Optimization of the substation protection storage system
According to «Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations» SO 153-34.03.603-2003 According to Appendix No. 8 they must be equipped with the following protective devices.
Name of remedies Quantity
Switchgear with a voltage above 1000 V
Insulating rod (operational or universal) 2 pcs. for each voltage class Voltage indicator Also Insulating pliers (in the absence of a universal bar) 1 pc. for each voltage class (with suitable fuses) Dielectric gloves At least 2 pairs Dielectric boots (for outdoor switchgear) 1 pair Portable earthing At least 2 for each voltage class Protective fences (shields) Not less than 2 pcs. Safety posters and signs (portable) According to local conditions Insulating gas mask 2 pcs. Protective shields or glasses 2 pcs.
Switchgear up to 1000 V
Insulating rod (operational or universal) According to local conditions Voltage indicator 2 pcs. Insulation pliers 1 pc. Dielectric gloves Two pairs Dielectric overshoes Two pairs Dielectric carpet or insulating mat According to local conditions Safety fences, insulating mats, portable placards and safety signs Also Safety shields or glasses 1 pc. Portable earthing According to local conditions Switchboards and control panels of power plants and substations, premises (workplaces) of electricians on duty Voltage indicator 1 computer. for each voltage class over 1000 V and 2 pcs. for voltage up to 1000 V Insulating clamp for voltage over 1000 V 1 pc. for each voltage class above 1000 V Isolation clamps for voltage up to 1000 V 1 pc. Electric clamp According to local conditions Dielectric gloves Two pairs Dielectric overshoes Two pairs Insulating tool 1 set Portable grounding According to local conditions Dielectric carpets and insulating mats Also Posters and safety signs (portable) Also Safety helmets 1 pc. for each employee Protective shields or glasses 2 pcs. Hoods 2 pcs.
A large range of used protective equipment requires special conditions for storage in substations (point 1.3. Procedure for storing protective equipment).
1.3. STORAGE PROCEDURE FOR SAFEGUARDS
1.3.1. Protective equipment must be stored and transported in conditions that guarantee its operation and suitability for use, must be protected from mechanical damage, dirt and moisture.
1.3.2.Protective equipment must be stored in closed rooms.
1.3.3. Protective equipment made of rubber and polymer materials that are used must be stored in cabinets, on racks, shelves, separately from tools and other protective means. They must be protected from the effects of acids, bases, oils, gasoline and other destructive substances, as well as from direct exposure to sunlight and thermal radiation from heating devices (no closer than 1 m from them).
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymer materials that are used should not be stored in bulk in bags, boxes, etc.
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymer materials in stock should be stored in a dry room at a temperature of (0-30) ° C.
1.3.4. Insulating rods, clamps and indicators for voltages above 1000 V must be stored in conditions that do not allow them to bend and touch the walls.
1.3.5. Respiratory protection equipment must be stored in dry rooms in special bags.
1.3.6. Protective equipment, isolating devices and live devices must be stored in a dry, ventilated room.
1.3.7. Shielding protective equipment must be stored separately from electrical protective equipment.
Separate shielding sets are stored in special cabinets: coveralls — on hangers, and special shoes, head, face and hand protection — on shelves. During storage, they must be protected from moisture and corrosive environments.
1.3.8. Protective equipment for use by field crews or for personal use by personnel should be stored in cases, bags, or boxes separately from other tools.
1.3.9. Protective equipment is placed in specially equipped places, as a rule, at the entrance to the premises, as well as on the control panels. Storage areas should have a list of protective equipment. Storage areas should be equipped with rod hooks or clamps, insulating tongs, portable earthing devices, safety placards, as well as cabinets, racks, etc. for other remedies.
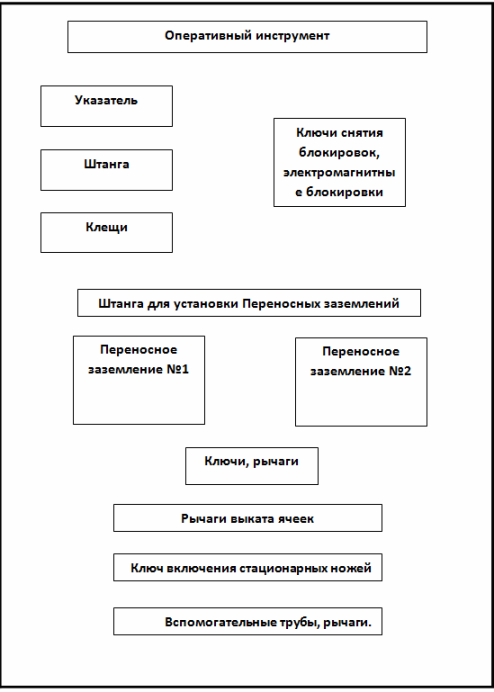
Today, storage is done on racks, hooks, in cabinets — where there is no clear distinction between the placement of protective equipment and tools. For rational use and reduction of search and operation time, which in turn helps to reduce switching time and therefore increase labor productivity: I suggest, in the absence of storage cabinets, to use shields with a clear distinction, Figure 1.
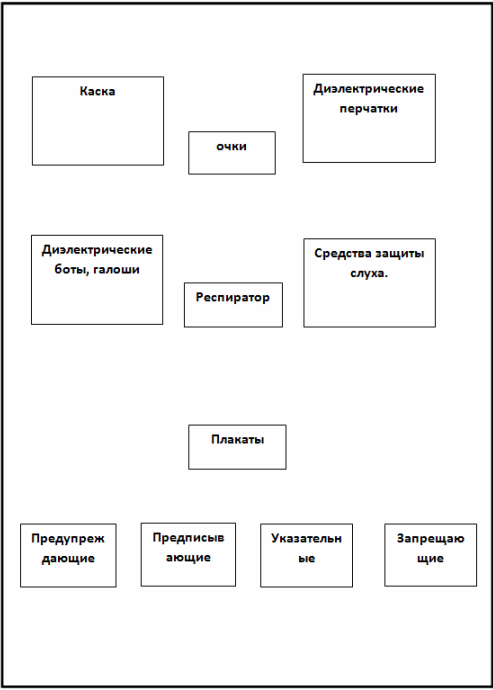
All defenses located on the shield must be signed. On the left place protective equipment (helmets, dielectric gloves, boots, etc.), in the lower left corner are posters and safety signs. which, in turn, should be divided into: prohibitive, warning, prescriptive and indicative.
On the right side, place the operating tool (insulating rods, insulating and electrical measuring pliers, assembly tools with insulating handles and voltage indicators.), which must also be separated and signed. In the lower right corner, place the portable ground, as well as the shift levers and handles, which must also be signed.
If there are cabinets, boxes in the substation, make a similar distinction.
Today, many enterprises apply the 5C system, this proposal is also one of the directions for the development of the 5C system in the energy sector.
