Calculation of the current according to Ohm's law
 Electrical voltage causes current to appear. However, for the occurrence of current, only the presence of voltage is not enough, a closed current circuit is also necessary.
Electrical voltage causes current to appear. However, for the occurrence of current, only the presence of voltage is not enough, a closed current circuit is also necessary.
Just as water difference (ie water pressure) is measured between two levels, so electric voltage is measured with a voltmeter between two points.
The unit of voltage and electromotive force is 1 volt (1 V). A voltage of 1 V has a Volta element (plates of copper and zinc in dilute sulfuric acid). A normal Weston cell has a constant and accurate voltage of 1.0183 V at 20 °C.
Ohm's law expresses the relationship between electric current Az, voltage U and resistance r. Electric current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance: I = U / r
See here for more details: Ohm's Law
Examples:
1. A flashlight bulb is connected to a dry battery with a voltage of 2.5 V. What current flows through the bulb if its resistance is 8.3 ohms (Fig. 1)?
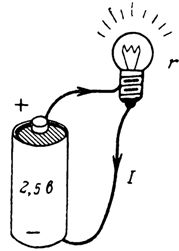
Rice. 1.
I = U / r = 4.5/15 = 0.3 A
2.A light bulb is connected to a 4.5 V battery whose coil has a resistance of 15 ohms. What current flows through the bulb (Fig. 2 shows the switching circuit)?

Rice. 2.
In both cases, the same current flows through the bulb, but in the second case, more energy is consumed (the bulb glows brighter).
3. The heating coil of an electric hob has a resistance of 97 ohms and is connected to the mains voltage U =220 V. What current flows through the coil? For the connection diagram, see fig. 3.
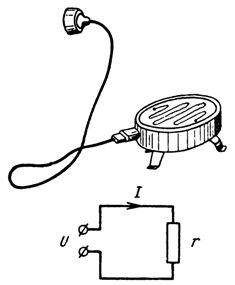
Rice. 3.
I = U / r = 220/97 = 2.27 A
The coil resistance of 97 ohms is given by taking heating into account. Cold resistance is less.
4. Voltmeter connected to the circuit according to the diagram in fig. 4, shows the voltage U =20th century What current flows through the voltmeter if it internal resistance rc = 1000 ohms?
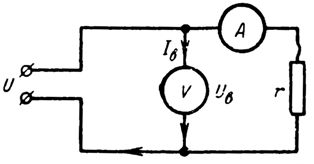
Rice. 4.
Iv = U / rh = 20/1000 = 0.02 A = 20 mA
5. A light bulb (4.5 V, 0.3 A) is connected in series with a rheostat r= 10 Ohm and battery voltage U =4 V. What current will flow through the bulb if the rheostat motor is in positions 1, 2 and 3 respectively (Fig. 5 shows the switching circuit)?
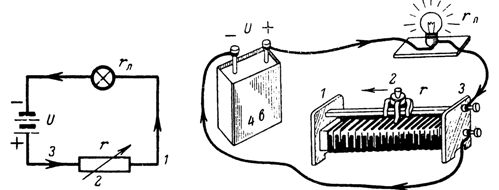
Rice. 5.
We calculate the resistance of the bulb according to its data: rl = 4.5 / 3 = 15 ohms
When the slider is in position 1, the entire rheostat turns on, that is, the circuit resistance increases by 10 ohms.
The current will be I1 = U / (rl + r) = 0.16 A = 4/25 = 0.16 A.
In position 2, the current flows through half of the rheostat, i.e. r = 5 ohms. I2 = 4/15 = 0.266.
In position 3, the rheostat is short-circuited (removed). Tok will be the largest, since it only passes through the bulb coil: Azh = 4/15 = 0.266 A.
6.The heat generated by the passage of an electric current through the transformer is to be used to heat a frozen iron pipe of internal diameter 500 mm and wall thickness 4 mm. A secondary voltage of 3 V is applied to points 1 and 2, 10 m apart. What current flows through the iron pipe (Fig. 6)?
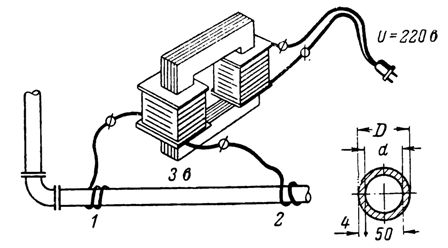
Rice. 6.
First we calculate the pipe resistance r, for which we need to calculate the cross-section of the pipe, that is, the area of the ring:
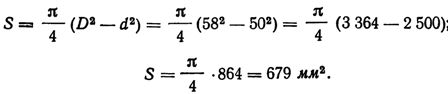
The electrical resistance of the iron tube r = ρl / S = 0.13 x (10/679) = 0.001915 Ohm.
The current flowing through the pipe is: I = U / r = 3 / 0.001915 = 1566 A.
See also on this topic: Calculating Ohm's Law Resistance
