The device of cable and string electric wires
Cable wiring
 Cable wiring is called electrical wiring made with special conductors with a built-in steel carrier cable, as well as wiring made with installed insulated wires or cables in which the conductors, insulating and supporting supports and structures are suspended freely or rigidly fixed on separate transverse or longitudinal steel supporting cables … The supporting cables, in turn, are suspended freely or in a tensioned position and are firmly attached at their ends to the building elements of buildings and structures by means of end and intermediate fastening structures.
Cable wiring is called electrical wiring made with special conductors with a built-in steel carrier cable, as well as wiring made with installed insulated wires or cables in which the conductors, insulating and supporting supports and structures are suspended freely or rigidly fixed on separate transverse or longitudinal steel supporting cables … The supporting cables, in turn, are suspended freely or in a tensioned position and are firmly attached at their ends to the building elements of buildings and structures by means of end and intermediate fastening structures.
Thread wiring
String wiring is called electrical wiring, in which, unlike cable wires, they are suspended on a tensioned steel wire (string) attached near the foundations of the building or their protrusions using end and intermediate fastening structures.In wired wiring, branches for connecting connectors, switches and other devices and devices fixed on building bases are more convenient than in wired wiring.
Conductors used for wiring cables and strings
For the device of cable and string electric conductors, as a rule, special conductors with a built-in supporting cable are used, as well as insulated conductors with conductors of arbitrary cross-section or light unarmored cables with conductors up to 16 mm2 inclusive and with a small number simultaneously suspended on the supporting cable and string wires with no more than three to four cores. However, this indication does not exclude the possibility, if necessary, of being suspended from a supporting cable. separate sections of electrical wiring and cable lines with a large number of wires and cables with wires with a cross section of 16 — 240 mm2 on the principle of structural arrangement of cable and string electric wires.
Ranges of cable and string electrical conductors
Cable and line electric wires are used for the device of the trunk, the distribution and the group of power and lighting lines in networks up to 380 V AC.
Wire and fiber cables are recommended to be used primarily for the installation of lighting networks. It is especially recommended to use them in lighting networks for indoor and outdoor warehouses, overpasses, galleries, sports grounds and open areas intended for vehicles.
In the premises of industrial enterprises, cable wiring is widely used for the installation of power and lighting networks in the aisles of workshops free from mobile overhead cranes.
In the presence of bridge cranes in workshops, the use of electric cable cables is limited to the construction of networks for general lighting, provided that they are placed in the free space between the lower chord of the trusses and the bridge of the crane.
Recently, cable wiring has been widely used in the construction of electrical networks in outdoor installations for lighting streets, squares, courtyards, rooms with a fire hazard and chemically active environment, and even explosion-hazardous rooms and outdoor installations.
Cable wiring is especially widely used in the construction of electrical networks outside and inside industrial and livestock premises in the countryside.
Cable wiring, depending on local conditions and environment, is used in combination with other types of wiring. This is due to the fact that the switchboards, points, cabinets and group boxes, with the help of which the distribution, protection, control and supply of lighting and power lines are carried out, are usually placed on the walls or mounted on the floor of the premises. In these cases, to connect cable wires to distribution boards and shields, it is necessary to lay connecting cables of other types.
Advantages of cable and string wiring
The simplicity of the structural device, the small number of fasteners and the possibility of hanging at any level greatly facilitate the installation, dismantling and, if necessary, the transfer of the electrical wiring to a new place.
The use of cable and string electric wires allows you to carry out most of the work on their installation, including the manufacture of all elements and parts of the wiring, installation of the wiring itself and the implementation of branches to lighting and power supply of electrical receivers in isolation from building also works outside the installation area of the construction site.
Cable and strand wiring differ from other types of wiring with a relatively small amount of labor-intensive punching work, required only for the installation of a limited number of fastening structures.
Cable wiring has a high degree of industrialization, which allows them to be almost completely manufactured and assembled in factories or in auxiliary assembly workshops in the form of completely ready transportable assembly blocks and units. The work of installing cable wiring at the installation site in this case is reduced to the installation of anchors and other structures on site, assembly of cable cables into one common thread, lifting and tensioning of individual ready-made assembly blocks and wiring.
Simultaneous use in the construction of cable cables mixed suspension cable systems reduce the time required to complete electrical work.
