Opening electrical circuits
Opening electrical circuits usually means transitional process, in which the circuit current changes from a certain value to zero. In the last stage of opening the circuit, a gap appears between the contacts of the disconnecting device, which, in addition to zero conductivity, must also have a sufficiently high dielectric strength to withstand the action of the circuit voltage restored to it.

Physical characteristics of the arc discharge
Electric arc can occur when the gap between the contacts (electrodes) breaks or when they open. When the contacts open, arcing between them is facilitated by the formation of glowing "spots" on the contact surface, which are a consequence of significant current densities over small areas of "separation". This causes an arc to form when the contacts are broken, even at a fairly low voltage (of the order of several tens of volts).
It is generally accepted that the minimum conditions for the occurrence of at least unstable arcing on the contacts are current about 0.5 A and voltage 15 — 20 V.
The opening of the contacts at lower values of voltage and current is usually accompanied by only small sparks. At higher open circuit voltages, but at lower currents, formation between the open contacts is possible glow discharge.
The presence of a glow discharge is characterized by a significant drop in the cathode voltage (up to 300 V). If a glow discharge turns into an arc discharge, for example, as the current in the circuit increases, then the cathode voltage drop decreases to 10 — 20 V.
The characteristic features of the arc discharge at high pressure of a gas medium are:
-
high current density in the arc column;
-
high temperature of the gas inside the arc channel, reaching 5000 K, and under conditions of intense deionization, 12000 — 15000 K and higher;
-
high current density and low voltage drop at the electrodes.
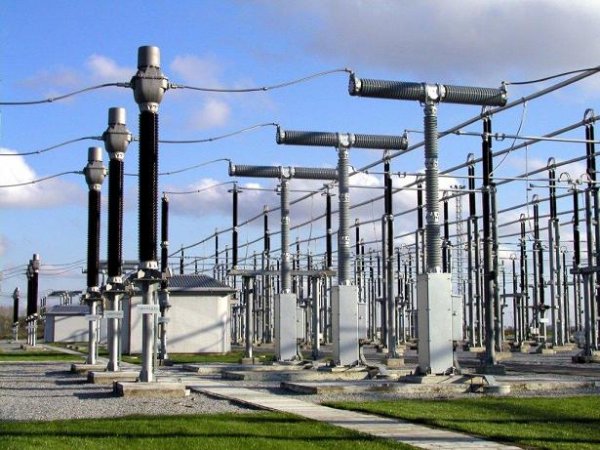
Usually, the goal is to ensure that the circuit opening process proceeds as quickly as possible. For this purpose, special switching devices (switches, circuit breakers, contactors, fuses, load breakers, etc.) are used.
Arcing phenomena are observed not only in circuit breakers. An electric arc may occur when the contacts are opened. high voltage disconnectors, when the insulation of the lines overlaps, when the protective elements of the fuses are burned out, etc.
The complexity of the devices of these devices depends on the requirements imposed on them in terms of operating voltage levels, rated currents and short-circuit currents, levels of overvoltages occurring, atmospheric conditions, speed ratings, etc.
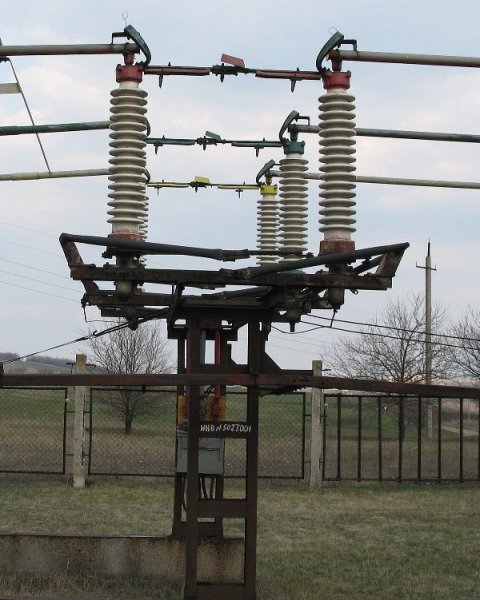
Features of opening electrical circuits through disconnectors
The question of extinguishing long open arcs of alternating current is most often encountered when working with simple disconnectors such as tripping devices. Such disconnectors do not have special arc suppression devices, and when the contacts open, they only extend the arc into the air.
To improve the conditions for arc stretching, disconnectors are equipped with horn or additional rod electrodes, along which the arc is lifted up and stretched to a large length.
There are many videos uploaded on the Internet that show the process of arcing when the contacts of disconnectors open on load (these can be easily found by searching for «arcing disconnector»).
Open arcing at disconnectors or between conductors and ground on power lines is strongly encouraged by wind. In the presence of wind, the arc may be shorter and therefore eliminated more quickly than in the absence of wind. However, such a factor as wind should not be taken into account due to its inconsistency, but based on more severe conditions — the complete absence of wind.
With the help of disconnectors, it is impossible to turn off a large current, since the arc at the same time reaches a considerable length, forming a lot of flame, strongly melting the contacts of the disconnecting device. A powerful open arc easily damages the insulators with which it comes into contact, causes an overlap between the phases, which leads to a short circuit in the network.
Conventional disconnectors are widely used to disconnect open circuit currents of small transformers, capacitive load line currents, low load currents, etc.
Ways to open electrical circuits
In principle, the following methods are possible for opening electric circuits with direct current and alternating current.
1. Simple arcing of electrical circuits
This group includes such methods of opening electric circuits with direct and alternating current, in which no special additional measures are taken to limit the current in the circuit before opening the contacts or special measures to reduce the energy of the arc in the arc gap of the breaker.
In this opening method, the circuit breaking conditions are provided by at most arc extinguishing chamber of the disconnecting device by creating the required dielectric strength of the gap when the current crosses zero (alternating current) or reaching a sufficient value of the arc voltage (direct current).
During arcing, the contacts of the apparatus can open in any phase of the current flowing in the circuit, therefore the contacts and elements of the arc chute must be designed for the impact of an arc of relatively high power and energy.
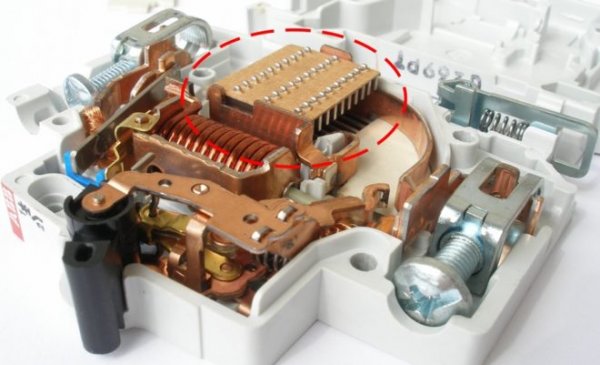
Arc extinguishing chambers for electrical devices
Circuit Breaker Arc Chute
2. Limited arc opening of electrical circuits
Such exclusion methods include those in which a relatively large active or reactivity, due to which the current in the circuit decreases quite significantly compared to its value that existed before the onset of the limitation. The switch turns off the limited current that remains in the circuit.
In this case, a power-limited arc occurs at the contacts, and extinguishing the arc on the remaining current is a simpler task than if the current were not limited.
Conventionally, we include such disconnection methods in the same group, in which the phase of current interruption is strictly fixed or the burning time of the arc on the contacts is limited by some special measures, for example, valve devices, etc.
3. Arcless opening of electrical circuits
The process of opening electrical circuits in this case is characterized by the fact that the arc discharge at the main contacts occurs completely or occurs in the form of a very short-term unstable arc due to the influence of the inductance and mutual inductance of the circuits. This type of circuit opening is usually achieved by means of high-power valves (silicon diodes or thyristors) used as shunting elements of the main circuit breaker contacts.

