Types of fuses
 Every electrical system works on the balance of supplied and consumed energy. When voltage is applied to an electrical circuit, it is applied to a certain resistance in the circuit. As a result, based on Ohm's law, a current is generated due to the action of which work is done.
Every electrical system works on the balance of supplied and consumed energy. When voltage is applied to an electrical circuit, it is applied to a certain resistance in the circuit. As a result, based on Ohm's law, a current is generated due to the action of which work is done.
In the case of insulation defects, assembly errors, emergency mode, the resistance of the electric circuit gradually decreases or drops sharply. This leads to a corresponding increase in current, which, when exceeding the nominal value, causes damage to equipment and people.
Safety issues have always been and will always be relevant when using electrical energy. Therefore, special attention is constantly paid to protective devices. The first such designs, called fuses, are still widely used today.

The electric fuse is part of the working circuit, it is cut on the section of the power wire, it must reliably withstand the working load and protect the circuit from the occurrence of excess currents.This function is the basis of the classification of rated current.
According to the applied principle of operation and method of breaking the circuit, all fuses are divided into 4 groups:
1. with fusible link;
2. electromechanical design;
3. Based on electronic components;
4. self-healing models with non-linear reversible properties after the action of overcurrent.
Hot link
Fuses of this design include a conductive element that, under the action of a current exceeding the nominal set value, melts from overheating and evaporates. This removes the voltage from the circuit and protects it.
Fusible links can be made of metals such as copper, lead, iron, zinc or some alloys that have a coefficient of thermal expansion that provides the protective properties of electrical equipment.
The heating and cooling characteristics of wires for electrical equipment under stationary operating conditions are shown in the figure.
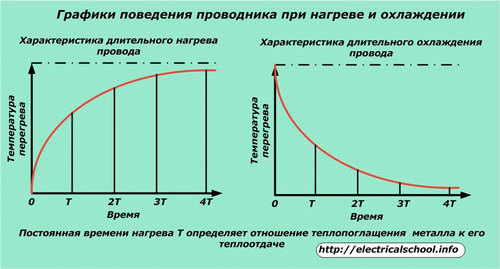
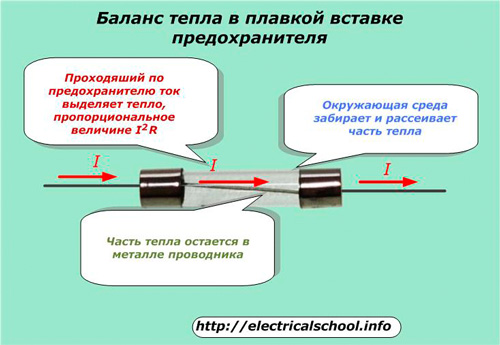
The operation of the fuse at design load is ensured by creating a reliable temperature balance between the heat released on the metal by the passage of an operating electric current through it and the removal of heat to the environment due to dissipation.
In case of emergency modes, this balance is quickly disturbed.
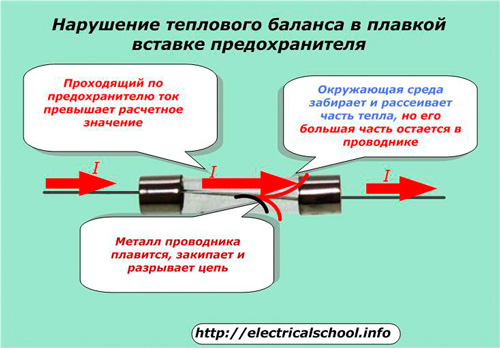
The metal part of the fuse increases the value of its active resistance when heated. This results in more heating as the heat generated is directly proportional to the value of I2R. At the same time, resistance and heat generation increase again. The process continues like an avalanche until melting, boiling and mechanical destruction of the fuse occurs.
When the circuit breaks, there is an electric arc inside the fuse. Until the moment of complete disappearance, a current dangerous to the installation passes through it, which changes according to the characteristic shown in the figure below.
