Interruption current
 Breaking current — instantaneous current protection, the selectivity of which with respect to the protection of adjacent sections is achieved by selecting the operating current Iss high maximum external short-circuit current Azkz.vn.mah.
Breaking current — instantaneous current protection, the selectivity of which with respect to the protection of adjacent sections is achieved by selecting the operating current Iss high maximum external short-circuit current Azkz.vn.mah.
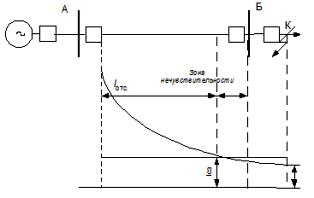
Protective operation in the protected area is ensured by the fact that the current in the line increases as the location of the fault approaches the power source. Response time current interruption is the sum of the operating time of the current and intermediate relay and is tnumber = 0.04 — 0.06 s.
An examination of the principle of operation of the current interruption is carried out for a radial line with a unidirectional supply. The maximum external short-circuit current in the protected line AB of length l occurs with a metallic short-circuit at the beginning of the next row, in the busbars of substation B (point K).
For the selective operation of the AB line current interruption, the operating current is selected for a three-phase short circuit as follows:
Azss = kot x Azkz.vn.mah.
Characteristic of current interruption: the protection zone that characterizes the sensitivity of the protection is only part of the line (Iss kz).According to the rules for electrical installations, current interruption is considered effective if the coverage area in the minimum mode is not less than 20% of the line length. Usually, overcurrent protection is installed together with overcurrent protection (MTZ) with a time delay in the first sections of the protected line.
Current interrupts can also be used to protect two-way lines.
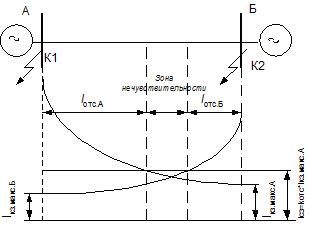
Interrupting currents are installed on both sides of line AB. For their selective operation, adjustment must be made from the maximum external fault current.
Several cases are considered:
Azss kz.mahA
Azss kz.mah B
A larger value is then selected. Because in this case azkz.mahA kz.mah B, then the limit operating current at both ends of the line is the same and is equal to Iss = cot x Azkz.mahA.
As you can see, a dead zone has formed, in the event of a short circuit, where none of the current breakers trip. At minimum load, the dead zone increases.
Since the shutdown time is short, almost instantaneous, when choosing the operating current, it is necessary to take into account the influence of aperiodic components, the values of which are high precisely in the first periods of the existence of the short-circuit current. The removal from the aperiodic component is carried out by choosing the limit factor kot = 1.2 — 1.3... In the case of using lines with bidirectional power supply, they are also disturbed by the oscillating currents.
For breaks whose coverage covers only part of the line, the same sensitivity is important for different types of short circuits.Therefore, to protect against polyphase faults in networks with an isolated neutral, a partial star scheme is usually used to connect the CTs.
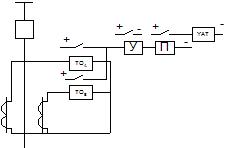
For surge protection of overhead lines that are not covered with cables, arresters are used that create artificial short circuits to ground, lasting up to 1.5 periods, which is proportional to the duration of the current interruption. To adjust from the operation of the limiters, an intermediate relay P with a trip time of 2-4 periods is used.
Current Interrupt Range: Used as auxiliary protection to reduce fault tripping time. In some cases, instantaneous current interruption can serve as primary protection, for example on radial lines feeding step-down transformers.
Advantages of the current outage:
1. Selectivity of operation in networks of any configuration with any number of power supplies.
2. Quick disconnection of the most severe short-circuits for the system, located near the buses of the stations and substations.
Disadvantages: Protect only part of the line length from metallic short circuits. In case of contact resistance failure, the breaking range can be reduced to zero.