What is power, thermal power, electric power and electrical systems
Energy (fuel energy complex) — an area of the economy that covers resources, production, transformation and use of various types of energy.
Energy in modern scientific understanding, it is understood as a general measure for all forms of movement of matter. Differentiation of thermal, mechanical, electrical and other forms of movement of matter.

Energy can be represented by the following interconnected blocks:
1. Natural energy resources and mining enterprises;
2. Refineries and transportation of finished fuel;
3. Production and transmission of electrical and thermal energy;
4. Consumers of energy, raw materials and products.
Summary of blocks:
1) Natural resources are divided into:
-
renewable (solar, biomass, water resources);
-
non-renewable (coal, oil);
2) Mining enterprises (mines, mines, gas wells);
3) fuel processing enterprises (enrichment, distillation, fuel purification);
4) Transportation of fuel (rail transport, tankers);
5) Production of electrical and thermal energy (CHP, NPP, HPP);
6) Transmission of electrical and thermal energy (electrical networks, pipelines);
7) Consumers of energy, heat (electricity and industrial processes, heating).
The main forms in which energy is used today are heat and electricity. Energy industries studying the production, transformation, transportation and use of thermal and electrical energy are called thermal power engineering, respectively.
The energy of water flows, previously used directly in the form of mechanical energy, is now converted into hydroelectric plants in electrical energy. The energy industry that studies the processes of converting water energy into electricity is called hydropower.
The opening of the way to the use of nuclear energy created a new branch of energy— nuclear or nuclear energy… The energy of nuclear processes is converted into thermal and electrical energy and used in these forms.
Questions about the use of the energy of moving air masses are considered wind energy. Wind energy used mainly in mechanical form. It deals with the use of solar energy solar energy.
Each of the branches of energy as a science has its theoretical basis based on the laws of physical phenomena in this field.
Energy, as the most important area of human activity, takes a long time for large-scale development.
Energy is a capital intensive industry. The power of the Earth's power plants exceeds one billion kilowatts.

A clear understanding of the unity and equivalence of different forms of energy took shape only in the middle of the nineteenth century, when a lot of experience had already been gained in converting some forms of energy into others:
-
a steam engine was created that converted heat into mechanical energy;
-
the first sources of electrical energy were discovered — galvanic cells, in which the direct conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy takes place;
-
by means of electrolysis, the reverse conversion is repeatedly carried out — electrical energy into chemical energy;
-
an electric motor was created in which electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy;
-
the phenomenon of direct conversion of electrical energy into heat was discovered.
In 1831, a method was discovered to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The natural conclusion of the huge amount of accumulated data on the transformation of some forms of energy into others was the discovery the law of conservation and transformation of energy — one of the basic laws of physics.
The need for energy conversion is due to the fact that different processes require different forms of energy.
Energy transformations are not limited to transforming some of its forms into others. Thermal energy is used at different values of the temperature of the cooling liquid (steam, gas, water), electrical energy — in the form of alternating or direct current and at different voltage levels.
The transformation of energy is carried out in various machines, apparatuses and devices, in general, constituting the technical basis of energy.
So in boiler plants the chemical energy of fuels is converted into heat, in a steam turbine this heat which is carried by water vapor is converted into mechanical energy which is then in an electric generator is converted into electrical energy.
In hydroelectric power plants, in water turbines and electric generators, the energy of water flows is converted into electrical energy, in electric motors, electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, etc.
The methods of creating and using various machines, apparatus, devices designed to receive, transform, transport and use various forms of energy are based on the relevant sections of the theoretical foundations of energy and make up sections of such technical sciences as thermal engineering, electrical engineering , hydraulic engineering and wind engineering.
Energy - a part of the energy sector that deals with the problems of obtaining large amounts of electricity, transmitting it over a distance and distributing it to consumers, its development is due to electric power systems.
An electrical system is a set of interconnected power plants, electrical and thermal systems, as well as consumers of electrical and thermal energy, united by the unity of the process of production, transmission and consumption of electricity.
 Electrical system: TPP — combined heat and power plant, NPP — nuclear power plant, KES — condensing power plant, Hydroelectric plant - hydroelectric plant, 1-6 — consumers of electricity from thermal power plants
Electrical system: TPP — combined heat and power plant, NPP — nuclear power plant, KES — condensing power plant, Hydroelectric plant - hydroelectric plant, 1-6 — consumers of electricity from thermal power plants
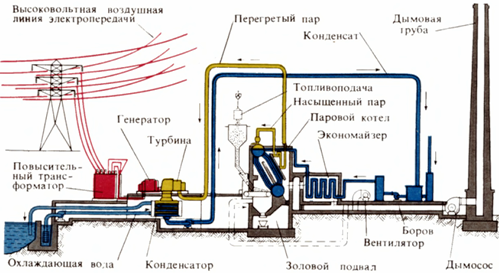
Schematic of a thermal condensing power plant
Electrical system (electrical system, ES) — the electrical part of the power system.

 Electrical system diagram
Electrical system diagram
The diagram is shown in a single-line image, that is, one line means three phases.
Technological process in the power system
The technological process is the process of converting the primary energy resource (fossil fuel, hydroelectric power, nuclear fuel) into a final product (electricity, thermal energy). The parameters and indicators of the technological process determine the efficiency of production.
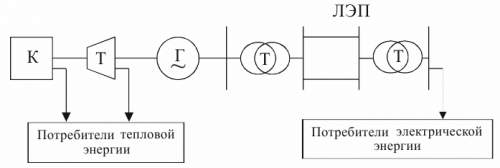
The technological process is schematically shown in the figure, from which it can be seen that there are several stages of energy conversion.
Scheme of the technological process in the power system: K — boiler, T — turbine, G — generator, T — transformer, power line — power lines
In the boiler K, the combustion energy of the fuel is converted into heat. The boiler is a steam generator. In a turbine, thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy. In the generator, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. The voltage of electrical energy in the process of its transmission along the power line from the station to the consumer is transformed, which ensures the efficiency of the transmission.
The efficiency of the technological process depends on all these connections. Therefore, there is a complex of regime tasks related to the operation of boilers, thermal power plant turbines, turbines of hydroelectric plants, nuclear reactors, electrical equipment (generators, transformers, power lines, etc.). It is necessary to choose the composition of the operational equipment, the mode of its charging and use and observe all restrictions.
Electrical installation - an installation in which electricity is produced, produced or consumed, distributed. It can be: open or closed (indoor).
Power plant — a complex technological complex on which the energy of a natural source is converted into the energy of electric current or heat.
It should be noted that power plants (especially thermal, coal-fired) are the main sources of environmental pollution from the energy sector.

Electric substation — electrical installation designed to convert electricity from one voltage to another with the same frequency.
Power transmission (power lines) — the structure consists of elevated substations of power lines and descending substations (system of wires, cables, supports) designed to transfer electricity from source to consumer.
Grid electricity — a set of power lines and substations, i.e. devices connecting power to energy consumers.