Integrated Temperature Sensors (IC Temperature Sensors)—Advantages and Applications
Perhaps the most modern way to measure temperature in electronics is the use of IC temperature sensors. Such sensors can be built directly into microcircuits, and due to the dependence of the I — V characteristic of a semiconductor compound on its temperature, today they provide developers with wide opportunities for creating accurate measuring devices. The direction is developing quite quickly, it has its own characteristics, which will be discussed later in this article.
Diode integral sensors offer advantages over thermocouples and platinum resistance thermometers, although they can work at relatively low temperatures — no more than 150 ° C. The sensors are very compact, which is why they are conveniently built-in, and they are also cheap to manufacture.
Such sensors are ideal for integration into regulators, amplifiers, microcontrollers and other electronic devices where accurate online temperature monitoring is required.Diode sensors are very sensitive and accurate — this is their main advantage for electronics.

There are more and more areas where integrated sensors will fit. Starting from temperature measurement systems of measuring modules, ending with temperature measurement of processors and application in control systems with many controlled parameters: temperature, pressure, etc.
It is extremely useful to integrate integrated diode sensors into remote temperature monitoring systems for fire safety purposes so that the alarm is triggered strictly when the temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold.
The first integral sensors have already shown superiority over thermistors, since for thermistors the dependence of resistance on temperature is far from linear, and for diode sensors the output characteristic immediately turns out to be linear.
Integral sensors are classified as analog and digital and can provide temperature-proportional current or voltage signals. Analog sensors do not lose popularity, because their operating voltage range is quite large — from 4 to 30 volts, while there is no sensitivity to voltage drops on the signal transmission lines. Although most instruments today require a digital format for input data, an analog signal can be easily converted to digital using an ADC.
In many solutions applied to monitoring and measurement tasks, diode sensors have an ADC inside them because the manufacturing technology allows it — the sensor turns out to be cost-effective.The output signal of a digital integral thermometer is now obtained in the format of 1 or 0, which is convenient for transfer to an external microcontroller.
Additional functions are also possible in integrated temperature sensors: monitoring of voltage changes, measuring the temperature of a remote object, measuring the flow rate, signaling that the set temperature has been exceeded.
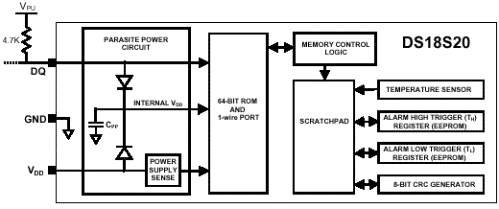
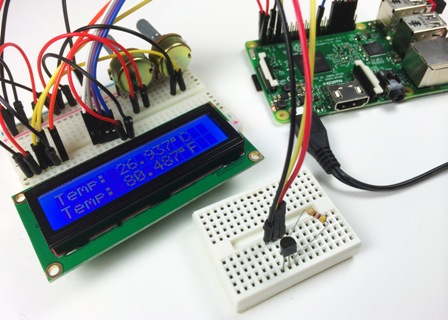
Integrated digital temperature sensors such as the DS18S20 have long gained popularity for 1-Wire technology worldwide, although they were originally known as the discontinued DS1820 sensors. These sensors feature noise isolation and high metrological performance, which is very important when the organization of highways.
For more than 15 years, DS1820 sensors have been used in the construction of multi-point temperature control systems in the range from -55 ° C to + 125 ° C, they allow real-time temperature monitoring and quickly signal the fact that the temperature exceeds the set point. This is possible thanks to the non-volatile memory built into the chip.
The DS18B20 sensors are more advanced — they allow programming of the bit width of the result via 1 -Wire, thus setting the conversion rate. The digital code coming out of the sensor is already the result of the temperature measurement and no further conversions need to be made.
The DS1822 sensor is a simplified, uncalibrated version of the DS18B20 sensor, it is cheaper and allows for low-cost multi-point temperature control systems. There is also an economical two-pin version, such as the DS1822-PAR, which is powered in parasitic single-wire mode.
There is also a DS1825 single-wire thermometer, which has 4 address pins for a maximum of 16 local addresses on a single-wire line. This feature allows the technician to find up to 16 multi-point temperature control thermometers located on a line in the 1-Wire network. This does not require matching tables of 64-bit individual addresses, that is, the performance of such a system will increase.
