Surge testing of cable lines
 In order to reduce damage to cable lines under working voltage, the rules of technical operation recommend periodic tests of these lines with increased voltage.
In order to reduce damage to cable lines under working voltage, the rules of technical operation recommend periodic tests of these lines with increased voltage.
What is the purpose of testing cable lines with increased voltage? It is believed that during the test the weakened point of the cable insulation is destroyed and therefore the probability of cable failure at operating voltage is reduced.
Testing of cable lines is carried out with increased DC voltage. At DC voltage it is possible to use bulky high power test equipment. Partial discharges in the solid insulation develop little during the test, active power losses and heat generation are negligible. At the same time, the test voltage can be quite high.
Cables with rubber insulation 3 — 10 kV are tested with a voltage of 2Un, cables with paper insulation and viscous impregnation with an operating voltage up to 10 kV are tested with a voltage of (5-6)Un, and with an operating voltage of 20 — 35 kV — voltage (4 — 5) Un.The duration of the test for each phase is 5 minutes.

For cables up to 1 kV, a post carrying out minor repairs only measures its insulation resistance with a megohmmeter at 2500 V for 1 min. The insulation resistance must be at least 0.5 MΩ.
Before and after testing cables with increased rectified voltage measure their insulation resistance with a megohmmeter at 2500 V.
In order to increase the labor productivity during the test, to reduce the disconnection time of the users, as well as to reduce the damage to the end connectors when disconnecting and connecting the ends of the cable lines, the cable lines connected to one section of the busbar of processors can be tested simultaneously without disconnecting them from the bus system. In addition, planned tests of cable lines tend to be combined with the repair of switchgear at the receiving and feeding ends of these lines.
It is most recommended to test cable lines laid in the ground with increased voltage in the summer, because in case of damage during the test, it is easier to carry out repair work.
The insulation of cable lines is tested using special high-voltage rectifiers, which can be mobile, portable or stationary.
All installations contain (see Fig. 1): test transformer 2, rectifier 3 with high voltage, control panel. High voltage is obtained from transformer 2 with a high voltage winding grounded through a milliammeter.
Rectification is done by a half-wave rectifier. The primary winding of the high voltage transformer is fed by the regulating autotransformer 1.The high voltage is measured with a kV kilovoltmeter connected to the primary circuit of transformer 2
The leakage current is monitored using a microammeter, one pole of which is grounded and the other is connected to the beginning of the secondary winding of the high-voltage transformer 2. The high-voltage transformer and rectifier include in series a resistor R , limiting the current in the event of a failure of the cable. A filament transformer 5 is used to power the cathode circuit of the kenotron.
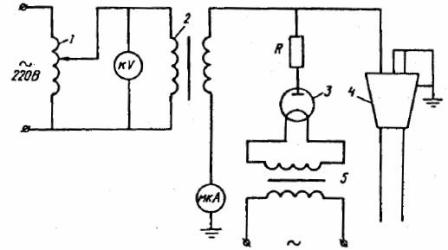
Rice. 1. Diagram of a high-voltage installation for testing cables
When testing three-core cables (4) with belt insulation, the voltage from the test plant is applied to each core in turn, the other two cores and the sheath being earthed.
When testing all cables, the voltage is gradually increased to the nominal value and the cables are kept under this voltage for 5 minutes from the moment the normalized voltage value is established.
How to determine the condition of the cable during a surge test
The condition of the cable is determined by the leakage current. For cables with paper insulation for voltages up to 10 kV, the leakage current is about 300 μA. In a satisfactory condition of the cable, in the case of increasing the voltage and charging its capacity, the leakage current increases sharply, then quickly drops to 10 — 20% of the maximum.
Creeping discharges, spikes in leakage currents, increase in the steady state value of the leakage current should not be observed during the tests. The insulation resistance of the cable measured with a megger before and after the test should be the same.
In the case of defects in the insulation of the cable, its failure mainly occurs within the first minute after establishing the test voltage. If the cable insulation is in good condition, the asymmetry of the leakage currents in the phases of a three-wire cable does not exceed twice their value.
Procedure in case of cable damage during the test
In case of damage to a cable line during the test or after its emergency stop, it is necessary to determine the location and nature of the cable damage.
In case of single-phase damage (destruction of the cable insulation from the core to the metal sheath), the cable can be repaired without cutting the core. For this, the armor, sheath, belt insulation and damaged core insulation are removed. The insulation is then restored to the damaged area.
Ensuring the density of the connection is done with the help cable seal. If the cores are damaged, this section of the cable is cut, a new section is inserted and two connectors are installed. If the connector is damaged, cut it and reconnect the cable with new connectors. In case of a small defect in the connector, it can be replaced with another (extended) one without additional wiring.

