Measurement of the resistance of the windings of electric motors to direct current
The purpose of measuring the resistance of the windings of the electric motor to direct current is to identify defects (poor connections, rotation circuits), errors in the electrical circuit, as well as to clarify the parameters used in the calculations and setting of modes, regulators, etc. n.
Measurements, especially for large electric motors, must be done with great care and precision. The resistance of the windings of electric motors to direct current is measured either with an ammeter and a voltmeter, or with a double bridge... If the resistance is more than 1 Ohm, then the necessary measurement accuracy is achieved single bridge.
In electric motors with only three terminals of the stator winding (the connection of the windings in a star or delta takes place inside the electric motor), the DC resistance is measured between the terminals in pairs. The resistance of the individual phases in this case is determined by the following expressions:
1. To connect to a star (Fig. 1, a)
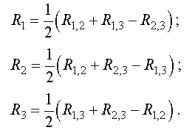
With the same values of measured resistances:
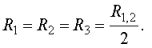
2. To connect in a triangle (Fig. 1, b)
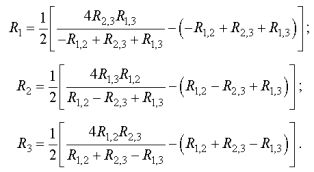
With the same values of measured resistances:
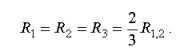
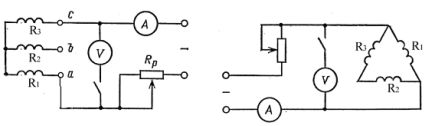
Rice. 1. Schemes for measuring the resistance of the windings of three-phase electric motors when connecting the windings: a — in a star; b — in a triangle
When measuring resistance, the correct determination of the winding temperature is of particular importance. For temperature measurement, both built-in temperature indicators and built-in thermometers and temperature indicators are used, which must be entered no later than 15 minutes before the start of the resistance measurement.
To measure the temperature of the windings of electric motors up to 10 kW, one thermometer or temperature indicator is installed, for electric motors up to 100 kW — at least two, for electric motors from 100 to 1000 kW — at least three, for electric motors over 1000 kW — at least four.
The arithmetic mean value of the measured values is taken as the temperature of the coils. When measuring the resistances of the windings of an electric motor in a practically cold state, the temperature of the windings should not differ from the ambient temperature by more than ± 3 ° C.
If a direct measurement of the winding temperature is not possible, the motor must be idled before measuring the winding resistance for a sufficient time to allow all parts of the motor to assume practically ambient temperature. The change in ambient temperature during this time should not be more than ± 5 ° C.In this case, the ambient temperature at the time of resistance measurement is taken as the temperature of the motor windings. The resistance measurement is repeated several times.
Ammeter and voltmeter measurements are performed three times at different current values. When using bridge circuits, the bridge must be unbalanced before each measurement. The results of measurements of the same resistance should not differ from the average by more than 0.5%; the arithmetic mean of the results of all measurements that meet this requirement shall be taken as the actual resistance.
The results of measurements for individual phases are compared with each other, as well as with the results of previous (including factory) measurements. In order to compare the results of measurements carried out at different coil temperatures, the measured values are reduced to the same temperature (usually 15 or 20 ° C).
Recalculation of resistances from one temperature to another can be done according to the expressions: (for aluminum):
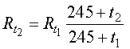
for honey:
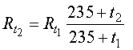
whereRt1 and Rt2 — resistance of windings at temperatures and respectively.

