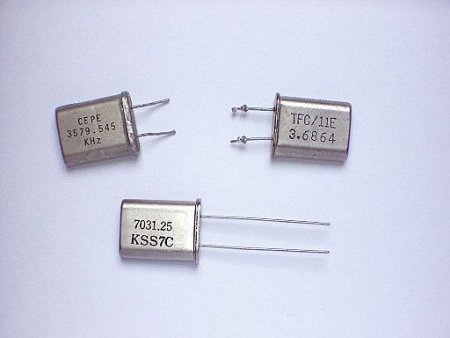
Quartz resonators: purpose, application, principle of action, characteristics of use
What are quartz resonators for?
Modern digital electronics, complete with microprocessors and microcontrollers, are simply unthinkable without clock oscillations. And where the oscillations of the clock are obtained, there is the operation of the generator and the oscillating system, and where the oscillating system is, both the resonance phenomenon and such an important parameter as the quality factor will necessarily appear. Here we are introduced to quartz resonators (oscillators).

The quartz resonator (quartz) is a generator of electromagnetic oscillations with a high degree of frequency constancy, which uses the piezoelectric and mechanical properties of the quartz plate.
According to the principle of operation, a quartz resonator is an oscillator with quartz frequency stabilization. Such generators are used as a highly stable master generator in measuring equipment, frequency and time standards, quartz clocks, as well as in various electronic equipment.
The disadvantage of quartz resonators is that it can only generate at fixed frequencies determined by the resonant frequency of the quartz, and practically does not allow frequency tuning.
All quartz resonator circuits are divided into two large groups depending on what quartz resonance (parallel or series) is used in them. The most widespread are quartz resonator circuits, in which the quartz operates close to its parallel resonance frequency.
So, a quartz resonator in an electronic circuit is an unbeatable alternative to any oscillating circuitconsisting of a capacitor and an inductor. The output is the highest Q-factor of quartz resonators. While a good LC circuit reaches a Q-factor of 300, the Q-factor of a quartz resonator can reach up to 10,000,000. As you can see, the superiority is tens of thousands of times. Thus, no oscillating circuit can be compared to a quartz resonator in terms of Q-factor.
Needless to say about the effect of temperature on the resonance frequency. The resonant frequency of the same oscillating circuit strongly depends on the TKE (temperature coefficient of capacitance) of the capacitor entering it. Quartz, on the other hand, has a very high temperature stability, for this reason quartz resonators firmly hold their positions as sources of oscillation for clock frequency generators for various purposes.
How a quartz resonator works
To understand how a quartz resonator works and works, it is enough to remember what it is piezoelectric effect… Imagine a slab of low-temperature quartz (silicon dioxide) cut from a crystal in a certain way.The angle at which a wafer is cut from the crystal determines the electromechanical properties of the resonator being produced. Electrodes are now attached to this plate on both sides by depositing layers of nickel, platinum, gold or silver, and solid wires are attached to them. The whole structure is placed in a small sealed housing.
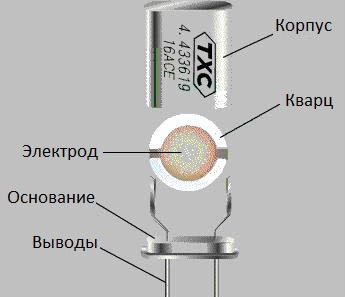
Thus, an electromechanical oscillating system was obtained, which has (due to the natural characteristics of low-temperature quartz) a piezoelectric effect and has its own resonant frequency.
If now an alternating voltage is applied to the electrodes, the frequency of which is close to the resonant frequency of the resulting oscillating system, then the plate will begin to mechanically contract and expand with maximum amplitude, and due to the piezoelectric effect, the closer the frequency of the applied voltage is to resonance, the lower the resistance of the resonator will be. This is the analogy of a quartz resonator with a high frequency oscillator circuit. The result is essentially analogous to a series LC circuit.
Characteristics of a quartz resonator
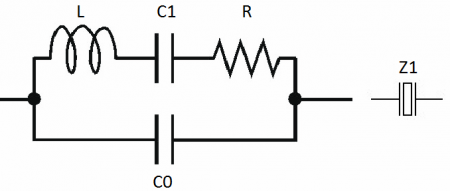
A quartz resonator can be represented in the form of an equivalent circuit, in which C0 is the mounting electrical capacitance formed by the metal cable holders and electrodes. C1, L and R are the capacitance, inductance and active resistance of the plate directly with electrodes, as an analogue of a real oscillating circuit obtained due to the electromechanical properties of the plate.
If we exclude the mounting capacitance C0 from the circuit, then we will explicitly get a series oscillating circuit.As for the designation of the resonator in the diagram, it looks like a capacitor with a rectangle symbolizing a quartz crystal between the plates.
In the process of assembly and disassembly of quartz resonators on boards by soldering, it should be remembered that overheating of quartz above 573 ° C is fraught with loss of the piezoelectric properties of the crystal.