What current does the motor consume from the network during start-up and operation?
The passport of the electric motor shows the current at the nominal load of the shaft. If, for example, 13.8 / 8 A is indicated, this means that when the motor is connected to the 220 V network and at nominal load, the current consumed from the network will be 13.8 A. When connected to the 380 V network, current will be consumed of 8 A, that is, the equality of forces is true: √3 x 380 x 8 = √3 x 220 x 13.8.
Knowing the rated power of the motor (from the passport), you can determine its rated current... When the motor is connected to a 380 V three-phase network, the rated current can be calculated using the following formula:
Азn = Пн /(√3Un x η x соsφ),
where Pn — rated engine power in kW, Un — network voltage, in kV (0.38 kV). Efficiency (η) and Power factor (сosφ) — engine power values, which are written on a plate in the form of a metal plate. See also — What passport data is indicated on the shield of an asynchronous motor.

Rice. 1. Passport of the electric motor. Rated power 1.5 kV, rated current at 380 V — 3.4 A.
If the efficiency and power factor of the motor are not known, for example, in the absence of a motor nameplate, then its rated current with a small error can be determined from the ratio «two amperes per kilowatt», i.e. if the rated power of the motor is 10 kW, then the current consumed by it will be approximately equal to 20 A.
For the motor indicated in the figure, this ratio is also fulfilled (3.4 A ≈ 2 x 1.5). More accurate current values using this ratio are obtained with a motor power of 3 kW.
When the engine is idling, a small current is consumed from the network (idle current). As the load increases, so does the current consumption. As the current increases, the heating of the windings increases. A large overload leads to the fact that the increased current causes overheating of the motor windings and there is a danger of carbonization of the insulation (burning of the electric motor).
At the moment of starting from the network, the electric motor consumes the so-called starting current, which can be 3 - 8 times more than the nominal one. The nature of the current change is shown in the graph (Fig. 2, a).
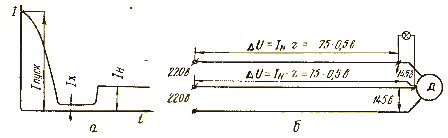
Rice. 2. The nature of the change in the current consumed by the motor from the network (a) and the effect of the large current on the fluctuations of the voltage in the network (b)
The exact value of the starting current for any particular motor can be determined by knowing the starting current multiple — Azstart/AzNo. The starting current multiple is one of the motor specifications that can be found in the catalogs. The starting current is determined by the following formula: Az start = Azn x (Azstart/Aznom).For example, with a rated motor current of 20 A and a starting current with a multiple of 6, the starting current is 20 x 6 = 120 A.
Knowing the actual value of the inrush current is necessary for choosing fuses, checking the operation of electromagnetic releases during motor starting when selecting circuit breakers and determining the amount of voltage drop in the network during starting.
The fuse selection process is detailed in this article: Selection of fuses for protection of asynchronous motors
A large starting current, for which the network is usually not designed, causes significant voltage drops in the network (Fig. 2, b).
If we take the resistance of the wires passing from the source to the motor equal to 0.5 Ohm, the rated current Azn = 15 A, and the starting current is equal to five times the rated one, then the voltage losses in the wires during starting will be 0, 5 x 75 + 0.5 x 75 = 75V.
On the terminals of the motor, as well as on the terminals, a number of working electric motors will be 220 — 75 = 145 V. This voltage drop can cause a shutdown of running motors, which will lead to an even greater increase in current in the network and blown fuses .
In the case of electric lamps, when the engines are started, the glow is reduced (the lamps «blink»). Therefore, when starting electric motors, they tend to reduce the starting currents.
A star-to-delta switching motor starting circuit can be used to reduce the starting current. In this case, the phase voltage will decrease by √3 times and the inrush current is limited accordingly.After the rotor reaches a certain speed, the stator windings are switched to the delta circuit and the voltage under them becomes equal to the nominal one. Switching is usually done automatically using a time or current relay.
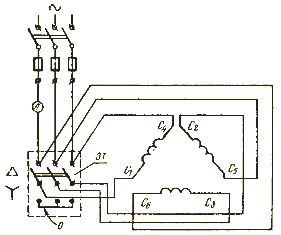
Rice. 3. Scheme of starting an electric motor with the switching of the stator windings from a star to a delta
It is important to understand that almost any engine can be connected according to this scheme. Most common induction motors with an operating voltage of 380/200 V, including the motor shown in Figure 1, when connected according to this scheme, will fail. Read more about it here: The choice of the connection scheme of the phases of the electric motor
Currently, in order to reduce the starting current of electric motors, especially microprocessor soft starters (soft starters)… Read more about the purpose of this type of device in the article What is induction motor soft start for?.
