Hardware interfaces
 An interface (interaction) is the connection between components and participants in a microprocessor system.
An interface (interaction) is the connection between components and participants in a microprocessor system.
V microprocessor system includes: hardware, software and people... Therefore, the following types of interfaces are distinguished:
-
hardware interface;
-
software interface;
-
user interface.
Programming interface provided by the operating system (if any). The most common user interfaces are a graphical interface (for example, a computer desktop with icons or command buttons in the Microsoft Office Word editor) and a joystick interface, where we select the command we need by navigating through menus (for example, mobile phones, programmable controllers) , which is also a type of GUI.
A hardware interface is a system of buses, connectors, matching devices, algorithms, and protocols that provide communication between all parts of a microprocessor system. The performance and reliability of the system depend on the characteristics of the interface.
In embedded microprocessor systems, the hardware interface is provided by the CPU offload controllers.Controller It is a specialized microcircuit designed to perform monitoring and control functions. The controller manages the operation of the device, for example, hard disk, random access memory, keyboard, and ensures the connection of this device with other participants in the MS.
Tires are controlled by bridges... In complex MS, for example, such as a personal computer, the central place is occupied by the «ChipSet» (ChipSet) - a set of bridges and controllers. The chipset contains two main chips, which are traditionally called the south bridge and the north bridge (Figure 1). The northbridge serves the system bus, memory bus, AGP (accelerated graphics port) and is the main controller of the computer. The south bridge handles work with external devices (PCI bus — I / O bus for connecting peripheral devices).
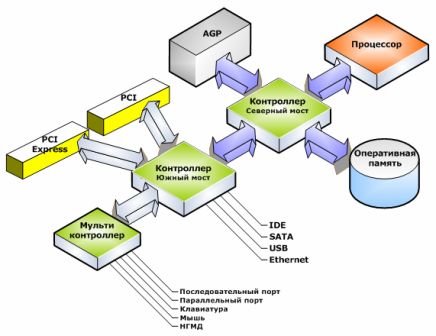
Figure 1 — Data Exchange Organizations in Personal Computers (PCs)
The organization of interaction between the processor and external devices is the most difficult, due to their great variety.
Parallel interfaces are characterized in that they use separate signal lines to transmit bits and the bits are transmitted simultaneously. The classic parallel interface is an LPT port.
A serial data transmission interface uses a single signal line over which bits of information are sequentially transmitted one after the other.
The simplest serial interface, which has become widespread both in computers and in industrial systems, is the RS-232 standard, which is implemented by COM — ports... In industrial automation, it is widely used RS-485.
A USB (Universal Serial Bus) bus connects a wide variety of peripheral devices to your computer, including cell phones and consumer electronics.
The first interface specification is called USB 1.0, the USB 2.0 specification is currently used, modern devices are connected to the USB 3.0 specification.
The USB 2.0 standard contains four lines: data reception and transmission, +5 V power supply and case. In addition to these, USB 3.0 adds four more communication lines (2 for receiving and two for transmitting) and a case.

 The USB bus has a high bandwidth (USB 2.0 provides a maximum data transfer rate of up to 480 Mbps, USB 3.0 — up to 5.0 Gbps) and provides not only data transfer, but also power supply to low-power external devices (maximum current consumption device through the power lines of the USB bus, should not exceed 500 mA for USB 2.0 and 900 mA for USB 3.0), which eliminates the need for external power supplies.
The USB bus has a high bandwidth (USB 2.0 provides a maximum data transfer rate of up to 480 Mbps, USB 3.0 — up to 5.0 Gbps) and provides not only data transfer, but also power supply to low-power external devices (maximum current consumption device through the power lines of the USB bus, should not exceed 500 mA for USB 2.0 and 900 mA for USB 3.0), which eliminates the need for external power supplies.
Wireless (wireless) interfaces allow you to move away from communication cables, which is especially important for devices of small size, in size and weight comparable to cables. Using wireless interfaces electromagnetic waves infrared (IrDA) and radio frequency ranges (Bluetooth, USB wireless).
