Operating modes of electric motors
 Possible modes of operation of electric drives They are distinguished by a huge variety in the nature and duration of cycles, load values, cooling conditions, the ratio of losses during the period of start-up and smooth movement, etc., therefore, the production of electric motors for each of the possible modes of operation of an electric drive have no practical meaning.
Possible modes of operation of electric drives They are distinguished by a huge variety in the nature and duration of cycles, load values, cooling conditions, the ratio of losses during the period of start-up and smooth movement, etc., therefore, the production of electric motors for each of the possible modes of operation of an electric drive have no practical meaning.
Based on the analysis of the real modes, a special class of modes was identified — nominal modes, for which serial engines were designed and manufactured.
Data contained in the passport of the electrical machine refer to a certain nominal mode and are called the nominal data of the electrical machine. Manufacturers guarantee that when the electric motor operates in rated mode at rated load, it is fully utilized thermally.

Distinguish the following modes of operation of engines under load, depending on their duration: long-term, short-term and intermittent.
In continuous mode, the engine runs without interruption, and the period of operation is so long that the engine warms up to the set temperature.
A continuous load can be constant or variable. In the first case the temperature does not change, in the second it changes along with the change in load. The engines of conveyors, sawmills, etc. operate in this mode with a slightly varying load, the engines of various metalworking and woodworking machines operate with a variable continuous load.
In short-term mode, the engine does not have time to warm up to the set temperature, but during the pause it cools down to the ambient temperature. The duration of short-term work of GOST on electrical machines is set equal to 10, 30, 60 and 90 minutes.
In intermittent mode During operation, the engine does not have time to warm up to the set temperature, and during the pause it does not have time to cool down to the ambient temperature. In this mode, the engine operates with continuously alternating periods of load and idle, or pauses.
In intermittent operation, the engine does not have time to warm up to the set temperature during the period of operation, and during the pause it does not have time to cool down to the ambient temperature. In this mode, the engine operates with continuously alternating periods of load and idle, or pauses.
The duration of the inclusion of an electrical product (electrical device, electrical equipment) — the ratio of the time spent in the switched-on state of an electrical product (electrical product, electrical equipment) operating in intermittent mode to the duration of the cycle (GOST 18311-80).
Intermittent mode is characterized by the relative duration of PV activation = [tp / (tp + tо)] 100%, where tp and tо are the time of operation and pause at the cycle duration (Tq = Tр + То) no more than 10 minutes.
The interrupt mode is:
-
with duty cycle PV= 15, 25, 40 and 60% and a cycle time of 10 minutes,
-
with frequent starts at duty cycle = 15, 25, 40 and 60% and number of starts per hour 30, 60, 120 and 240 with inertia factor 1.2, 1.6, 2.5 and 4,
-
with frequent starts and electrical stops at the same rated duty cycle, number of starts and inertia factor,
-
alternating with a cycle time of 10 minutes at load duty cycle = 15, 25, 40 and 60%,
- scattered with electric braking and frequent revolutions, the number of which per hour is 30, 60, 120 and 240 with an inertia factor of 1.2, 1.6, 2.5 and 4.

