Electric charge and its properties
Physical processes taking place in nature are not always explained by the action of the laws of molecular-kinetic theory, mechanics or thermodynamics. There are also electromagnetic forces that act at a distance and do not depend on body weight.
Their manifestations were first described in the works of ancient scientists from Greece, when they attracted light, small particles of individual substances with amber, rubbed against wool.
Historical contribution of scientists to the development of electrodynamics
Experiments with amber were studied in detail by the English researcher William Hilbert... In the last years of the 16th century, he made an account of his work and defined objects capable of attracting other bodies from a distance with the term "electrified".
French physicist Charles Dufay established the existence of charges with opposite signs: some were formed by rubbing glass objects on silk fabric, and others - resins on wool. That's what he called them: glass and resin. After completing the research, Benjamin Franklin introduced the concept of negative and positive charges.
Charles Visulka realizes the possibility of measuring the strength of charges by designing a torsion balance of his own invention.
Robert Milliken, based on a series of experiments, he established the discrete nature of the electric charges of any substance, proving that they consist of a certain number of elementary particles. (Not to be confused with another concept of this term — fragmentation, discontinuity.)
The works of these scientists served as the basis of modern knowledge of the processes and phenomena occurring in the electric and magnetic fields created by electric charges and their movement, studied by electrodynamics.
Determination of charges and principles of their interaction
Electric charge characterizes the properties of substances that provide them with the ability to create electric fields and interact in electromagnetic processes. It is also called the quantity of electricity and is defined as a physical scalar quantity. The symbols "q" or "Q" are used to indicate charge, and the unit "Pendant" is used in measurements, named after the French scientist who developed a unique technique.
He created a device, the body of which used balls suspended on a thin thread of quartz. They were oriented in space in a certain way and their position was recorded against a graduated scale with equal divisions.
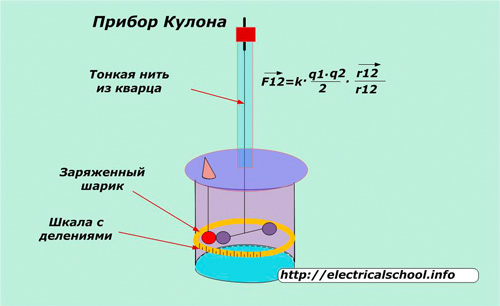
Through a special hole in the lid, another ball with an additional charge was brought to these balls. The resulting forces of interaction forced the balls to deflect, to rotate their swing. The difference in scale readings before and after charging made it possible to estimate the amount of electricity in the test samples.
A charge of 1 coulomb is characterized in the SI system by a current of 1 ampere passing through the cross-section of a wire in a time equal to 1 second.
Modern electrodynamics divides all electric charges into:
-
positive;
-
negative.
When they interact with each other, they develop forces whose direction depends on the existing polarity.
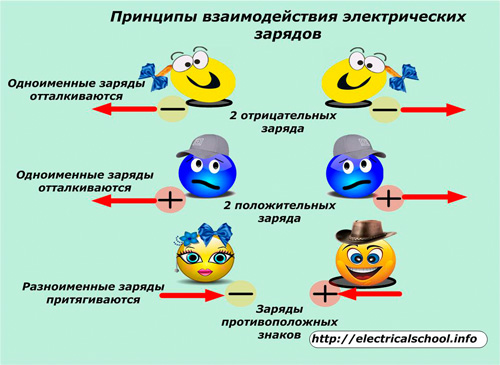
Charges of the same type, positive or negative, always repel in opposite directions, tending to move away from each other as far as possible. And for charges of opposite signs, there are forces that tend to bring them together and unite them into one. .
Principle of superposition
When there are several charges in a certain volume, the principle of superposition works for them.
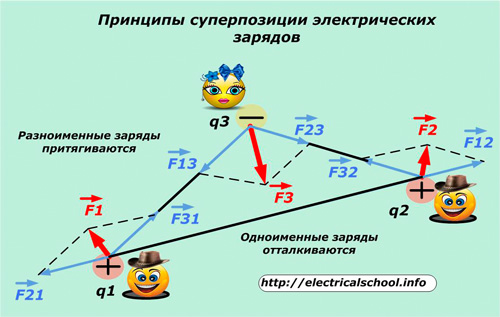
Its meaning is that each charge in a certain way, according to the method discussed above, interacts with all the others, being attracted by opposites and repelled by similar ones. For example, the positive charge q1 is affected by the attractive force F31 to the negative charge q3 and the repulsive force F21 from q2.
The resulting force F1 acting on q1 is determined by the geometric summation of the vectors F31 and F21. (F1 = F31 + F21).
The same method is used to determine the resulting forces F2 and F3 on the charges q2 and q3, respectively.
Using the principle of superposition, it was concluded that for a certain number of charges in a closed system, constant electrostatic forces act between all its bodies, and the potential at any particular point in this space is equal to the sum of the potentials of all separately charged charges.
The operation of these laws is confirmed by the created devices electroscope and electrometer, which have a common principle of operation.
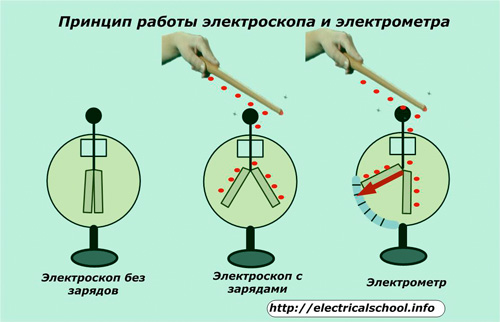
An electroscope consists of two identical thin sheets of foil suspended in an insulated space on a conductive thread attached to a metal ball. In a normal state, the charges do not act on this ball, therefore the petals hang freely in the space inside the bulb of the device.