An infrared IrDA interface allows wireless communication between two devices at a distance of up to 1 meter. Infrared communication - IR (infrared) connection - safe for health, does not cause interference in the radio frequency range and ensures the privacy of the transmission. Infrared rays do not pass through walls, so the reception area is limited to a small, easily controllable area.
Bluetooth (blue tooth) is a low-power radio interface (transmitter power only about 1 mW) for organizing personal networks providing real-time data transmission over short distances. Each Bluetooth device has a 2.4 GHz radio transmitter and receiver. The range of the radio interface is about 100 m — to cover a standard house.
Wireless USB (USB wireless) — a short-range radio interface with high bandwidth: 480 Mbps at a distance of up to 3 meters and 110 Mbps at a distance of up to 10 meters. It works in the frequency range 3.1 — 10.6 GHz.
An RS-232 (RS — Recommended Standard) interface connects two devices — a computer and a data transfer device. The transmission speed is 115 Kbps (maximum), the transmission distance is 15 m (maximum), the connection scheme is point-to-point.
Signals from this interface are transmitted by a voltage drop of (3 … 15) V, therefore the length of the RS-232 communication line is, as a rule, limited to a distance of several meters due to low noise immunity. It is most often used in industrial equipment, in a personal computer it is used to connect a "mouse" type manipulator, a modem. The RS-232 interface generally does not allow networking as it only connects 2 devices.
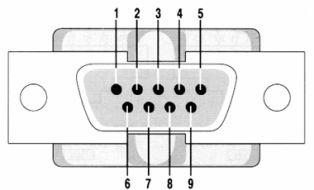
Figure 2 — DB9 type RS-232 connector
RS-485 interface is a widely used high-speed, anti-jamming industrial serial interface for two-way data transmission. Almost all modern computers in industrial design, most sensors and drives contain one or another implementation of the RS-485 interface.
One twisted pair of wires (twisted pair) is sufficient for data transmission and reception.Data transmission is carried out using differential signals (the original signal goes on one wire, and its reverse copy is on the other.). The voltage difference of one polarity between the wires means a logical one, the difference of the other polarity means zero.
In the presence of external interference, the taps in adjacent wires are the same, and since the signal is the potential difference in the wires, the signal level remains unchanged. This provides high noise immunity and a total length of the communication line up to 1 km (and more with the use of special devices — repeaters).
The RS-485 interface provides data exchange between several devices over a two-wire communication line in half-duplex mode (reception and transmission pass through one pair of time-separated wires). It is widely used in industry to create process control systems.
Ethernet (ether — ether) — data transmission technology used in most local computer networks. This interface is based on the IEE 802.3 standard. While the RS-485 interface can be considered on a one-to-many basis, Ethernet works on a many-to-many basis.
There are several options depending on the bit rate and the transmission medium:
-
Ethernet — 10 Mbps
-
Fast Ethernet — 100 Mbps
-
Gigabit Ethernet — 1 Gbps
-
10 Gigabit Ethernet
Coaxial cable, twisted pair (low cost, high noise immunity) and optical cable (creation of longer lines and high-speed communication channels) are used as transmission media.
Twisted pair (twisted pair) — a type of communication cable, is one or more pairs of insulated wires twisted together and covered with a plastic sheath.
For example, FTP cable (twisted pair — twisted pair with a common foil shield and copper conductor for draining induced currents), 4 pairs (solid), category 5e (Figure 3). The cable is intended for stationary installation in buildings, structures and work in structured cable systems. Designed for applications operating in the frequency range with an upper limit of 100 MHz.
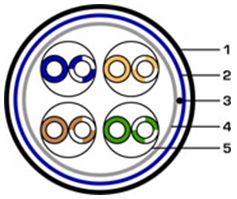
Figure 3 — twisted pair: 1 — outer sheath, 2 — foil shield, 3 — drain wire, 4 — protective film, 5 — twisted pair
At the physical level, the Ethernet protocol is implemented in the form of network cards embedded in microprocessor systems and hubs that connect the systems to each other.
Industrial networks (Profinet, EtherNet / IP, EtherCAT, Ethernet Powerlink) are built on the basis of Ethernet, which successfully compete with the previously developed networks Profibus, DeviceNet, CANopen, etc.

