Sources of electric current
Electric Current—How to Create and Maintain It
 The orderly movement of charged particles is called an electric current. To get an electric current in a wire, you need to create an electric field in it. If a charged body is connected by a wire to the ground, then a short-term electric current occurs in the wire. To obtain and maintain an electric field in a wire, use sources of electric current.
The orderly movement of charged particles is called an electric current. To get an electric current in a wire, you need to create an electric field in it. If a charged body is connected by a wire to the ground, then a short-term electric current occurs in the wire. To obtain and maintain an electric field in a wire, use sources of electric current.
In any current source, work is done to separate positively and negatively charged particles. The separated particles accumulate at the poles of the source. An electric field is generated between the poles. If you connect them with a wire, then the field arises in the wire.
In an electric machine, the separation of charges is done with the help of mechanical energy. At the same time, it becomes electric. In a thermocouple, internal energy is converted into electrical energy. Nuclear batteries convert atomic energy into electricity.
The photocell converts light energy into electrical energy. Solar cells are made up of photocells.They are used where light energy is most readily available.
The energy of rivers, coal, oil and atoms is converted into electrical energy in power plants. The most common sources of electric current are galvanic cells and batteries.
Galvanic cells
A galvanic cell is a current source in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
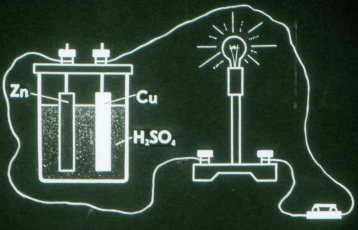
This is how the simplest galvanic cell works.
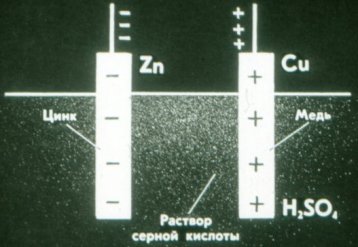
The first electrochemical cell was invented by Volt in 1799. From individual elements he constructed a battery which he called a "volt pole". In a galvanic cell, the electrodes must necessarily interact with the solution in different ways, which is why the electrodes are made of different materials.

The zinc plate in the Volta cell is negatively charged and the copper plate is positively charged.
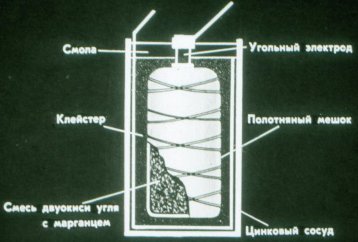
And this is how a dry galvanic cell works. Instead of liquid, it uses a thick paste:
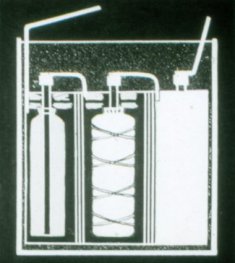
A battery can consist of several elements:
Light bulbs in electric lamps, as well as various other portable electrical appliances and children's toys, are powered by galvanic cells. When the electrodes in the galvanic cell are used up, the cell is replaced with a new one.
Batteries
Batteries are chemical sources of electric current in which the electrodes are not consumed. The simplest battery consists of two lead plates immersed in a solution of sulfuric acid.
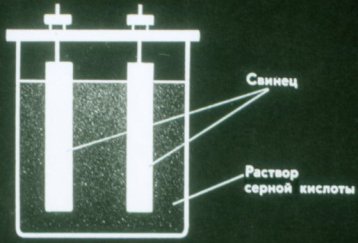
Such a battery still does not supply current. It must be charged before use. To do this, connect the poles of the battery to the same poles of each current source.
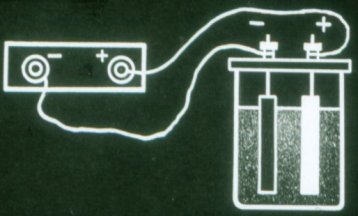
The current that flows through the battery during charging changes the chemical composition of its plates. The chemical energy of the battery increases.
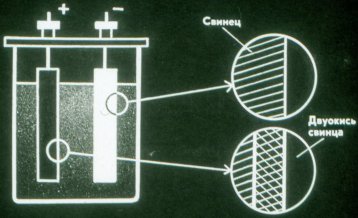
When a battery discharges, it converts chemical energy into electrical energy. A discharged battery can be recharged.
Batteries are collected from separate batteries.
In addition to acid (lead) batteries, alkaline (iron-nickel) batteries are used.
Nickel Iron Battery:
Nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries are also widely used today. Silver-zinc batteries are used in aviation and space. New types of batteries: lithium-ion, lithium-polymer are used in mobile phones, tablets and other modern portable equipment.
Batteries are used in cases where the source of electric current is more profitable to recharge than to replace with a new one. In a car, the battery is used to start the engine and operate various devices. In space, the battery is charged by solar panels. When discharged, it powers radio transmitters and equipment.
See also: Batteries. Calculation examples

