Main characteristics of insulators
 Insulators must have certain Electrical characteristics… These include: dry discharge, wet discharge and breakdown voltage.
Insulators must have certain Electrical characteristics… These include: dry discharge, wet discharge and breakdown voltage.
Dry discharge is the voltage applied to the metal electrodes of an insulator at which a bona fide discharge occurs on its surface under normal atmospheric conditions.
Wet discharge is the voltage applied to the insulator, in which a discharge occurs on the surface of the insulator, which is under the influence of rain streams falling on it at an angle of 45 ° (Fig. 1). In this case, the force of the rain should be equal to 5 mm / min, and the specific volume resistance of water should be in the range of 9500 — 10 500 ohm NS cm (at 20 ° C).
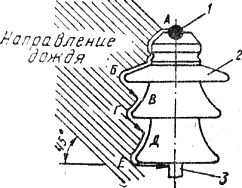
Rice. 1. Pin Insulator Test to Determine Wet Discharge Voltage: 1 — Conductor, 2 — Insulator, 3 — Steel Pin, A — B — C — D — D — E — Electric Discharge
The value of the wet discharge voltage of the insulator, determined during the tests, makes it possible to estimate how the insulator will behave under operating conditions in the rain.For any insulator, the wet-discharge voltage value is always less than its dry-discharge voltage value, because when exposed to rain, a significant portion of the insulator's surface becomes wet with water and begins to conduct current.
Insulator breakdown voltage is the voltage at which the breakdown of the insulator material occurs between the main electrodes, for example between the rod and the cap of a suspension insulator.
The breakdown voltage of any insulator is always greater than its dry-discharge voltage, and even more so its wet-discharge voltage.
In addition to electrical characteristics, insulators specify mechanical characteristics… These are the mechanical stresses measured when testing insulators for breaking, bending, and head shear (for pins).
So, in order to determine the breaking load of the bushing (Fig. 2), it is firmly fixed with a flange on a steel plate (using bolts). A loop of steel cable is placed on the conductor rod of the insulator and a bending force is applied to it. This force gradually increases to a value at which the insulator breaks.
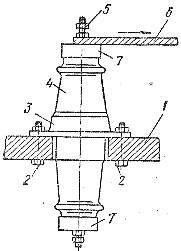
Rice. 2. Mechanical testing of the sleeve: 1 — steel plate, 2 — fixing bolts, 3 — cast iron flange, 4 — porcelain insulator element, 5 — conducting rod, 6 — steel cable, 7 — cap
The numerical values of the electrical and mechanical characteristics of insulators are established by the relevant GOSTs.
A very important feature of insulators is their heat resistance resistance to sudden changes in temperature.This characteristic is determined by double heating and cooling of the insulator and water at a temperature difference between hot and cold water of 70 ° C (for porcelain insulators) and 50 ° C (for glass insulators).
After these thermal changes, the insulators must withstand without damage a three-minute electrical voltage test in which a continuous stream of sparks forms on the surface of the insulator.
Suspended insulators, which are most responsible for their purpose, are subjected to a three-fold cycle of cooling and heating at a temperature from - 60 to + 50 ° C with the simultaneous application of a mechanical load equal to 3000 - 4500 kg or more, depending on for the type of insulator. These are thermomechanical strength tests that end with electromechanical tests.
Each test cycle begins by cooling the insulators to -60 ° C. At this temperature, the insulators are held for one hour, then the heating of the insulators to 50 ° C is started and again held for one hour. After each heat exchange cycle, the insulators are checked with a voltage of 45 — 51 kV at a temperature of 20 ± 5 ° C.
The test ends with a smooth increase in mechanical tensile load after the third cycle when the insulators are heated to 50 °C.
All insulator tests described are typical, that is, not every insulator produced by the factory is tested, but a certain percentage (0.5%) of the entire batch of insulators produced.
Each of the high-voltage insulators produced is subjected to a three-minute voltage test in which a stream of sparks forms on the surface of the insulators. All insulators that pass this electrical test are considered operational.
All manufactured suspension insulators are subjected to an additional one-minute mechanical tensile test. Before electrical tests, one-minute mechanical tests are performed to reject weakly reinforced, as well as insulators with defective porcelain or glass elements and defective reinforcement (cracks, etc.). Insulators that have passed the one-minute mechanical test are then subjected to the electrical mass test described above.