How can charge be transferred between bodies
If you bring a charged body, such as a rod, to the ball of the electroscope, then the charge will pass through the ball along a conductive thread to the petals. They will receive the same charge and begin to move away from each other at an angle proportional to the amount of electricity applied.
The electrometer has the same basic structure, but there are small differences: one petal is fixed motionless, and the second moves away from it and is equipped with an arrow that allows you to read the graduated scale.
Intermediate carriers can be used to transfer charge from a distant stationary and charged body to an electrometer.
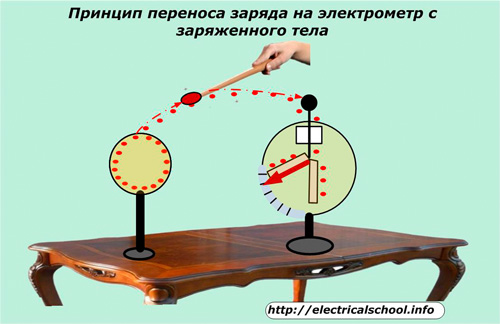
Measurements made by an electrometer do not have a high class of accuracy, and on their basis it is difficult to analyze the forces acting between charges. Coulomb torsion balance is more suitable for their study. They used balls with diameters much smaller than their distance from each other. They have the properties of point charges — charged bodies whose dimensions do not affect the accuracy of the device.
The measurements made by Coulomb confirmed his assumption that a point charge is transferred from a charged body to the same in properties and mass, but uncharged in such a way that it is evenly distributed between them, decreasing by a factor of 2 at the source.In this way, it was possible to reduce the amount of the fee by two, three and other times.
The forces that exist between stationary electric charges are called Coulombic or static interactions. They are studied by electrostatics, which is one of the branches of electrodynamics.
Types of electric charge carriers
Modern science considers the smallest negatively charged particle electron, and positively — positron... They have the same mass 9.1 × 10-31 kilograms. The particle proton has only one positive charge and a mass of 1.7 × 10-27 kilograms. In nature, the number of positive and negative charges is balanced.
In metals, the movement of electrons is created electricity, and in semiconductors its charge carriers are electrons and holes.
In gases, the current is formed by the movement of ions — charged non-elemental particles (atoms or molecules) with positive charges, called cations, or negative — anions.
Ions are formed from neutral particles.
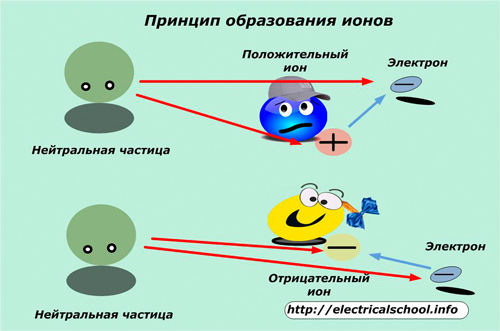
A positive charge is created in a particle that has lost an electron under the influence of a powerful electric discharge, light or radioactive radiation, wind flow, movement of water masses or a number of other reasons.
Negative ions are formed from neutral particles that have additionally received an electron.
The use of ionization for medical purposes and everyday life
Researchers have long noticed the ability of negative ions to affect the human body, improve the consumption of oxygen in the air, deliver it faster to tissues and cells, and accelerate the oxidation of serotonin.All this in the complex significantly increases immunity, improves mood, relieves pain.
The first ionizer used to treat people was named Chizhevsky chandeliers, in honor of the Soviet scientist who created a device that has a beneficial effect on human health.
In modern electrical appliances for work in a home environment, you can find built-in ionizers in vacuum cleaners, air humidifiers, hair dryers, hair dryers ...
Special air ionizers purify its composition, reduce the amount of dust and harmful impurities.
Water ionizers are able to reduce the amount of chemical reagents in their composition. They are used to clean pools and lakes, saturating the water with copper or silver ions that reduce the growth of algae, destroy viruses and bacteria.
Useful terms and definitions
What is volume electric charge
This is an electric charge distributed throughout the volume.
What is surface electric charge
It is an electric charge that is considered to be distributed over the surface.
What is a linear electric charge
It is an electric charge that is considered to be distributed along a line.
What is the volume density of electric charge
It is a scalar quantity characterizing the distribution of the volume electric charge, equal to the limit of the ratio of the volume charge to the volume element in which it is distributed when this volume element tends to zero.
What is the surface electric charge density
It is a scalar quantity characterizing the distribution of the surface electric charge, equal to the limit of the ratio of the surface electric charge to the surface element over which it is distributed when this surface element tends to zero.
What is linear electric charge density
It is a scalar quantity that characterizes the distribution of a linear electric charge, equal to the limit of the ratio of a linear electric charge to an element of the length of the line along which this charge is distributed when this element of length tends to zero.
What is an electric dipole
It is a set of two point electric charges equal in magnitude and opposite in sign and located at a very small distance from each other compared to the distance from them to the observation points.
What is the electric moment of an electric dipole
It is a vector quantity equal to the product of the absolute value of one of the charges of the dipole and the distance between them and directed from negative to positive charge.
What is the electric moment of the body
It is a vector quantity equal to the geometric sum of the electric moments of all the dipoles that make up the body under consideration. "The electric moment of a given volume of matter" is defined in a similar way.
