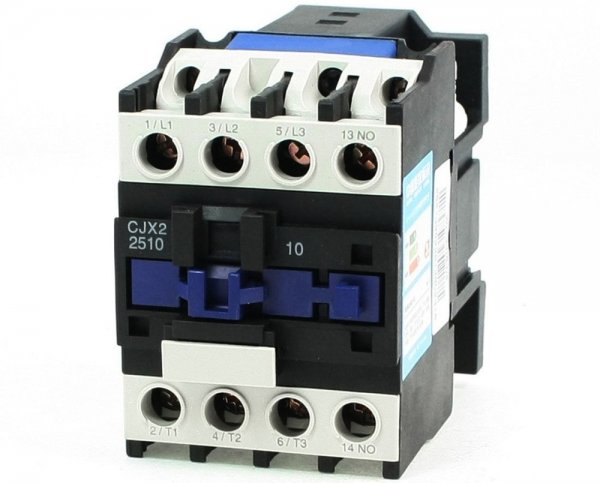
Electric motor control device: electromagnetic contactors, starters, relays
This type of equipment serves the main purpose electric motors… For the most part, the control device consists of various types of switching devices (contactors, magnetic starters, controllers, switches, control buttons, limit switches, etc.), whose purpose is also to turn on and off.
However, if there is a significant difference between a switching device (e.g. a switch) and a ballast, even if the latter served the same purpose of switching current (e.g. a contactor).
The switch, having performed the closing operation, is held in the closed position without expending any energy on it (circuit breaker device), the contactor is arranged as follows: to turn it on, it is necessary to give current to the "pulling coil", it will attract the armature, the contacts will close and the weight will close, while the current flows around the closing coil. As soon as the current in this coil is interrupted, the contactor will open.
In this way, the contactor drive is energized all the time the contactor is closed, while the circuit breaker is energized only during the closing process and its contacts are held in the closed position by the mechanism and has a special "opening coil" to open the breaker, the purpose of which f — Knock out your thumbs while holding the switch in the on position.
This difference in design is explained by the fact that the circuit breaker can be in the closed position for a very long time, since it switches objects in long-term operation, and the contactor serves short-term processes (for example, starting and stopping machines).
There are also "normally closed" contactors, whose contacts are closed when there is no current in their drive, and when current is applied to the coil, they turn off.
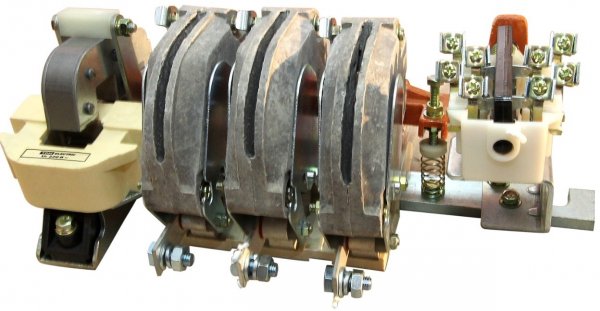
Magnetic switch differs fundamentally from a contactor only in that its construction contains thermal relay, disconnection of the starter at unacceptably high current (overload current). In addition, magnetic starters are generally designed for lower currents than contactors.
How does a reversible starter differ from a conventional starter?
Motor control circuits using a magnetic starter
Explanation of designations of PML series starters
In addition to the devices listed above, the control equipment includes rheostats and resistances, as well as special types of relays (starting — pendulum, motor), which regulate the start (or stop) time and the start mode.
Relay — a device whose purpose is to come into action by changing any parameter of the circuit, and this action is ultimately reduced to closing (or opening) the electrical circuit of devices or machines that control the parameter to which the relay responds .
For example, a current relay, at a certain value of current at which the relay is installed, closes the breaker contacts of the switch coil, and the switch turns off that part of the circuit to which the relay responds.
Therefore, relays can be classified primarily according to their purpose, that is, according to the parameter from which the relay operates.
Each relay consists of two main elements:
- the motor part of the relay, which operates from one of the above parameters;
- the movable part of the relay carrying contacts to close (or open) the circuit of the control device (or machine) that controls the parameter to which the relay responds.
In addition, many types of relays have damping devices that create some time delay between the state of the circuit in which the relay is supposed to operate and the moment the relay contacts close.
In some cases this «relay delay» is created by a special device — time relay, so the main relay activates the time relay and the time relay now closes the contacts of the control device after a certain period of time.
The relay element, which performs mechanical work to close the contacts, can be arranged in different ways, and in some cases the principle of its construction depends on the parameter to which the relay must respond.
What are the differences between sensors and relays
Technical characteristics of the RPL relay
Device, principles of operation, characteristics of solid state relays
Other devices which are classified as ballasts for electric motors:
Control knobs and sealing posts



