Parallel operation of transformers
Parallel operation of transformers — connection of transformers for joint operation, with such a connection, the terminals of the same name on the windings on the high voltage side and the windings on the low voltage side are connected to each other.
Connection of primary windings only or secondary windings only should not be confused with parallel operation of transformers. Such a connection is defined as the operation of two transformers together.
If it is necessary to connect transformers for parallel operation in order to avoid negative consequences for the equipment, several factors must be taken into account. Let's consider in detail the conditions for turning on power transformers for parallel operation.
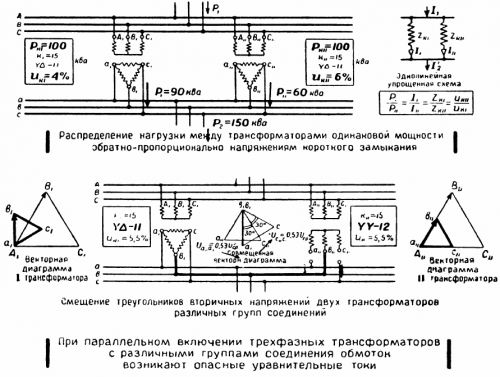
Equality of coil connection groups
There are some groups of connections of transformer windings… Each group differs in its phase angle of primary and secondary voltage.Therefore, if you connect two transformers with different groups of winding connections for parallel operation, this will lead to the appearance of large equalizing currents in the windings, which will cause damage to the transformers.
Therefore, the first condition for connecting transformers for parallel operation is the equality of their groups of winding connections.
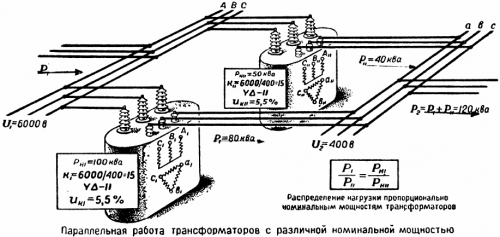
Rated power of transformers
The second condition necessary for the possibility of including transformers for parallel operation is the ratio of their rated power no more than 1 to 3. For example, if rated power of a power transformer 1000 kVA, may then be connected for parallel operation with another transformer, rated from 400 kVA to 2500 kVA — all values in this power range in a ratio of 1000 kVA not exceeding 1 to 3.
Parallel operation of transformers with different capacities:
Nominal voltage of the windings, transformation ratio
The third condition is the equality of the nominal voltages of the windings of the transformers connected for joint operation. If the voltages of the secondary windings of the transformers differ, this will cause equalizing currents to occur, which in turn leads to voltage drops and unwanted losses.
A slight voltage deviation is allowed - a difference transformation ratios in the range of up to 0.5%.
In transformers, where it is possible to adjust the transformation ratio by increasing or decreasing the number of turns of the coils, it is necessary to take into account the position of the switching devices-circuit breaker or load switch.If necessary, with the help of these devices, you can adjust the transformer voltage to the required values, then you can connect the secondary windings — turn on the transformers for parallel operation.
Short circuit voltage
Each transformer in the passport shows such a parameter as short circuit voltage… This value indicates the percentage of the rated primary voltage of the power transformer that must be applied to the primary in order for the rated current to flow through the winding when the secondary terminals are short-circuited.
Short-circuit voltage characterizes the internal resistance of the windings of the power transformer. Therefore, if transformers with different short-circuit voltage indicators are connected in parallel, then the internal resistances of the transformers will be disproportionate, and when the load is connected, the transformers will be loaded unevenly: one of the transformers may be overloaded and others underloaded.
In this case, the load will be distributed inversely proportional to the short-circuit voltage - that is, the transformer with a lower short-circuit voltage value will be overloaded.
Therefore, the fourth condition for connecting transformers for parallel operation is the equality of short-circuit voltages. Short circuit voltage difference is 10%.
Load distribution between transformers of different power
If it is necessary to connect transformers for parallel operation, the question arises: how will the load be distributed between transformers of different rated power? If the above conditions are met, the load on the transformers will be distributed proportionally, in accordance with their rated powers.
But despite the compliance of the passport data with the above conditions, the actual parameters of the transformers included for parallel operation may differ slightly.
First of all, this is due to the technical condition of the transformer, possible inconsistencies in production or design changes during repair and restoration work. In this case, when connecting transformers for parallel operation, a disproportionate load distribution may be observed.
A possible solution to this problem is to change the transformation ratio by switching the on-load tap-changer or on-load tap-changer. In this case, it is necessary to experimentally adjust the voltage on the secondary winding of the transformers so that the voltage on the winding of the underloaded transformer is higher than on the other transformer.
After selecting the transformers, taking into account the above conditions, one more important condition needs to be fulfilled — proceed gradually when connecting the terminals of the secondary windings to avoid creating an emergency situation in the electrical network-phase-phase short circuit.
That is, before connecting the terminals of the secondary windings, you must make sure that the same terminals will be connected - for this, a step-by-step check is carried out with special phasing indicators.
When connecting transformers for parallel operation, it is equally important to choose the right equipment for their connection to the electrical network.
The selection of switching devices and connecting wires on the LV and LV side of the transformers is carried out according to the rated current of the transformer windings, taking into account the permissible short-term overloads.
Protective devices - high-voltage switches, circuit breakers or fuses must be selected in such a way that the windings are not exposed to overloads beyond the permissible values, they are protected from possible short circuits in the electrical network.