Current density
 The value equal to the ratio of the current to the cross-sectional area of the conductor S current density (designation δ) is called.
The value equal to the ratio of the current to the cross-sectional area of the conductor S current density (designation δ) is called.
The current density can be determined as follows:
δ = I / S
In this case, it is assumed that the current is uniformly distributed over the cross section of the conductor. Current density in wires is usually measured in a / mm2.
 Current density is a vector quantity. The current density vector and wires connecting energy sources and consumers are directed normal to the cross-sectional area of the wire.
Current density is a vector quantity. The current density vector and wires connecting energy sources and consumers are directed normal to the cross-sectional area of the wire.
In a non-branched electric circuit, the current and the different cross-sections of the wires, the current density in different cross-sections of the wires has the same value.
If we assume that the magnitude of the direct current in sections S1 and C2 is not the same (Fig. 1), then the charges that pass per unit time through the cross sections S1 and S2 would be different. As a result, a positive or negative charge would build up in the volume of the conductor between these sections. With direct current, an infinite accumulation of charges would occur, which is impossible with direct current.
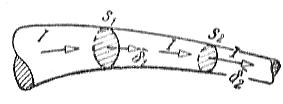
Rice. 1. Electric current and current density in different sections of an unbranched electric circuit.
Current density in different areas of the cross section of the wire S1 and S2 is not the same:
δ1 = I / S1, δ2 = I / S2. When S1> S2, we get δ1 δ2
