Circuit breaker, circuit breaker, RCD — what's the difference
 At any time, various failures of electrical devices can occur in the wiring. To reduce the risk of dangerous factors of electric shock, household protective devices are used that perform various functions.
At any time, various failures of electrical devices can occur in the wiring. To reduce the risk of dangerous factors of electric shock, household protective devices are used that perform various functions.
A circuit breaker, circuit breaker and RCD in the complex increase electrical safety, quickly turn off emerging accidents, save people from receiving electrical injuries… However, they have significant differences in operation and design.
To analyze them, first consider the types of possible faults in the electrical network that eliminate these devices. They can manifest themselves:
1. a short circuit that occurs when the electrical resistance of the load is reduced to very small values due to the shunting of the voltage circuits by metal objects;
 2. overloading of wires... Modern powerful electrical appliances cause high currents, creating increased heating of wires with current in poor-quality wiring. During this process, the insulation overheats and ages, losing its dielectric properties;
2. overloading of wires... Modern powerful electrical appliances cause high currents, creating increased heating of wires with current in poor-quality wiring. During this process, the insulation overheats and ages, losing its dielectric properties; 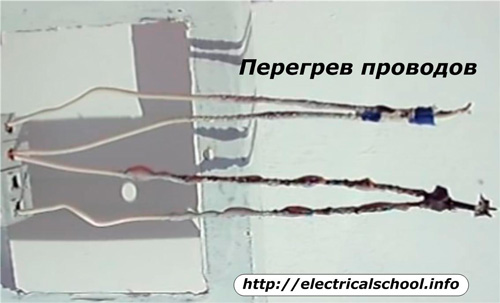
3.the appearance of leakage currents arising through broken insulation through randomly formed circuits to ground.
To worsen the situation with the occurrence of malfunctions can be:
-
old aluminum wiring laid decades ago using outdated technology. It has long been used to the limits of its capabilities when powering modern electrical appliances;
-
poor-quality installation and the use of crude protective devices even in a new electrical circuit.
To simplify the explanation of the differences between protective devices, we will consider only those devices that are designed for a single-phase network, since three-phase structures work in exactly the same way according to the same laws.
Differences between protective devices by purpose
Circuit breaker
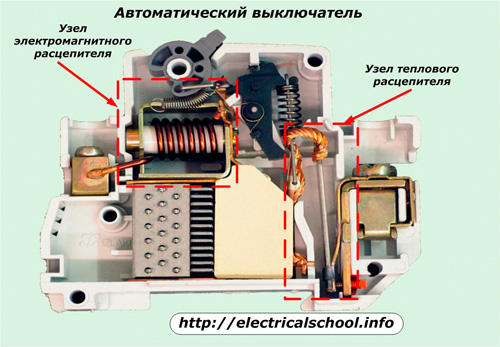
Industry produces many of its varieties. They are designed to eliminate the first two types of malfunctions noted. To this end, their design includes:
-
a high-speed electromagnetic trip coil that eliminates short-circuit currents and a system for extinguishing the resulting electric arc;
-
time-delayed thermal release based on a bimetallic plate, eliminating the resulting overloads inside electrical circuits.
The circuit breaker for residential buildings is connected to a single phase conductor and monitors only the currents passing through it. It does not react at all to the resulting leakage currents.
Read more about circuit breakers here: Breaker device
Residual current device
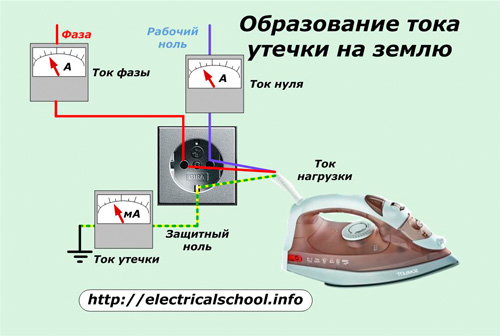
An RCD in a two-wire circuit is connected through two wires: phase and zero. It constantly compares the currents circulating in them and calculates their difference.
When the current leaving the neutral wire corresponds in magnitude to that entering the phase wire, the RCD does not disconnect the circuit, but allows it to operate. In case of small deviations in these values that do not affect the safety of people, the residual current device also does not block the power supply.
The RCD removes the voltage from the conductors suitable for it in the event that a leakage current of a dangerous magnitude occurs inside the controlled circuit, which can harm human health or the operation of electrical equipment. For this purpose, the residual current device is configured to turn off when the current difference reaches a certain setting.
