Permissible overload of transformers
 At operation of power transformers it is necessary to overload them at certain times of the day, so that due to underloading at other times, the daily wear of the insulation of the winding from overheating is not higher than the wear that corresponds to the rated mode of operation of the transformer, because the change in temperature of the insulation by 6 °C results in a double change in its service life.
At operation of power transformers it is necessary to overload them at certain times of the day, so that due to underloading at other times, the daily wear of the insulation of the winding from overheating is not higher than the wear that corresponds to the rated mode of operation of the transformer, because the change in temperature of the insulation by 6 °C results in a double change in its service life.
Duration t daily permissible systematic overload of the transformer, calculated by the coefficient of excess load K2, depends on the initial load coefficient K1 transformer, its rated power Snom, cooling system, time constant of heating and equivalent temperature of the cooling air corresponding to a given period of the year.
Coefficients K1 and K2 are determined by the ratios of the equivalent initial and maximum currents respectively to the nominal current of the transformer, and the equivalent values are understood as their root mean square values before the beginning of the greatest load and for the period of its maximum.
Graphs of carrying capacity of transformers DA CE2 (K1) corresponding to different duration T systematic overload (Fig. 1), allow a given initial state of the transformer, characterized by the coefficient K1 is determined by the daily load schedule Az(T) 10 hours before the beginning of its maximum and a given duration t of systematic overload, find the permissible overload factor K2 for the period of maximum load of the transformer.
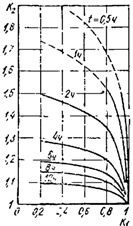
Rice. 1. Graphs of the load capacity of three-phase transformers with a rated power up to 1000 kVA with natural air and oil circulation and a constant heating time of 2.5 h at an equivalent cooling air temperature of 20 ° C.
Equivalent cooling air temperature — its constant temperature at which there is the same wear on the insulation of the windings of a transformer carrying a constant load as with the existing variable air temperature. With a practically unchanged load and the absence of systematic daily and seasonal fluctuations, the equivalent temperature of the cooling air is assumed equal to 20 ° C.
If the maximum average load curve I(t) less in summer rated power of the transformer, then in the winter months an additional 1% overload of the transformer is allowed for each percent of the underload in the summer, but not more than 15%, and the total load should not be more than 150% of the rated one.
In an emergency, allow short-term overloading of transformers above the rated one, which is accompanied by increased wear of the winding insulation and a decrease in the service life of the transformers (see table).
Permissible short-term overloads of transformers in emergency modes
Transformers
oil-filled dry overload of super-rated current,% duration of transformer overload, min. 60 5 200 1.5
Such overloads are permissible for all cooling systems, regardless of the previous mode, the temperature of the cooling air and the location of the transformers, provided that the oil temperature in the upper layers does not exceed 115 ° C. In addition, for oil-filled transformers operating with initial load factor K1 <0.93, an overload of 40% above the rated current is allowed for no more than 5 days for a maximum load time of a total duration of no more than 6 hours per day, with all measures taken to improve cooling on the transformer...
At a variable load of a substation with several transformers, it is necessary to prepare a schedule for turning on and off parallel operating transformers in order to achieve economical modes of their operation.
In real conditions, it is necessary to deviate somewhat from the design mode so that the number of operating switchings of each transformer does not exceed ten during the day, i.e. it is not necessary to turn off the transformers for less than 2-3 hours.
At parallel operation of transformers the total load of the transformer substation must provide sufficient load for each of them, as judged by the readings of the respective ammeters, the installation of which for transformers with a rated power of 1000 kVA and above is mandatory.
Modern transformers operating at high magnetic induction should not operate with a significant increase in the primary voltage, as this is accompanied by an increase in electrical energy losses for heating the magnetic circuits. A continuous increase in the primary voltage when the transformer is loaded, which does not exceed the rated one, is allowed up to 5% of the voltage of this branch, and when it is loaded at 25% of the rated power - up to 10%, which can be tolerated even under load , which does not exceed the nominal duration of up to 6 hours per day.
The degree of unevenness of the load in the phases of the transformer should not exceed 20%. It is defined as:
Kn = (Azlyulka — AzSr. / Azcf) x 100,
where, Azmax is the current of the overloaded phase at the moment of the greatest load of the transformer, AzCr. — the average current of the three phases of the transformer at the same time.

