Influence of frequency changes on the operation of electrical systems
 For electricity, the main quality indicators: voltage and frequency, for thermal energy: pressure, temperature of steam and hot water. Frequency is related to active power (P) and voltage is related to reactive power (Q).
For electricity, the main quality indicators: voltage and frequency, for thermal energy: pressure, temperature of steam and hot water. Frequency is related to active power (P) and voltage is related to reactive power (Q).
All rotating machines and assemblies are designed in such a way that economic efficiency is achieved at a nominal number of revolutions per minute: n = 60f / p,
where: n — the number of revolutions per minute, f — network frequency, p is the number of pole pairs.
The AC frequency generated by generators is a function of turbine speed. The number of revolutions of the mechanisms is a function of the frequency.
In fig. 1 shows the relative static load characteristics for the power system with respect to frequency.
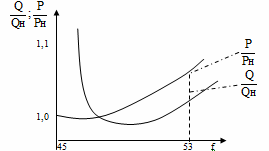
Rice. 1.
The dependency analysis in Fig. 1 shows that with a decrease in frequency, the number of revolutions of the engine decreases, the productivity of machines and mechanisms decreases.
An example.
1.A textile mill produces rejects when the frequency is changed from nominal as the thread speed changes and the machine tools produce rejects.
2. The pumps (supply), ventilation (flues) of the thermal power plant depend on the speed: the pressure is proportional to «n2″, Energy consumption»n3», where n — the number of revolutions per minute;
3. The active load power of synchronous motors is proportional to the frequency (when the frequency decreases by 1%, the active load power of the synchronous motor decreases by 1%);
4. The active load power of asynchronous motors is reduced by 3% when the frequency is reduced by 1%;
5. For the power system, a 1% reduction in frequency results in a 1-2% reduction in total load power.

The change in frequency affects the operation of the power plants themselves. Each turbine is designed for a certain number of revolutions, that is, when the frequency drops, the torque of the turbine decreases. The drop in frequency affects the plant's own needs, and as a result, a malfunction of the plant units may occur.
As the frequency decreases due to lack of active power, the user load is reduced to keep the frequency at the same level. The degree of change in the load when changing the frequency per unit by the regulating effect of the load on the frequency is called... The process of disturbing the stable operation of the power plant due to a drop in frequency and in the absence of a reserve of active power is called a frequency avalanche.
If f = 50 Hz, the critical frequency at which the performance of the main mechanisms of the auxiliary needs of power plants decreases to zero and an avalanche of frequencies occurs — 45 — 46 Hz.
As the frequency decreases, the emf decreases. generator (as the exciter speed decreases) and decreases mains voltage.