In this way, false alarms are excluded and opportunities for reliable operation of the protection to eliminate leakage currents are created.
However, the very design of this device does not have any protection against the possible occurrence of short-circuit currents and even overload in the controlled circuit. This explains the fact that the RCD itself must be protected from these factors.
A residual current device is always connected in series with a circuit breaker.
Differential automatic
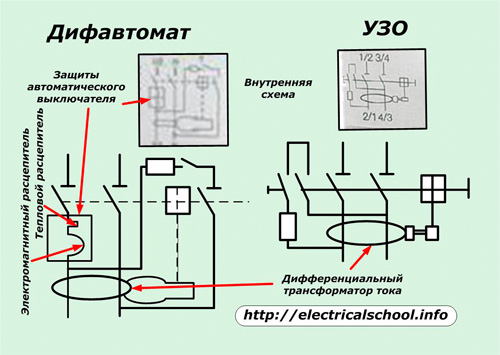
Its device is more complex than that of a circuit breaker or RCD. During operation, it eliminates all three types of faults (short circuit, overload, leakage) that can occur in the wiring. The circuit breaker has an electromagnetic and thermal release in its design, which protects the RCD built into it.
The differential automatic device is made in one unit, it has the functions of circuit breaker and combined residual current device.
Considering all of the above, we can conclude that it is necessary to further compare the characteristics of only two structures:
-
differential automaton;
-
RCD protection unit with circuit breaker.
This will be technically justified and correct.
Differences in protection against performance
Dimensions (edit)
The modern modular design of din-rail mountable devices significantly reduces the space required for their installation in an apartment or floor panels. But even this technique does not always exclude the lack of space to complete the wiring with new protective devices. RCDs with a circuit breaker are manufactured in separate housings and installed in two separate modules, and the differential switch is only one.
This is always taken into account when creating a project for electrical work in new houses, and shields are selected even when providing a small supply of internal space for future circuit modifications. But in the reconstruction of wiring or minor repair of premises, they are not always engaged in replacing shields, and the lack of space in them can become a problem.
Completed tasks
At first glance, an RCD with a circuit breaker and a circuit breaker solve the same problems. But let's try to make them concrete.
Let's say that a block of several sockets is installed in the kitchen to power various devices with uneven power: a dishwasher, a refrigerator, an electric kettle, a microwave oven ... They are switched on randomly and create a load of a random value. In certain situations, the power of several operating devices can exceed the rated value of the protections and create an overcurrent for them.
The installed difavtomat will have to be changed to a more powerful one. When using an RCD, it is enough to replace a cheaper breaker.
When it is necessary to protect an electrical device connected to a separate, dedicated line, it is better to use a differential machine. It just needs to be chosen according to the technical characteristics of a particular user.
Installation works
There are no big differences when fixing one or two modules to a din-bus. But when you connect the wires, the workload becomes greater.
If the difavtomat and the RCD break the phase and neutral wire, then you will need to put jumpers to the circuit breaker to connect to the phase wire in series with the RCD. In some cases, this can complicate circuit assembly.
Quality and reliability
There is a certain opinion among some practicing electricians that the durability and effectiveness of protections depends not only on the factory installation by their manufacturer, but also on the complexity of the design, the number of parts involved in the design, the adjustment and fine-tuning of their technologies.
Difautomat is more complex, requires more operations to set up the interaction of parts, and at this point can play somewhat with the design of the RCD of the same manufacturer.
Applying this technique to all manufactured devices is, to put it mildly, not quite right, although many electricians abuse it. This is a rather controversial statement and is not always confirmed in practice.
Maintenance and replacement
Fracture can occur in any protective device. When it cannot be removed in place, a new device will need to be purchased.
Buying a difavtomat is more expensive. In the case of RCD operation with a circuit breaker, one of the devices will remain intact and will not require replacement. And that's a significant cost savings.
