Linear electrical circuits
 An electrical circuit is called a set of elements that form paths for passage electricity… An electrical circuit consists of active and passive elements.
An electrical circuit is called a set of elements that form paths for passage electricity… An electrical circuit consists of active and passive elements.
Active elements are considered sources of electrical energy (sources of voltage and current), passive elements include resistors, inductors, electrical capacitors.
The quantitative characteristics of the elements of an electric circuit are called its parameters... For example, the parameters of a constant voltage source are its EMF and internal resistance… The parameter of the resistor is its coil resistance — its inductance L and capacitor — capacitance C.
The voltage or current supplied to the circuit will be called an acting or input signal… Acting signals can be viewed as different functions of time varying according to some law z(T)… For example z(T) can be constant, changing in time according to a periodic law or have an aperiodic character.
Voltages and currents arising under the influence of external influences in the part of the electric circuit that interests us and which are also functions of time NS (T), we will call chain reaction or weekend signal.
Every passive element of a real electrical circuit has some degree of active resistance, inductance, and capacitance. However, in order to facilitate the study of processes in an electric circuit and its calculation, the real circuit is replaced by an idealized one consisting of separate spatially separated elements R, L, S.
In this case, it is considered that the wires connecting the elements of the circuit have no active resistance, inductance and capacitance. Such an idealized circuit is called a folded-parameter circuit, and calculations based on it give in many cases results that are well confirmed by experience.
NSElectrical circuits with constant parameters are such circuits in which the resistances of the resistors R, the inductance of the coils L and the capacity of the capacitors C are constant, independent of the currents and voltages acting in the circuit. Such elements are called linear.
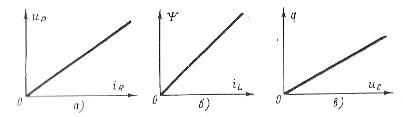
If the resistance of the resistor R does not depend on the current, then the linear relationship between the voltage drop and the current is expressed Ohm's Law ur = R NS ir, and the current-voltage characteristic of the resistor (is a straight line (Fig. 1, a).
If the inductance of the coil does not depend on the value (of the current flowing in it, then the connection of the self-induction flux of the coil ψ directly proportional to this current ψ= L NS il (Fig. 1, b).
Finally, if the capacitance of the capacitor C does not depend on the voltage uc applied to the plates, then the charge q accumulated on the plates and the voltage u° C are interconnected by a linear relationship, graphically shown in fig. 1,v.
Rice. 1. Characteristics of linear elements of the electric circuit: a — current-voltage characteristic of the resistor, b — dependence of the flux connection on the current in the coil, c — dependence of the capacitor charge on the voltage across it.
The linearity of resistance, inductance and capacitance is conditional, because in reality all real elements of an electrical circuit are non-linear. So, when passing current through the last resistor heats up and its resistance changes.
Excessively increasing the current in a ferromagnetic coil can slightly change its inductance. The capacity of capacitors with different dielectrics changes to one degree or another, depending on the applied voltage.
However, in the normal mode of operation of the elements, these changes are usually so insignificant that they may not be taken into account in the calculations, and such elements of the electrical circuit are considered linear.
Transistors operating in modes when straight-line sections are used with their current-voltage characteristics can also be conditionally considered as linear devices.
An electrical circuit consisting of linear elements is called a linear electrical circuit. Linear circuits are characterized by linear equations for currents and voltages and substituted linear equivalent circuits. Linear equivalent circuits consist of linear passive and active elements whose volt-ampere characteristics are linear.For the analysis of processes in linear electrical circuits are used Kirchhoff's laws.