Arc extinguishing characteristics when opening DC and AC electrical circuits
AC arc extinguishing conditions with active deionization of the switching device gap are fundamentally excluded from the extinguishing conditions of DC arcs and long open AC arcs.
In a permanent arc or in an open long alternating arc, extinction occurs mainly because when the arc is stretched, the source of electrical energy is unable to cover the voltage drop in the arc column, as a result of which an unstable condition occurs and the arc is extinguished.
When an arc occurs in an AC circuit, when the arc column is actively deionized or breaks into a series of short arcs, the arc can be extinguished even when the source still has a large supply voltage to maintain the arc burning, but which turns out to be insufficient to ensure its ignition—at a current zero crossing.
Under conditions of active deionization during the current zero crossing, the conductivity of the arc column decreases so much that, at least for a short time, a significant voltage must be applied to it to start the arc in the next half-cycle.
If the circuit is not able to provide sufficient voltage and the rate of its increase in the gap, after the current passes zero, the current is interrupted, that is, the arc does not appear in the next half-cycle and the circuit is finally turned off.
Then consider the most common ones simply opening arc circuits.

If the circuit source voltage and current exceed certain critical values, then at the contacts of the electrical disconnection device when they open, a stable arc discharge occurs… If the contacts further diverge or the arc is blown into the arc extinguishing chamber of the disconnector, unstable arc burning conditions are created and the arc can be extinguished.
As circuit voltage and current increase, the difficulty in creating unstable arcing conditions increases rapidly. At voltages reaching thousands and tens of thousands of volts and relatively high currents (thousands of amperes), a very powerful arc occurs in the contacts of the disconnecting device, in order to extinguish it and therefore break the circuit, measures must be taken to use more or less sophisticated arc extinguishing devices ... Particularly significant difficulties arise when switching off DC circuits.
Considerable difficulties must also be overcome during a rock. short circuit currents in AC circuits for short periods of time (hundredths and thousandths of a second).
Quick breaking of the circuit and removal of the resulting short circuits in electrical installations are dictated by a number of circumstances and first of all by the need to maintain stability of operation. electrical systems, protection of wires and equipment from the thermal effects of short-circuit currents, protection of contacts and arc chambers of disconnecting devices from the destructive action of a powerful arc.
Rapid removal of the open circuit arc is also of great importance and in devices for low voltage control circuits, which are usually designed for a very large number of switching processes. Reducing the duration of arc burning leads to a reduction in the burning of contacts and other elements of the apparatus and, therefore, to an increase in service life.
However, very rapid elimination of the arc can result in very large surges in the circuit because the arc, when the circuit is open, absorbs the electromagnetic energy stored in the circuit, which can be converted into electrostatic surge energy. Thus, arc discharge can play a positive role in some cases. This should be accounted for.
The problem of creating reliable high-speed high- and low-voltage disconnecting devices, first of all, is based on the correct solution of the issue of arc quenching in them.
Interruption of low and high voltage electrical circuits with the formation of a powerful arc in the contacts of electrical devices is a complex process, the study of which is devoted to a huge number of theoretical and experimental studies and design developments.
There are a large number of methods of extinguishing AC and DC arcs that are used in practice depending on the operating voltage levels, the magnitude of the currents, the required operating time of the disconnecting devices, safety conditions, etc.
At present, simple arcing is still the main path that high and low voltage AC and DC switching device technology continues to take.
See also:High Voltage Vacuum Circuit Breakers — Design and Principle of Operation