How grounding works
In this article, we will consider briefly, but quite clearly, such a simple thing as grounding. So that anyone hearing this term for the first time can understand what it is for and how it works. So what is grounding? The name seems to make it clear that it is somehow connected to the earth.
According to the prescription of PUE, (1.7.28), with grounding are equipped: electrical equipment, electrical installations and electrical networks. This simply means that their grounded parts must be electrically connected to a grounding device, which is a grounded electrode and connecting wires. The earthing switch is located directly below the surface of the earth where it is in direct electrical contact with the ground.

What is a ground electrode
In practice ground electrode often a conductive circuit (consisting of several metal pipes, strips, plates or electrodes of different shapes) exits through which the current is provided with a path of minimum resistance from the electrical installation to the ground.
In everyday life, the ground electrode is also called the ground loop, because it is customary to place the electrodes of the ground electrode during installation along the perimeter around the object as a closed circuit. In the event of an accident, electric current will enter this circuit, and the personnel, thanks to this protective measure, will be protected from electric shock.

If the appliance is not grounded
What possible incidents are we talking about and what should be substantiated? Hazardous voltages may be applied to the case in the event of instrument failure. What dangerous things can happen if the chassis is not grounded?
If under these conditions a person comes into contact with the body of the device (for example, we can talk about a washing machine), then he will be shocked, since the human body has a limited electrical resistance and through the floor and through the surrounding objects, it is connected in some way with the neutral conductor of the network (which is usually earthed - solid earthed neutral).
And since the current is trying to close the circuit, then it (current), tending to the neutral wire (and to the ground), will flow through a person - this is an electric shock that can be fatal. Therefore, to protect against such troubles, the boxes of electrical devices are grounded — they are connected to the ground through a grounding rod.
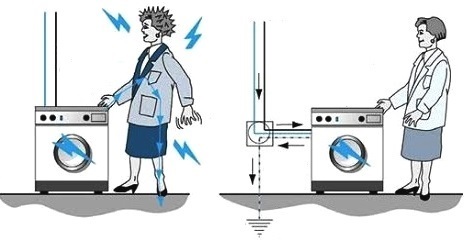
What will grounding the device do
Now, when the body of the device is connected to the earth electrode as the neutral, if the phase voltage hits the body, then a short circuit will immediately occur in the phase-neutral circuit. This will cause the circuit breaker to trip before anyone touches the enclosure with dangerous voltage. This is the protective function of grounding.
In addition, as noted above, the resistance of the grounding electrode is minimal, it is a fraction of an ohm, which means that even with a delay in the operation of the circuit breaker, the potential of the device case will be almost equal to the potential of the grounding electrode. that is, the earth. And if a person is on the ground, then he will not be electrocuted.
Grounding for lightning protection
To lead to the ground lightning currentstriking a building, grounding is also used. But since the lightning current seeks a path from the lightning rod to the ground along the building elements of least resistance, water pipes and wet walls and other conductive parts of the building can end up that way, which is very dangerous.
Therefore, the lightning rod is laid with a separate conductor on the outside of the building so that it directly connects the air terminal to the grounding electrode, providing a path to earth for lightning discharge with minimum resistance. At the same time, people and sensitive electrical equipment in the building remain safe.