Structures of cable and string electric wires
The cable wiring is designed and executed in accordance with the design options shown in the figure, namely: with simple suspension and rigid fixing of wires and cables transversely (located transverse wiring) carrying cables.
This wiring is mainly used for the installation of group lighting networks in the corridors of production workshops and closed warehouses, and for outdoor installations - for the lighting of open warehouses. and sports grounds, parking lots in cities; with a single longitudinal chain suspension of wires and cables on one longitudinal (located along the axis of the wiring) carrier cable that takes the entire load; with elastic double longitudinal chain suspension of cables and cables of two longitudinal cables. In this wiring, the intermediate attachments of the main bearing cable are made to the second (auxiliary) cable, which has a large sag and takes the entire line load.
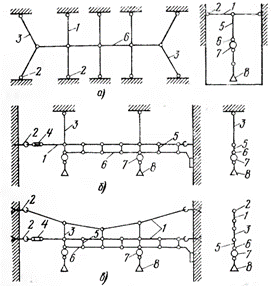
Constructive options for wiring the device cable. a — with transverse supporting cables; b — with one longitudinal supporting cable; c — with two longitudinal supporting cables; 1 — carrying cables; 2 — final fastening of cables; 3 — vertical wire hangers, inclined and horizontal guys; 4 — tensioning devices; 5 — insulating and supporting supporting structures for suspended wires; b — wires or cables; 7 — junction boxes or clamps; 8 — lamps.
In some cases, in order to evenly distribute the load on the supporting cables, both cables in a tensioned state are placed in a vertical or horizontal plane along the longitudinal axis of the electrical wiring on both sides. In this arrangement, the supporting cables take the load equally.
Cable wiring with a chain suspension of wiring is used for the device of trunk, distribution and group lighting and power lines located inside the premises along the lines of industrial enterprises, and in external installations - for the device of trunk lines. In some cases, depending on local conditions, mixed-type wiring is carried out, i.e. with the simultaneous use of longitudinal and transverse bearing cables.
When using special cable wiring for the device wires with a built-in steel carrier cable, the suspension of the wires and the fastening of the cable are carried out according to the option shown in the figure.
If the actual load on the cable exceeds the established one, the cable wiring is carried out according to the option shown in figure c, that is, by additional installation of the second auxiliary support cable.
Carrier cables for cable guides
As carrier cables for cable electric wires, steel ropes-cables with a diameter of 1.95 - 6.5 mm.
For cable electric wires, it is also allowed to use galvanized steel or ordinary quality wire as a supporting cable or steel wire and hot-rolled wire (wire rod) with a varnish coating with a diameter of 5.5-8 mm as the simplest, cheapest and the cheapest material.
When using a carrier cable as a grounding neutral wire for hanging electric wires, it is recommended to use steel non-insulated single-core and multi-core wires of the PSO, PS or PMS brands. These wires, like the cable, do not require pre-treatment.
The choice of the carrier cable is made during the development of the electrical installation project by comparing two interrelated quantities — the sag arrow and the diameter of the carrier cable, taking into account the length of the cable span of the cable and the calculated loads on the cable.
The distance between the attachment points of the carrier cable (calculated range, taking into account the intermediate fasteners) in cable wiring is in most cases no more than 6-12 m (typical distances between trusses and beams in rooms).
The suspended arrows of the carrier cable for conventional electrical wires corresponding to these distances are in the range of 0.03 — 0.6 m and do not require special calculation.
End fixing structures for cable and string electrical conductors
The load-bearing cables are suspended between end fixing anchors attached to building structures. Forms of end fasteners have different designs and depend on the characteristics of their attachment points.
The figure shows the methods of fastening end fastening structures of string and cable guides to various building surfaces.
The most reliable fastening of anchor structures to building surfaces is fastening in brick and concrete walls and ceilings with the help of bolts and anchors or fixing anchors with the help of spikes with the installation of enlarged square washers on the back side of the fastening. In anchors with such In fasteners, the pulling forces correspond to the actual value of the strength of the material itself, from which the anchor is made, depending on the steel brand and the cross-section of the threaded part of the fastening rods.
Fastening of anchor structures to walls and ceilings is also done using built-in spikes or expansion dowels. Such fasteners are less reliable, since they largely depend on the quality of execution and the accuracy of the prepared holes in terms of the size and reliability of the anchors in them. Therefore, these methods of fastening anchors are used for less critical intermediate fastenings of supporting cables and wires.
