Parallel and series connection of capacitors
Chosen capacitors can be interconnected in different ways. In this case, in all cases, you can find the capacity of some equivalent capacitor that can replace a number of interconnected capacitors.
For an equivalent capacitor, the condition is fulfilled: if the voltage applied to the plates of the equivalent capacitor is equal to the voltage applied to the end terminals of the group of capacitors, then the equivalent capacitor will accumulate the same charge as the group of capacitors.
Parallel connection of capacitors
In fig. 1 shows the parallel connection of several capacitors. In this case, the voltages applied to the individual capacitors are the same: U1 = U2 = U3 = U. Charges on the plates of the individual capacitors: Q1 = C1U, B2 = C2U, B3 = C3U, and the charge received from the source Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3.
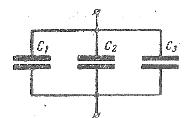
Rice. 1. Scheme of parallel connection of capacitors
The total capacity of an equivalent (equivalent) capacitor:
C = Q / U = (Q1 + Q2 + Q3) / U = C1 + C2 + C3,
that is, when the capacitors are connected in parallel, the total capacitance is equal to the sum of the capacitances of the individual capacitors.
Series connection of capacitors
When the capacitors are connected in series (Fig. 3) on the plates of individual capacitors, the electric charges are equal in magnitude: Q1= Q2= Q3 = B
In fact, from the power source, charges arrive only on the outer plates of the capacitor circuit, and on the interconnected inner plates of adjacent capacitors, only the transfer of the same charge from one plate to another occurs (electrostatic induction is observed), therefore, equal and different electric charges.
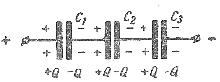
Rice. 3. Scheme of series connection of capacitors
The voltages between the plates of the individual capacitors when they are connected in series depend on the capacities of the individual capacitors: U1 = Q / C1, U1 = Q / C2, U1 = Q / C3 and the total voltage U = U1 + U2 + U3
The total capacity of an equivalent (equivalent) capacitor C = Q / U = Q / (U1 + U2 + U3), when the capacitors are connected in series, the reciprocal value of the total capacity is equal to the sum of the reciprocal values of the capacities of the individual capacitors.
Equivalent capacitance formulas are similar to equivalent conductance formulas.
Example 1… Three capacitors whose capacitance C1 = 20 microfarads, C2 = 25 microfarads and C3 = 30 microfarads are connected in series, it is necessary to determine the total capacitance.
The total capacitance is given by the expression 1 / C = 1 / C1 + 1 / C2 + 1 / C3 = 1/20 + 1/25 + 1/30 = 37/300, whence C = 8.11 μF.
Example 2. 100 capacitors with a capacity of 2 microfarads are connected in parallel.Determine the total capacity. The total capacitance is C = 100 CK = 200 microfarads.

