What is electricity
In a broad sense, electricity is the whole set of electromagnetic phenomena, which are various manifestations of the electromagnetic field and its interaction with matter; in a narrow sense it is used in the expression "quantity of electricity", which is synonymous with "electric charge" in the quantification of the latter.
What comes to mind when you hear the word "electricity" or "electricity"? One person will imagine an electrical socket, another - a power line, a transformer or a welding machine, a fisherman will think of lightning, a housewife will think of a battery with her finger or a mobile phone charger, a turner will think of an electric motor, and someone will even imagine Nikola Teslasitting in his laboratory near a resonating induction coil erupting lightning.
In one way or another, there are many manifestations of electricity in the modern world. Today's civilization as a whole is impossible to imagine without electricity. But what do we know about him? Let's clarify this information.
From power plant to electrical appliance
When we plug in the socket at home, turn on the kettle or press the switch, basically wanting to light the bulb, then at that moment we close the circuit between source and receiver of electricityto provide a path for the electric charge to travel, for example through the spiral of a kettle.
The source of electricity in our home is usually an outlet. An electric charge moving through a wire (which in our example is a nichrome coil on a kettle) is electricity… The wire connects the socket to the user with two wires: along one wire the charge moves from the socket to the user, along the second wire at the same time — from the user — to the socket. If the current is alternating, then the wires change their roles 50 times every second.
The source of energy for the movement of electric charges (or, more simply, the source of electricity) in the city network is primarily a power plant. In a power plant, electricity is generated by a powerful generator, the rotor of which is driven into rotation by a nuclear installation or a power plant of another type (for example, a hydro turbine).
Inside the generator, the magnetized rotor crosses the stator wires, causing electromotive force (EMF)generating voltage between the terminals of the generator. And it always is alternating voltage with a frequency of 50 Hz, because the rotor of the generator has 2 magnetic poles and rotates at a frequency of 3000 rpm, or has 4 poles and a speed of 1500 rpm.

It is the tension in our contact that we use every day without even thinking. about the long way electricity travels from the power station to our outlet at the speed of light (299,792,458 meters per second — the speed of propagation of an electric field along the wires, which pushes the electrons inside them, creating a current).
AC voltage 220 volts at the output
The generated voltage for the outputs is variable because: first, it can be easily transformed (decrease or increase), and second, it is generated more easily and transmitted with less loss in the wires than a constant voltage.
By powering the wires to which it is connected transformer, alternating voltage, we obtain alternating current, which harmonically changes its direction 50 times per second, is able to generate an alternating magnetic field in the magnetic circuit of the transformer, which, in turn, is again able to excite an electric current in the wires of the secondary windings that wind the magnetic circuit ...
If the magnetic field were constant in the space covered by the coil, the current in the coils would simply not be directed (cf. law of electromagnetic induction).
To get a current, it is necessary to change the magnetic flux in space, after which it will end up around electric field, it will act on an electric charge, which for example can be located inside a copper wire (free electrons) located around this space with a changing magnetic flux.
The operation of both generators and transformers is based on this principle, with the only difference that in a transformer there are no moving working parts: the source of alternating magnetic flux in a transformer is the alternating current of the primary winding, and in a generator there is a rotating rotor with permanent magnetic field.
And here and there, the changing magnetic field, according to the law of electromagnetic induction, generates an eddy electric field, which acts on the free electrons inside the wires, setting these electrons in motion. If the circuit is closed to the consumer, the current will flow through the consumer.
Electricity storage and direct current
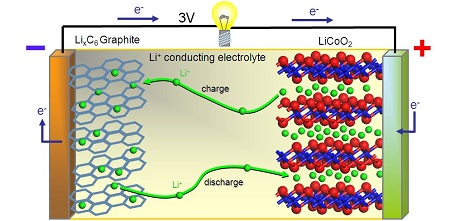
It is most convenient to accumulate electricity in everyday life in the form of chemical energy, namely in batteries… The chemical reaction with the electrodes is able to create a current when the external circuit is closed to the user, and the larger the area of the battery electrodes, the more current can be obtained from it and depending on the material of the electrodes and the number of cells connected in series in the battery, the voltage generated by the battery can be different.
So, for a lithium-ion battery, the standard voltage of a single cell is 3.7 volts and can go up to 4.2 volts. During discharge, positively charged lithium ions move in the electrolyte from the anode (-) based on copper and graphite to the cathode (+) based on aluminum, and during charging from the cathode to the anode, where under the action of the EMF of the charger a graphite-lithium compound is formed, as a result of which energy is accumulated in the form of a chemical compound.
Electrolytic capacitors work in a similar way, differing from batteries with a lower electrical capacity, but in a large number of charge-discharge cycles.
For a lithium-ion battery, the full life is limited to a maximum of 1000 charge-discharge cycles, and the specific energy content reaches 250 Wh / kg. As for electrolytic capacitors, their corrected current life is estimated at tens of thousands of hours, but the energy consumption is usually less than 0.25 Wh / kg.
Static electricity
If you put a silk sheet on top of a woolen blanket, press them well together, and then try to spread them apart, then there will be electrification... This will happen because under the conditions of friction of bodies with different dielectric constants, a separation of charges occurs on their surfaces: a material with a higher dielectric constant will be positively charged, and a material with a lower dielectric constant - negatively.
The greater the difference in these parameters, the stronger the electrification. When you rub your feet with a woolen carpet, you charge negatively, and the carpet positively. Potential levels can reach tens of thousands of volts here, and touching, for example, a water faucet connected to something grounded will give you an electric shock. But since the electrical capacity is scarce, this unpleasant event will not pose a great threat to your life.
Another thing is an electrophoretic machine, in which a static charge generated by friction accumulates in a capacitor. The charge accumulated in the Leyden Bank is already life-threatening.
Most important terms and definitions
What is an electromagnetic field
The electromagnetic field is a special type of matter characterized by a continuous distribution in space (electromagnetic waves) and revealing the discreteness of the structure (photons), characterized by the ability to spread in a vacuum (in the absence of strong gravitational fields), exerting a force effect on charged particles, depending on their speed.
What is electric charge
Electric charge is a property of particles of matter or bodies that characterizes their relationship with their own electromagnetic field and their interaction with an external electromagnetic field. It has two types known as positive charge (charge of proton, positron, etc.) and negative charge (charge of electron, etc.). As a quantity, it is quantified by the strong interaction of one charged body with another charged body.
What is a charged particle
A charged particle is a particle of matter that has an electrical charge.
What is an electric field
The electric field is one of the two sides of the electromagnetic field, caused by electric charges and changes in the magnetic field, exerting a force effect on charged particles and bodies and revealed by the force effect on stationary charged bodies and particles.
What is a magnetic field
The magnetic field is one of the two sides of the electromagnetic field caused by the electric charges on moving charged particles and bodies and by the change in the electric field that exerts a force on the moving charged particles and is revealed by the force action directed generally relative to the direction of movement of these particles and proportional to their speed.
What is electric current
Electric current is a phenomenon of the movement of charged particles and a phenomenon of changes in the electric field over time, accompanied by a magnetic field.
What is the energy of an electric field
Electric field energy — energy associated with an electric field and converted to other forms of energy when the electric field changes.
What is magnetic field energy
Magnetic Field Energy — Energy associated with a magnetic field and converted to other forms of energy by three changes in the magnetic field.
What is electromagnetic energy (electrical energy)
Electric energy — the energy of the electromagnetic field, which consists of the energy of the electric field and the energy of the magnetic field.
See also:
Conditions for the existence of electric current