Fastening of anchor structures to metal trusses and building structures is carried out with the help of fastening steel fasteners or similar parts, as well as with the help of bolted connections or welding of the anchor along its perimeter by electric welding. In each case, the choice of the anchor structure and the method of attachment is made depending on the specific local conditions, the material from which the parts of the anchor structure are made, and the compliance of the structure with the calculated pull-output force created by the cable wiring.
Connection of cables with end fixing structures when cable and string electrical conductors
The cables are connected to the end fasteners using a loop at the end of the cable, made using the so-called fittings and clamps.
The cable clamp consists of two rectangular strips with symmetrically located, stamped, indentations, entering each other or without them. The strips are fastened with bolts or screws and serve to firmly grip the cable when forming a loop.
In the case of using a steel rope or a wire rod, the contours at the ends are made without the use of clamps, simply twisting the wire with a spiral of 60 - 80 mm in length or fixing the end with a steel clamp or a piece of steel pipe.
Suspended from both ends of the hooks of the end anchor fastening structures, the carrier cable is usually stretched until the structural boom is reached in the electrical cable wiring sections.
In some cases and when carrying out cable wiring using rigid and semi-rigid electrical structures (steel trays, boxes, etc.), the carrier cable hangs freely with a little slack. The alignment of the wires suspended from the cable is done using different length wire hangers.
During operation, it may be necessary to tighten the cable wiring. Tensioning and tensioning of the supporting cable is carried out using tensioning devices built into the cables in series with the supporting cable.
Some end anchor structures are tensioned carrying cable with a nut due to the presence of a hook at the free end of an extended thread.
The number of fasteners in each cable string depends on the total length of the latter.
With a cable length leading to 10-15 m, they usually manage without special tensioning connectors, tensioning the cable using a nut and thread available on the fastening structures of the end anchors. For long distances, it is recommended to install one or two clips at the ends of the carrier cable.
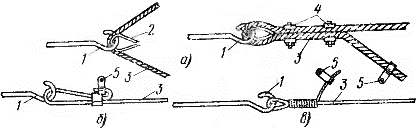
End fittings of carrier cables.a — with the help of a thimble and matrix; b — using a steel clamp; c — by twisting the end of the wire (rod) in a spiral, 1 — hook 2 — thimble; 3 — rope or wire (wire); 4 — bracket for a ram; 5 — cable grounder.
Suspension and tensioning of the carrier cable
The suspension of the carrier cable and its tensioning are carried out in two stages. First, the cable is pulled along the length of the wiring and one end is fixed to the final anchor structure, the tension bolt of which is previously weakened. The second free end of the cable is measured according to the actual length of the lining, taking into account the length of the cable required to close the loops, install tensioners and compensate for the sag boom, and attach it to a pre-slack special tensioner, if necessary. The carrier cable is then pre-tensioned together with the tensioning device, which is then placed on the second end anchor hook. The tension of the carrier cable, depending on its length, is done manually for small distances, and for large ones with the help of blocks, rollers or winches.
As already mentioned, tensioning of the cable should be carried out until the calculated sag is obtained, but with a force that does not exceed the allowable for a given cable tensioning force. The control of the correct tension of the supporting cable is carried out by a dynamometer connected in series with the cable or block of the chain hoist, with the help of which the cable is pulled, or by measuring the sag. The final tensioning and adjustment of the carrier cable is done by tightening the previously loosened tensioning devices.It is recommended to carry out work on suspension and tensioning of carrier cables at an ambient temperature not lower than -20 group S.
Various unloading devices in the form of additional vertical, longitudinal and transverse auxiliary suspensions and clamps are used to unload the supporting cable and its end fasteners and reduce sagging in cable pipelines.
To make the cable wiring more immovable and to prevent lateral swaying, side clamps are installed.
Vertical wire hangers are installed approximately every 3-12 m, placing in places the location of branches of wires and cables, installation and suspension of junction boxes, branches and lamps.
Vertical wire suspensions are made of steel wire with a diameter of 2-6 mm for power lines such as heavier and 2-3 mm in diameter for lighter lighting wires.
Longitudinal lateral and transverse guys are made of steel wire with a diameter of 2 — 6 mm.
For electric string wiring, unlike cable wires, the carrier string in a tensioned state is attached near ceilings, trusses, beams, walls and projecting walls, columns and other foundations of buildings in various ways.
