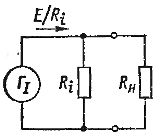
Equivalent current generator
 Each generator is always characterized by an electromotive force E and an internal resistance Ri. It creates a certain EMF that does not depend on the resistance of the load. Therefore, such a generator is called an EMF generator. Sometimes it is presented in the form of some ideal EMF generator that has no internal resistance and is connected in series with a resistor whose resistance is equal to Ri.
Each generator is always characterized by an electromotive force E and an internal resistance Ri. It creates a certain EMF that does not depend on the resistance of the load. Therefore, such a generator is called an EMF generator. Sometimes it is presented in the form of some ideal EMF generator that has no internal resistance and is connected in series with a resistor whose resistance is equal to Ri.
In some cases, to simplify the calculations, replace the EMF generator with the so-called equivalent current generator of current generation independent of the load. This substitution can be justified by the following mathematical transformations.
The current supplied by the EMF generator
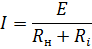
Multiplying both sides of the equation by Rn, we get an expression for the voltage at the generator terminals, that is, the voltage at the load
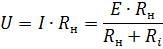
Now let's multiply and divide the right side of Ri
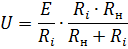
In the resulting formula, E / Ri is the short-circuit current, and the expression RnRi / (Rn + Ri) is the total resistance of the parallel-connected branches with resistances RH and Ri.It follows that the EMF generator can be replaced by a current generator giving the current E / Ri, but in this case Ri must be considered the resistance of the branch connected in parallel to the load RH (Fig. 1).
Sometimes it is convenient to use the replacement of the EMF generator with an equivalent current generator for calculations, in particular, if the load has several branches connected in parallel, since then everything comes down to a parallel circuit calculation.
Fig. 1. Equivalent current generator
If an EMF generator is used in the calculation, then a mixed connection will result, since Ri will be connected in series with the load, which is itself a parallel circuit. Mixed coupling is more difficult to calculate, especially for AC circuits.
However, it should be remembered that with the help of a current generator it is possible to correctly calculate the current, voltage and power only in the load. It is impossible with the help of a current generator to calculate the current, voltage and power inside the generator, because completely incorrect results will be obtained.
Thus, the use of a circuit diagram with a current generator does not correspond to reality and serves only to calculate the electrical load mode. And with an EMF generator, a correct reflection of the actual processes in the electrical circuit is always obtained, and the calculation results for each part of the circuit will be correct.