Similarities and differences between an RCD and a residual current device
Similarities:
-
 The same principle of leakage current monitoring — using a differential current transformer
The same principle of leakage current monitoring — using a differential current transformer
- The same way to protect personnel is by disconnecting from the mains all working wires suitable for the electrical installation, using a highly reliable mechanical release with a powerful contact group and a mechanism for charging the opening springs with a position indicator.
- The same way to check for operability is through an artificially created differential current using a special electrical test circuit.
Differences:
- Availability only for RCD(differential switch) a sensitive element that has no power consumption of its own and therefore always remains in operation.
In a differential automaton, this sensitive element is an electronic threshold device with a power source, which can lose its operation in the event of failure of electronic components, as well as in the event of a break in a phase or neutral wire to the place of installation of the differential automaton.
- Only the differential circuit breaker has built-in protection against overload and all types of short-circuit currents in the electrical network and therefore has more powerful power contacts with an arc extinguishing system.
In contrast, it is recommended to install it in series with an RCD circuit breaker with a rated release current one step lower than the rated current, which is why the tripping of single-phase short-circuit currents by the RCD itself is not allowed (the RCD does not respond to three-phase and two-phase short-circuit currents).
- Only the differential automatic has a reset solenoid that reliably pulls the latch on the shunt tripping mechanism. However, this electromagnet is also fed from a power source using an electronic amplifier with a threshold device.
With an RCD, the impact on the free release mechanism is carried out by a magnetoelectric lock, which does not have a dedicated power source and therefore always remains in operation.
Electrical diagrams and conventional graphic designation of the RCD and the differential machine
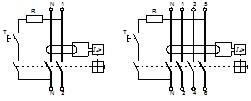
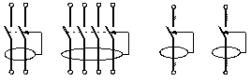
Rice. 1. Differential switch (RCD): a) electrical diagrams b) conventional graphic designation
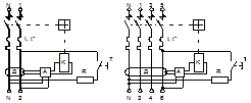
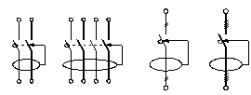
Rice. 2. Differential machine: a) electric circuits b) conventional graphic notation