Electrolysis. Calculation examples
 Electrolysis is the decomposition of an electrolyte (a solution of salts, acids, bases) by means of an electric current.
Electrolysis is the decomposition of an electrolyte (a solution of salts, acids, bases) by means of an electric current.
Electrolysis can only be done with direct current. During electrolysis, the hydrogen or metal contained in the salt is released at the negative electrode (cathode). If the positive electrode (anode) is made of metal (usually the same as in salt), then the positive electrode dissolves during electrolysis. If the anode is insoluble (e.g. carbon), then the metal content of the electrolyte decreases during electrolysis.
The amount of substance released during electrolysis at the cathode is proportional to the amount of electricity that has passed through the electrolyte.
The amount of substance released by one coulomb of electricity is called the electrochemical equivalent of A, therefore G = A • Q; G = A • I • t,
where G is the amount of isolated substance; Q is the amount of electricity; I — electric current; t is time.
Each metal has its electrochemical equivalent A.
Calculation examples
1. How much copper will be released from copper sulfate (CuSO4) (Fig. 1) with a current I = 10 A for 30 minutes.Electrochemical equivalent of copper A = 0.329 mg / A • sec.
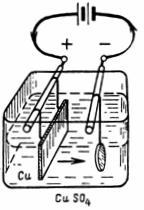
Rice. 1. Scheme for example 1
G = A • I • t = 0.329 • 10 • 30 • 60 = 5922 mg = 5.922 g.
An object suspended at the cathode will release 5.9 g of pure copper.
2. Permissible current density in copper electrolytic coating • = 0.4 A / dm2. The area of the cathode to be covered with copper is S = 2.5 dm2. What current is required for electrolysis and how much copper is released at the cathode in 1 hour (Fig. 2).
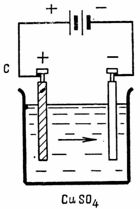
Rice. 2. Scheme for example 2
I = •• S = 0.4-2.5 = l A; G = A • Q = A • I • t = 0.329 • 1 • 60 • 60 = 1184.4 mg.
3. Oxidized water (for example, a weak solution of sulfuric acid H2SO4) during electrolysis decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen. Electrodes can be carbon, tin, copper, etc., but platinum is best. How much oxygen will be released at the anode and how much hydrogen will be released at the cathode in 1/4 hour at a current of 1.5 A. The amount of electricity 1 A sec releases 0.058 cm3 of oxygen and 0.116 cm3 of hydrogen (Fig. 3).
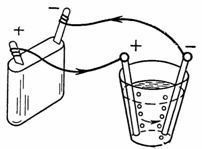
Rice. 3. Scheme for example 3
Ga = A • I • t = 0.058 • 1.5 • 15 • 60 = 78.3 cm3 of oxygen will be released at the cathode.
Gc = A • I • t = 0.1162 • 1.5 • 15 • 60 = 156.8 cm3 of hydrogen will be released at the anode.
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen in this ratio is called an explosive gas, which, when ignited, explodes, forming water.
4. Oxygen and hydrogen for laboratory experiments are obtained using electrolysis of water (oxidized sulfuric acid) (Fig. 4). Platinum electrodes are soldered into the glass. Using the resistance, we set the current I = 0.5 A. (A battery of three dry cells of 1.9 V is used as a current source) How much hydrogen and oxygen will be released after 30 minutes.
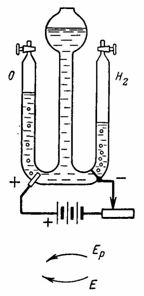
Rice. 4… Figure 4 for example
In the right vessel, Gc = A • I • t = 0.1162 • 0.5 • 30 • 60 = 104.58 cm3 of hydrogen will be released.
In the left vessel, Ga = A • l • t = 0.058 • 0.5 • 30 • 60 = 52.2 cm3 of oxygen will be evolved (the gases displace water in the middle vessel).
5. The converter block (motor-generator) provides current for obtaining electrolytic (pure) copper. In 8 hours you should get 20 kg of honey. What current should the generator provide? • The electrochemical equivalent of copper is A = 0.329 mg / A • sec.
Since G = A • I • t, then I = G / (A • t) = 20,000,000 / (0.329 • 8 • 3600) = 20,000,000 / 9475.2 = 2110.7 A.
6. It is necessary to chrome 200 headlights, of which 3 g of chrome is required for each. What current is required to do this work in 10 hours (electrochemical equivalent of chromium A = 0.18 mg / A • sec).
I = G / (A • t) = (200 • 3 • 1000) / (0.18 • 10 • 3600) = 92.6 A.
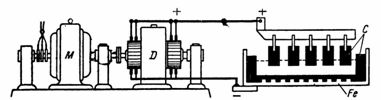
7. Aluminum is obtained by electrolysis of a solution of kaolin clay and cryolite in baths at a working voltage of the bath of 7 V and a current of 5000 A. The anodes are made of coal, and the bath is made of steel with coal blocks (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5Figure 5 for example
Aluminum production baths are connected in series to increase the working voltage (for example, 40 baths). To produce 1 kg of aluminum, approximately 0.7 kg of carbon anodes and 25-30 kWh of electricity are required. Based on the given data, determine the power of the generator, the energy consumption for 10 hours of operation, and the weight of the resulting aluminum.
Power of the generator when working on 40 baths P = U • I = 40 • 7 • 5000 = 1400000 W = 1400 kW.
Electrical energy consumed for 10 hours, A = P • t = 1400 kW 10 h = 14000 kW • h.
The amount of aluminum obtained G = 14000:25 = 560 kg.
Based on the theoretical electrochemical equivalent, the amount of aluminum obtained should be equal to:
GT = A • I • t = 0.093 • 5000 • 40 • 10 • 3600 = 0.093 • 720,000,000 mg = 669.6 kg.
The efficiency of the electrolytic installation is equal to: Efficiency = G / GT = 560 / 669.6 = 0.83 = 83%.