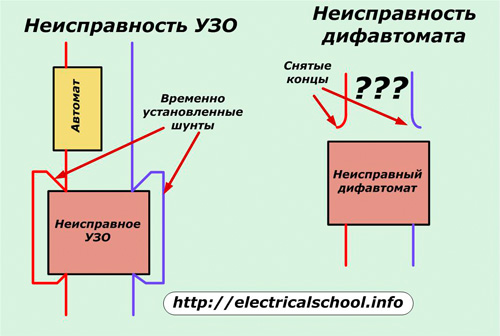
In case of failure of any protective device, the consumers supplied through it are disconnected. In the event that the RCD is faulty, its circuits may be temporarily bypassed and power supplied through the circuit breaker. But when the difavtomat is defective, this will not work. It will have to be replaced with a new one or the circuit breaker shipped for some time.
Working conditions in different situations
The leakage current monitoring scheme for RCD and differential machine can be done on a different basis of elements using:
-
an electromechanical relay that does not require an additional power source for the logic to operate;
-
electronic or microprocessor technologies that require a power supply and a stabilized voltage from it.
They work the same way in the normal condition of suitable voltage circuits. But if there is a fault in the circuit, for example, to break the contact of one of the wires, say zero, as soon as they will be visible advantages of electromechanical models… They work better and more reliably in the outdated two-wire circuit.
Determining the cause of a protection trip
After triggering the RCD, it is immediately clear that leakage currents have occurred in the circuit and it is necessary to check the insulation resistance of the protected area.
When the circuit breaker operates, the cause lies in circuit overload or a short circuit.
But after disconnecting the differential machine on most models, it will take more time to look for the cause of de-voltage and deal with both the insulation resistance of the wiring and the loads created in the circuit. It is impossible to immediately determine the cause.
However, it is now possible to use expensive circuit breaker designs with signal indicators to activate a certain type of protection.
Differences in hull markings
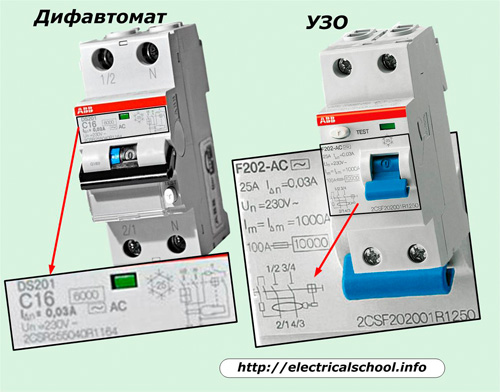
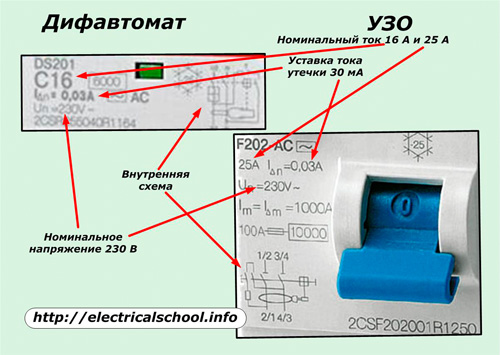
Despite the same appearance of RCD and difavtomat (identical case, «Test» button, manual switching lever, similar terminals for mounting wires), it is enough to simply deal with them according to the diagrams and inscriptions made on their front side.
The data plates of the device always show the nominal values of its load and controlled leakage current, the operating voltage in the wiring, the internal connection of the elements.
For both devices, the diagrams show the differential current transformer and the circuits it controls. The residual current device has no circuit breaker overload protection and is not displayed. And in the case of the difavtomat, they are shown.
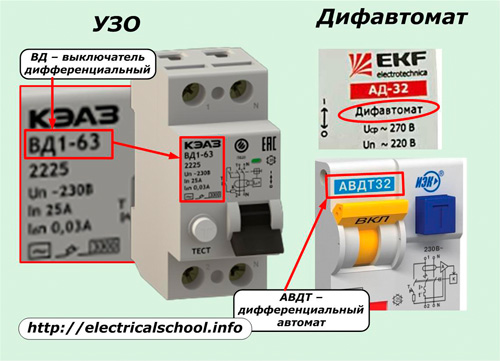
The devices of domestic manufacturers are marked so that the buyer can easily navigate the selected models. Directly on the buildings you can see the inscription "Difavtomat" in a prominent place. The «RCD» marking is located on the back wall.
The designation "VD" on the plate informs that in front of us is a differential switch (correct technical name), which reacts exclusively to leakage currents and does not protect against overcurrent and short circuit. They are marked with RCD.
The inscription «AVDT» (residual current circuit breaker) begins with the letter «A» and emphasizes the presence of circuit breaker functions. This is how the difatomat is indicated in the technical documentation.