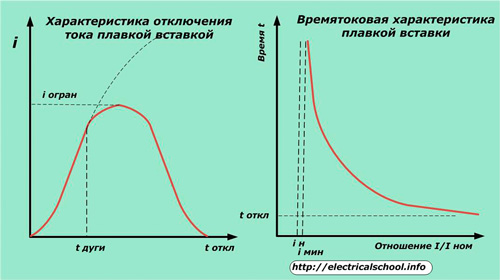
The main operating parameter of the fuse is its characteristic current over time, which determines the dependence of the multiple of the emergency current (relative to the nominal value) on the response time.
To speed up the operation of the fuse at low rates of emergency currents, special techniques are used:
-
creating variable cross-sectional shapes with areas of reduced area;
-
using the metallurgical effect.
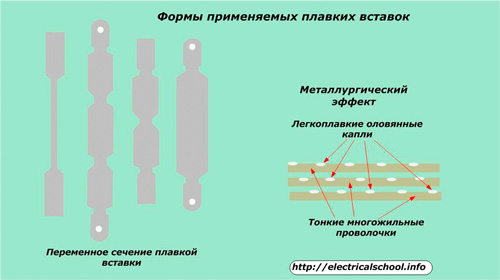
Change section
As the plates narrow, the resistance increases and more heat is generated. In normal operation, this energy has time to spread evenly over the entire surface, and in case of overload, critical zones are created in narrow places. Their temperature quickly reaches a state where the metal melts and breaks the electrical circuit.
To increase the speed, the plates are made of thin foil and are used in several layers connected in parallel. Burning each area of one of the layers speeds up the protective operation.
The principle of the metallurgical effect
It is based on the property of certain low-melting metals, for example lead or tin, to dissolve more refractory copper, silver and certain alloys in their structure.
To do this, drops of tin are applied to the stranded wires from which the fusible link is made.At the permissible temperature of the metal of the wires, these additives do not create any effect, but in an emergency mode they quickly melt, dissolve part of the base metal and provide an acceleration of the operation of the fuse.
The effectiveness of this method is manifested only on thin wires and decreases significantly with an increase in their cross-section.
The main disadvantage of a fuse is that when it is triggered, it must be manually replaced with a new one. This requires maintaining their stocks.
Electromechanical fuses
The principle of cutting a protective device into the supply wire and ensuring its breaking in order to relieve the voltage makes it possible to classify the electromechanical products created for this as fuses. However, most electricians classify them in a separate class and call them circuit breakers or abbreviated as automatic machines.

During their operation, a special sensor constantly monitors the value of the passing current. After reaching a critical value, a control signal is sent to the drive — a charged spring from a thermal or magnetic release.
Electronic component fuses
In these designs, the function of protecting the electrical circuit is taken over by non-contact electronic switches based on power semiconductor devices of diodes, transistors or thyristors.
These are called electronic fuses (EP) or current control and switching modules (MKKT).
As an example, the figure shows a block diagram showing the principle of operation of a transistor fuse.
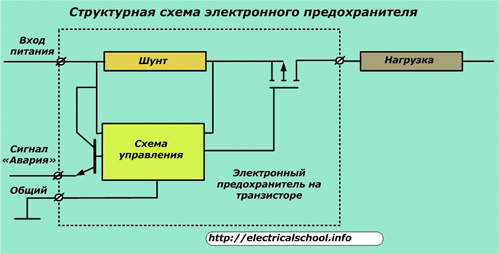
The control circuit of such a fuse removes the measured current value signal from the resistive shunt.It is modified and applied to the input of the isolated semiconductor gate MOSFET type field effect transistor.
When the current through the fuse begins to exceed the permissible value, the gate closes and the load is turned off. In this case, the fuse is switched to self-locking mode.
If a lot of video surveillance is used in the circuit, it becomes difficult to determine the blown fuse. To make it easier to find, the "Alarm" signaling function has been introduced, which can be detected by the flash of the LED or by triggering a solid or electromechanical relay.
Such electronic fuses are fast-acting, their response time does not exceed 30 milliseconds.
