Industrial boilers
 Flow, battery, electrode water heaters and electric steam generators are used for electric water heating.
Flow, battery, electrode water heaters and electric steam generators are used for electric water heating.
Flow-through and flow-through water heaters for industrial elements equipped with tubular electric heaters (Heating elements), are used for low consumption of hot water. They have low power, are simple in design, electrically safe enough that they can be serviced by unskilled personnel.
Storage boilers are used in open water supply systems with an uneven schedule of hot water consumption. Instantaneous water heaters are used in systems for drinking animals, preparing fodder, for heating small rooms, etc.
Electric water heating is carried out by elemental and electrode water heaters. Elementary non-flowing and flowing electric heaters are equipped with tubular electric heaters (TENs) and are used for low consumption of hot water. They have low power, are simple in design and sufficiently electrically safe.
Inaccurate boilers are used in open water intake systems with an uneven schedule of hot water consumption.
Flow-through (quick-acting) elementary boilers are used in systems for watering animals, preparing fodder, for heating small rooms.
Electrode water heaters they have a relatively high power and are designed to work in closed systems, because with a slightly open water intake, the electrodes are quickly covered with scale deposits and quickly fail.
Electrode steam boilers used to generate steam. Electrode water heaters and water heaters represent a higher degree of electrical safety compared to elementary water heaters.
Storage water heaters SAOS, SAZS, EV-150... Legend: C — resistance heating, A — accumulation, OC — open system, ЗС — closed system, E — electric, V — water heater, 150 — tank capacity, l.
Designed for heating and hot water storage. They are a metal heat-insulated tank inside which one or two (tank volume 800 l and more) heating units are installed. In the SAOS and EV-150 boilers, hot water is displaced through the upper manifold by supplying cold water from the water supply system.
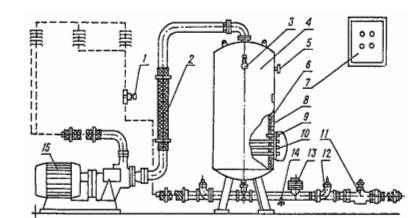
At the gas station (Fig. 1), hot water is pumped through a closed irrigation or heating system. Water losses are replenished by the water supply system due to natural inflow through a non-return valve. Maximum water temperature 90OC. The water temperature in the SAOS and GASS tanks is maintained by means of a thermostat.
Figure 1.Boiler SAZS — 400/90 — I1: 1 — water temperature sensor in the water supply system, 2 — insulating insert, 3 — thermometer, 4 — housing, 5 — emergency protective thermal contactor, 6 — tank, 7 — control box, 8 — thermal insulation, 9 — boiler water temperature sensor, 10 — heating unit, 11 — valve, 12 — non-return valve, 13 — overpressure valve, 14 — drain plug, 15 — electric pumping device.
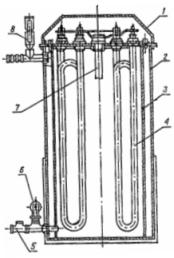
Boiler with flow element EV-F-15 (fig. 2). It consists of a boiler and a control cabinet. The temperature of the water is regulated by its supply and controlled by a thermometer. At 75 ... 80 ° C, the thermal relay disconnects the water heater from the network. In automatic mode of operation, the boiler is switched on 15 ... 45 s after it is connected to the network.
Figure 2. Water heater EV -F -15: 1 — cover, 2 — housing, 3 — housing, 4 — tube boilers, 5 — non-return valve, 6 — overpressure valve, 7 — thermal relay, 8 — thermometer.
Instantaneous induction boiler PV-1, is a three-phase step-down transformer. The primary coil is made of copper wire, the secondary is made of 20 mm diameter steel pipe and is electrically short-circuited.
Currents reaching thousands of amperes heat the secondary coil, which gives off heat to the water flowing inside it. The temperature of the water is regulated by the flow. The electrical circuit contains protection against overheating of the water (manometric thermometer) and step-down transformer (UVTZ-1 device).
Electrode boilers are designed for heating water in centralized hot water systems for technological processes, heating and ventilation of various agricultural facilities.
Boilers are classified:
— by operating voltage - low voltage (0.4 kV), high voltage (6 and 10 kV),
— according to the design of the electrodes — plate, ring-shaped, cylindrical,
— by the power regulation method — by changing the active surface of the working electrodes, changing the active surface of the regulating electrode, changing the distance between the electrodes,
— by the type of drive of the power regulator — manual, electric. Electrode water heaters are classified as installations for direct heating with electric resistance.
Electrical energy is converted to heat when an electric current passes through the water between the conducting electrodes.
Electrode boiler type EPZ... It has two versions, different in the drive of the power control mechanism (I2 — manual, I3 — electric). The design of the electrodes depends on the capacity of the water heater.
Water fills the space formed by the phase and control electrodes. Current flows from the electrodes of one phase through the water along the control metal electrode, then through the water and to the electrodes of the other phase. The power of the water heater is regulated by changing the area of the active surface of the control electrode.
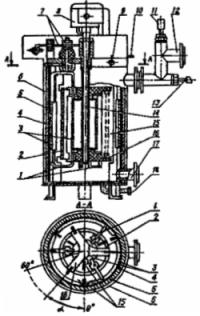
Electrode boiler for hot water KEV-0.4 (Fig. 3) is manufactured with plate electrodes and is designed for heating water with a specific resistance of more than 10 mΩ. The power is regulated from 25 to 100% of the nominal change in the active height of the electrodes by moving the adjusting plates of dielectric in the interelectrode space. The drive of the power regulator can be manual or electric.
Figure 3.Electrode hot water boiler KEV — 0.4: 1 — body, 2 — dielectric plates, 3 — supports, 4 — phase electrodes, 5 — jumpers, 6 — drain plug, 7 — power supply unit, 8, 9 — inlet and outlet for water, 10 — outlet for air, 11 — mechanism for moving dielectric plates.
Electric steam generators are designed to produce saturated steam with an overpressure of up to 0.6 MPa. They are used to meet technological needs, as well as in water supply and heating systems.
In general, steam generators are connected to direct electrical resistance installations, their principle of operation and device are similar to electrode boilers. The classification of steam generators is similar to the classification of electrode boilers.