What materials are modern insulators made of?
Materials of modern insulators
Today, everywhere on our planet, on land and under water, there are power lines. Only in the territory of the former Soviet Union, the length of all power lines is such that it is many times greater than the length of the equator. And no overhead power line can do without the use of insulators today. Thanks to insulators, it became possible to build reliable and stable energy systems with a constant operating voltage of up to 0.5 megavolts.

A large number of different insulators, each of which is suitable for solving its own problems, are structurally different, but at the same time quite functional. They provide reliable insulation of high-voltage power lines from conductive supports, as the dielectric properties of insulating materials ensure this.
Each of the sections of the insulator, like the insulator as a whole, serves throughout the entire period of operation of the high-voltage line, therefore the main requirement for the insulator is durability. And the material of the insulator is obliged to provide this condition. The main materials of insulators are glass, porcelain and polymers.
The glass used in the insulators is not ordinary, it is made of tempered glass, which is particularly durable, and the suspension insulators based on it, assembled in the garland, have excellent dielectric properties, while the price is quite low for products of this kind that are so important.
Porcelain has the highest strength among traditional insulating materials. It is painlessly able to withstand even lightning, due to the fact that the raw mass of porcelain is plastic, and the shape can be given the most optimal, so that the configuration of the finished insulator turns out to be the least vulnerable even to such a great atmospheric phenomenon.
Polymer insulators — the most modern solution, they began to be made and applied relatively recently. Polymer insulators for power lines are durable, have excellent dielectric properties, and their production is not associated with large material costs. For hundreds of kilovolts a polymer insulator won't work, but for tens of kilovolts a polymer insulator is exactly what you need. Next, we will look in detail at the materials of modern insulators.
The production of insulators based on silicone rubber, which has been developing in recent years, is a more progressive solution.
Silicone rubber — that's it rubber which is elastic in nature… For this reason, silicone rubber is widely used as an insulating material for very flexible cables. In general, various rubbers are used in the energy sector: styrene-butadiene, butadiene, silicon silicon and ethylene-propylene, as well as natural. Organosilicon rubber is based on polyorganosiloxanes.
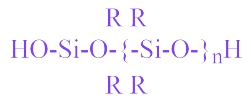
In this formula, R is organic radicals. The type of radicals determines the characteristics of silicone rubber.The main chain can contain both silicon and oxygen, as well as nitrogen, boron and carbon. Accordingly, this will result in siloxane, borosiloxane and silica rubbers.
Organosilicon rubber is obtained by vulcanization of rubber, that is, the molecules are cross-linked in spatial complexes. A chemical bond is formed by radicals or by terminal OH and H groups. The reaction is carried out by exposure to radiation or by using chemical agents at high temperatures. The manufacturer supplies the mass ready for vulcanization.

Pure silicon silicon rubber does not have high electrical properties; it turns out to be fragile, vulnerable to ozone and light. Therefore, in order to obtain a sufficiently reliable insulator, a composite material based on silicon silicon rubber is needed. To achieve acceptable quality, an active reinforcing filler, which is titanium dioxide and silica nanopowders, is added. The result is a material with acceptable properties. Here are the average specs:
-
Density: 1350 kg / m3;
-
Tear strength: 5 MPa;
-
Heat capacity: 1350 J / kg-K;
-
Thermal conductivity: 1.1 W / m-k;
-
Electrical strength: 21 kV / mm;
-
Dielectric loss tangent: 0.00125;
-
Specific surface resistance: 50.5 TΩ;
-
Bulk resistance: 5.5 TΩ-m.
-
Dielectric constant: 3.25.
As a result, regarding silicon rubber, it can be noted that its electrophysical properties are satisfactory, thermal conductivity is high enough, mechanical strength leaves much to be desired. Remarkable resistance to light, ozone, oil. Operating temperatures in the range from -90 ° C to + 250 ° C. The material is waterproof, but oil-resistant and gas-permeable.

Porcelain.Speaking of porcelain, electric porcelain for insulators, remember that it is an artificial mineral based on clay, quartz and feldspar. The final product is obtained by heat treatment using ceramic technology.
The most remarkable properties of electric porcelain are heat resistance, chemical resistance, resistance to any atmospheric influences, electrical and mechanical strength and low cost. Based on these advantages, porcelain is used to manufacture insulators. Here are its average specs:
-
Density: 2400 kg / m3;
-
Tear strength: 90 MPa;
-
Heat capacity: 1350 J / kg-K;
-
Thermal conductivity: 1.1 W / m-k;
-
Electrical strength: 27.5 kV / mm;
-
Dielectric loss tangent: 0.02;
-
Specific surface resistance: 0.5 TΩ;
-
Bulk resistance: 0.1 TΩ-m.
-
Dielectric constant: 7.
If we compare porcelain and silicone rubber, then compared to rubber, porcelain is fragile, very heavy, has a high dielectric loss tangent.

As for the glass, electrotechnical glass, compared to porcelain, has a more stable raw material base, its production technology is simpler, easier to automate, and most importantly, it is easy to identify the malfunction or damage of the insulator with an eye. Breaking a series of glass insulators causes the dielectric skirt to fall to the ground, and breaking porcelain does not damage the skirt. Damaged glass insulator is immediately visible and for the diagnosis of porcelain one must resort to the use of additional devices, night vision devices.
Chemically, electric glass is a set of oxides of sodium, boron, calcium, silicon, aluminum, etc. It's actually a very, very thick liquid.Electric glass is different from ordinary alkaline glass, it is low alkali glass, it does not crack and fog during operation. Here are its features:
-
Density: 2500 kg / m3;
-
Tear strength: 90 MPa;
-
Heat capacity: 1000 J / kg-K;
-
Thermal conductivity: 0.92 W / m-k;
-
Electrical strength: 48 kV / mm;
-
Dielectric loss tangent: 0.024;
-
Specific surface resistance: 100 TΩ;
-
Specific volume resistivity: 1 TOM-m.
-
Dielectric constant: 7.
Disadvantages of glass insulators include high energy consumption in the production of electrical glass, as it must be cooked for a long time.