The scheme discussed above is considered simple, it can be significantly expanded with new additional functions:
-
continuous monitoring of the current in the load circuit with the formation of shutdown commands when the current exceeds 30% of the nominal value;
-
shutdown of the protected zone in case of short circuits or overloads with a signal when the current in the load increases above 10% of the set setting;
-
protection of the power element of the transistor in case of temperatures above 100 degrees.
For such schemes, the ICKT modules used are divided into 4 response time groups. The fastest devices are classified as class «0». They interrupt currents exceeding the setting by 50% for up to 5 ms, by 300% in 1.5 ms, by 400% in 10 μs.
Self-healing fuses
These protective devices differ from fuses in that after the emergency load is turned off, they retain their operability for further repeated use.That is why they were called self-healing.
The design is based on polymer materials with a positive temperature coefficient of electrical resistance. They have a crystalline lattice structure under normal, normal conditions and abruptly transform into an amorphous state when heated.
The tripping characteristic of such a fuse is usually given as the logarithm of resistance versus material temperature.
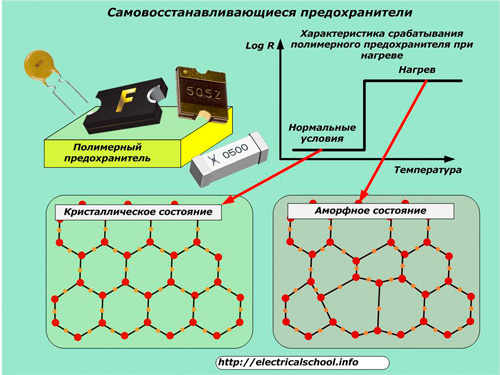
When a polymer has a crystal lattice, it is good, like a metal, to conduct electricity. In the amorphous state, the conductivity is significantly degraded, which ensures that the load is turned off when an abnormal mode occurs.
Such fuses are used in protective devices to eliminate the occurrence of repeated overloads when replacement of the fuse or manual actions of the operator are difficult. It is the field of automatic electronic devices widely used in computer technology, mobile gadgets, measuring and medical technology, and vehicles.
The reliable operation of self-resetting fuses is affected by the ambient temperature and the amount of current flowing through it. In order to be accounted for, technical conditions have been introduced:
-
transmission current, defined as the maximum value at a temperature of +23 degrees Celsius, which does not trigger the device;
-
the operating current, as a minimum value that, at the same temperature, leads to the transition of the polymer into an amorphous state;
-
the maximum value of the applied operating voltage;
-
response time, measured from the moment the emergency current occurs until the load is turned off;
-
power dissipation, which determines the ability of the fuse at +23 degrees to transfer heat to the environment;
-
initial resistance before connecting to work;
-
resistance reaches 1 hour after the end of the operation.
Self-healing protectors have:
-
small sizes;
-
quick response;
-
Stable job;
-
combined protection of devices from overload and overheating;
-
no need for maintenance.
Varieties of fuse designs
Depending on the tasks, fuses are created to work in circuits:
-
industrial installations;
-
household electrical appliances for general use.
Because they operate in circuits with different voltages, the enclosures are manufactured with distinctive dielectric properties. According to this principle, fuses are divided into structures that work:
-
with low voltage devices;
-
in circuits up to and including 1000 volts;
-
in high voltage industrial equipment circuits.
Special designs include fuses:
-
explosive;
-
perforated;
-
with arc extinction when the circuit opens in narrow channels of fine-grained fillers or the formation of autogas or liquid explosion;
-
for vehicles.
The limited fault current of a fuse can vary from fractions of an ampere to kiloamperes.
Sometimes electricians, instead of a fuse, install a calibrated wire in the housing. This method is not recommended, because even with an accurate selection of the cross-section, the electrical resistance of the wire may differ from the recommended due to the properties of the metal or alloy itself. Such a fuse will not work for sure.
An even bigger mistake is the accidental use of homemade "bugs".They are the most common cause of accidents and fires in electrical wiring.