Operating modes of electric motors in accordance with GOST
The current GOST provides 8 nominal modes, which in accordance with the international classification have symbols S1 — S8.
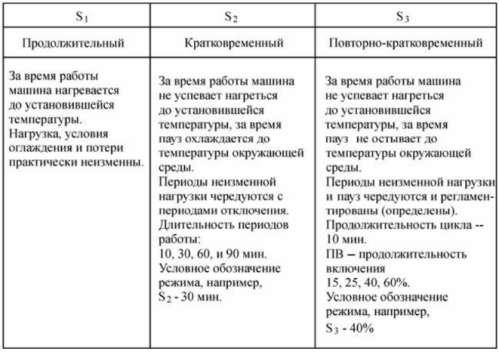
Continuous duty S1 — operation of the machine at a constant load for a long enough time to achieve a constant temperature of all its parts.
Continuous operation of the electric motor S1
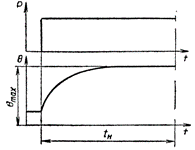
Short-term duty S2 — operation of the machine at a constant load for a time insufficient for all parts of the machine to reach the set temperature, followed by stopping the machine for a time sufficient to cool the machine to a temperature not more than 2 ° C from the ambient temperature .
For short-term work, the duration of the work period is 15, 30, 60, 90 minutes.
Short-term operation of the electric motor S2
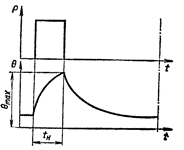
Intermittent duty S3 — a sequence of identical duty cycles, each of which includes the time of continuous load operation during which the machine is not heated to the set temperature and the parking time during which the machine is not cooled to ambient temperature.
In this mode, the duty cycle is such that the inrush current does not significantly affect the temperature rise. The cycle time is insufficient to achieve thermal equilibrium and does not exceed 10 minutes. The mode is characterized by the value duration of inclusion in percentages:
PV = (TR / (Tр + Tn)) x 100%
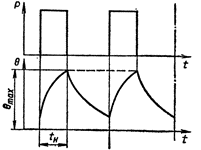
Intermittent operation of electric motor S3
Standardized values of the duration of inclusion: 15, 25, 40, 60% or relative values of the duration of the working period: 0.15; 0.25; 0.40; 0.60.
For S3 mode, the rated data only corresponds to a certain duty cycle and refers to the duty period.
Modes S1 — S3 are currently the main ones, the nominal data of which are included by the local electrical machine manufacturing plants in the catalogs and passport of the machine.
Nominal modes S4 — S8 were introduced to subsequently simplify the task of equivalent random modes of nominal, expanding the scope of the latter.

Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes S4 — a sequence of identical duty cycles, each of which includes a start-up time long enough for the start-up losses to affect the temperature of the machine parts, the time of constant load operation during which the machine does not heat up to steady-state temperature and the parking time during which the machine does not cool down to ambient temperature.
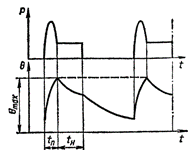 Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes S4: tn and Tn — start-up and delay times Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes and electrical shutdown S5 — a sequence of identical duty cycles, each of which includes a sufficiently long start-up time, the operating time at constant load during which the machine does not heat up to the set temperature, electrical quick stop time and parking time during which the machine does not cool down to the ambient temperature.
Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes S4: tn and Tn — start-up and delay times Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes and electrical shutdown S5 — a sequence of identical duty cycles, each of which includes a sufficiently long start-up time, the operating time at constant load during which the machine does not heat up to the set temperature, electrical quick stop time and parking time during which the machine does not cool down to the ambient temperature. 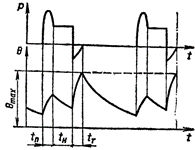 Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes and electrical shutdown S5
Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes and electrical shutdown S5
Intermittent duty S6 — a series of identical cycles, each of which includes a time of constant load operation and a time of idle time, the duration of these periods being such that the temperature of the machine does not reach a steady-state value.
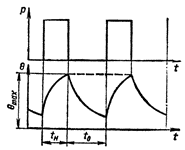
Intermittent operation S6: to — idle

Intermittent operation with the influence of starting processes and electrical stop S7 — a sequence of identical cycles, each of which includes a sufficiently long start, constant load operation and a rapid electrical stop. The mode contains no pauses.
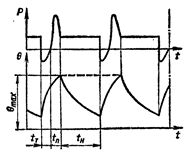
Intermittent operation with influence of start-up processes and electrical shutdown S7
Intermittent duty with intermittently variable speed S8 — a series of identical cycles, each of which includes the duty time at constant load and constant speed, followed by one or more periods with other constant loads, each corresponding to its own speed (for example, this mode is applied when switching the number of pole pairs of an asynchronous motor). The mode contains no pauses.
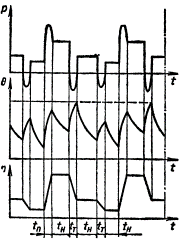
Intermittent working time with intermittently variable speed S8
Consideration of the mode of operation is of great importance when choosing an engine. The engine power shown in the catalogs is for S1 mode and normal operating conditions, except for engines with increased slip.
If the motor is running in S2 or S3 mode, it heats up less than in S1 mode and therefore allows more power to the shaft.
When operating in S2 mode, the permissible power can be increased by 50% with a load duration of 10 minutes, by 25% — with a load duration of 30 minutes and by 10% — with a load duration of 90 minutes.
Recommended for S3 mode high slip engines.

