How the power grid works
Electric network — a set of electrical installations for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy, consisting of substations, distribution devices, wires, overhead and cable power lines operating in a certain area. Another definition is possible: a set of substations and distribution devices and the electric lines connecting them, located on the territory of the district, settlement, consumer of electricity.
Power plants in Russia are united in the federal power system, which is the source of electric power for all its users. The transmission and distribution of electricity is carried out with the help of overhead power lines that cross the entire country. In order to reduce losses during electricity transmission, very high voltages — tens and (more often) hundreds of kilovolts — are used in power lines.
Due to its cost-effectiveness, when transferring energy, the invention invented by the Russian engineer M.O. Dolivo-Dobrovolsky is a three-phase alternating current system in which electricity is transmitted using four wires.Three of these wires are called line or phase, and the fourth is called neutral or simply neutral.
Electricity consumers are designed for a lower voltage than the voltage in the power system. The voltage is reduced in two stages. First, at the step-down substation, which is part of the power system, the voltage is stepped down to 6-10 kV (kilovolts). Further lowering of the voltage takes place at transformer substations… Their familiar standard “transformer booths” are scattered throughout the factories and residential areas. After the transformer substation, the voltage drops to 220-380 V.
The voltage between the line conductors of a three-phase AC system is called the line voltage. Nominally r.m.s. mains voltage value in Russia it is equal to 380 V (volts). The voltage between the neutral and any of the line conductors is called a phase. It is three times smaller than the linear root. Its nominal value in Russia is 220 V.
The source of energy for the power system is three-phase alternators installed in power plants. Each of the windings of the generator induces a line voltage. The coils are symmetrically located around the circumference of the generator. Accordingly, the line voltages are phase-shifted relative to each other. This phase shift is constant at 120 degrees.
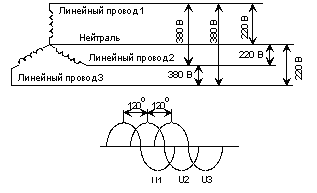 Three phase AC system
Three phase AC system
After the transformer substation, the voltage is supplied to consumers through switchboards or (in enterprises) distribution points.
Some consumers (electric motors, industrial equipment, mainframes and powerful communication equipment) are designed for direct connection to a three-phase electrical network.There are four wires connected to them (not counting the protective ground).
Low-power consumers (personal computers, household appliances, office equipment, etc.) are designed for a single-phase electrical network. Two wires are connected to them (not counting the protective ground). In most cases, one of these wires is linear and the other is neutral. According to the standard, the voltage between them is 220 V.
The above rms voltage values do not completely exhaust the parameters of the electrical network. Variable electricity also characterized by frequency. The nominal standard frequency in Russia is 50 Hz (Hertz).
The actual values of the voltage and frequency of the electrical network may, of course, differ from the nominal values.
New consumers of electricity are permanently connected to the network (the current or load on the network increases) or some consumers are disconnected (as a result, the current or load on the network decreases). As the load increases, the network voltage drops, and as the load decreases, the network voltage increases.
To reduce the effect of load change on the voltage, in step-down substations there is an automatic voltage regulation system… It is designed to maintain a constant (within certain limits and with a certain accuracy) voltage when the load in the network changes. Regulation is carried out by repeatedly switching the windings of powerful step-down transformers.
AC frequency set by the rotation speed of generators in power plants.As the load increases, the frequency tends to decrease slightly, the power plant control system increases the flow rate of the working fluid through the turbine, and the generator speed is restored.
Of course, no regulation system (voltage or frequency) can work perfectly, and in any case the user of the electrical network must accept some deviations of the characteristics of the network from the nominal values.
In Russia, the requirements for the quality of electrical energy are standardized. GOST 23875-88 gives definitions power quality indicators, and GOST 13109-87 establishes the values of these indicators. This standard establishes the values of indicators at the connection points of electricity consumers. For the consumer, this means that he can demand from the power supply organization that the established norms are not respected somewhere in the power system, but directly in his outlet.
The most important indicators of power quality are voltage deviation from the nominal value, non-sinusoidal voltage factor, frequency deviation from 50 Hz.
According to the standard, at least 95% of the time each day, the phase voltage should be in the range of 209-231 V (deviation 5%), the frequency should be within 49.8-50.2 Hz, and the coefficient of non-sinusoidality should not exceed 5%.
The remaining 5 percent or less of the time each day, the voltage may vary from 198 to 242 V (deviation 10%), the frequency from 49.6 to 50.4 Hz, and the non-sinusoidal factor must be no more than 10 %.Stronger changes in frequency are also allowed: from 49.5 Hz to 51 Hz, but the total duration of such changes must not exceed 90 hours per year.
Power outages are situations when power quality indicators for a short time exceed established limits. The frequency can deviate by 5 Hz from the nominal value. The voltage can drop to zero. Quality indicators should be restored in the future.
A. A. Lopukhin Uninterruptible power supplies without secrets
