates ultrasound. The acoustic concentrator increases the amplitude of the outgoing vibrations in the cutting area.
The material is softened and cut by ultrasonic energy, and the knife blade simply plays the role of positioning the cut and outputting ultrasonic energy. Cutting forces are reduced by about 75% and the productivity of the cutting process is significantly increased compared to other cutting methods.
Abrasives can be used to increase cutting efficiency.
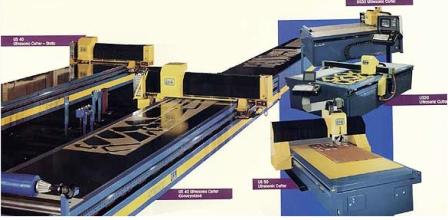
Ultrasonic cutting machines
The cutting speed depends on the material being processed and is generally determined by the ratio: V = 4 * X * e, where X is the maximum vibration amplitude, m, e is the ultrasonic frequency, Hz.
Thus, with an amplitude of 12 microns and a frequency of 35 kHz, the cutting speed will be: 4 * 0.000012 * 35000 = 1.68 m / s.
As is known from other technologies (for example, in mechanical cutting), with an increase in the cutting speed, not only the cutting forces, but also the wear of the blade of the cutting tool decreases. Therefore, carbide blades are also recommended for ultrasonic cutting. The durability of carbide metal blades can be up to 20,000 m or more.
Handheld ultrasonic cutting device
Ultrasonic cutting is suitable for materials such as rubber, PVC, printed circuit boards, films, composites, plastics, all kinds of paper, fabrics, carpets, leather, food (frozen meat, candy, bread, chocolate, etc.), thin film and materials from honeycomb, for cleaning fossils, for removing rust and paint, for metal engraving and carving, for metal marking.
Ultrasonic cutting can be done both in manual mode and with the help of automated installations and robots, there are also models for 3-D cutting of bee materials.

