Optocoupler — characteristics, device, application
What is an optocoupler
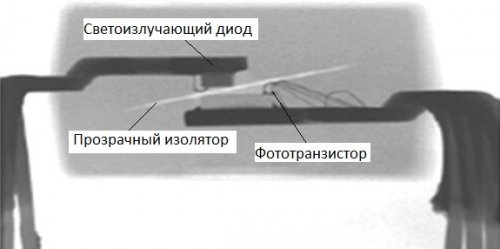
The optocoupler is an optoelectronic device, the main functional parts of which are a light source and a photodetector, which are not galvanically connected to each other, but are located in a common sealed housing. The principle of operation of an optocoupler is based on the fact that an electrical signal applied to it causes a glow on the transmitting side, and already in the form of light, the signal is received by the photodetector, initiating an electrical signal on the receiving side. That is, a signal is transmitted and received through optical communication within the electronic component.

An optocoupler is the simplest type of optocoupler. It consists only of the transmitting and receiving parts. A more complex type of optocoupler is an optoelectronic chip that contains several optocouplers connected to one or more matching or amplifying devices.
Thus, an optocoupler is an electronic component that provides transmission of an optical signal in a circuit without galvanic coupling between the signal source and its receiver, since photons are known to be electrically neutral.
The structure and characteristics of optocouplers
Optocouplers use photodetectors that are sensitive in the near-infrared and visible regions, since this part of the spectrum is characterized by intense sources of radiation that can work as photodetectors without cooling. Photodetectors with pn junctions (diodes and transistors) based on silicon are universal, the region of their maximum spectral sensitivity is close to 0.8 μm.
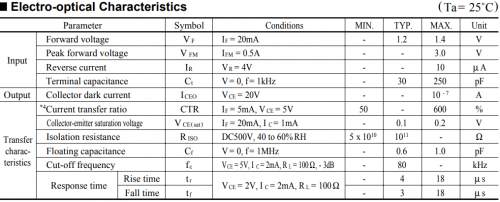
The optocoupler is primarily characterized by the current transmission ratio CTR, that is, the ratio of the input and output currents. The next parameter is the signal transmission rate, actually the cutoff frequency fc of the optocoupler operation, related to the rise time tr and the cutoff tf for the transmitted pulses. Finally, the parameters characterizing the optocoupler from the point of view of galvanic isolation: the insulation resistance Riso, the maximum voltage Viso and the throughput Cf.
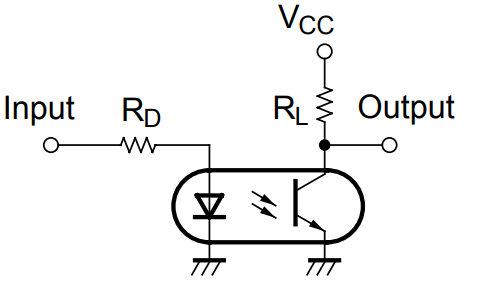
The input device, which is part of the optocoupler structure, is designed to create optimal operating conditions for the emitter (LED) to shift the operating point into the linear region of the I — V characteristic.
The input device has sufficient speed and a wide range of input currents, ensuring the reliability of information transmission even at low (threshold) current. The optical medium is located inside the housing through which the light is transmitted from the emitter to the photodetector.
In optocouplers with a controlled optical channel, there is an additional control device, through which it is possible to influence the properties of the optical medium using electrical or magnetic means.On the photodetector side, the signal is recovered at a high optical-to-electrical conversion rate.
The output device on the side of the photodetector (for example, a phototransistor included in the circuit) is designed to convert the signal into a standard electrical form, convenient for further processing in blocks following the optocoupler. An optocoupler often does not contain input and output devices, so it requires external circuits to establish normal operation in the circuit of a particular device.
Application of optocouplers
Optical connectors are widely used in circuits for galvanic isolation blocks of various equipment, where there are circuits for low and high voltage, control circuits are separated from power circuits: control of powerful triacs and thyristors, relay circuits, etc.
Diode, transistor and resistor optocouplers are used in radio engineering modulation and automatic gain control circuits. By exposing the optical channel, the circuit is controlled contactlessly and brought to the optimal mode of operation.
Optical connectors are so versatile that they are used in such a variety of industries and in so many unique functions, even simply as galvanic isolation and contactless control elements, that it is impossible to list them all.
Here are just a few of them: computers, communication technology, automation, radio equipment, automated control systems, measuring instruments, control and regulation systems, medical technology, visual display devices and many others.
Advantages of Optocouplers
The use of optocouplers on printed circuit boards allows you to achieve ideal galvanic isolation when the requirements for isolation of high voltage and low voltage, input and output circuits in terms of resistance are extremely high. The voltage between the transmit and receive circuits of the popular PC817 optocoupler is, for example, 5000 V. In addition, an extremely low bandwidth of about 1 pF is achieved by optical isolation.
Using optocouplers, contactless control is very easy to implement, while leaving room for unique design solutions in terms of direct control circuits. It is also important here that there is absolutely no reaction of the receiver to the source, that is, the information is transmitted one-way.
The widest bandwidth of the optocoupler eliminates the limitations imposed by low frequencies: with the help of light, you can transmit at least a constant signal, even a pulse, and with very steep edges, which is fundamentally impossible to implement using pulse transformers. The communication channel inside the optocoupler is absolutely immune to the effects of electromagnetic fields, so the signal is protected from interference and capture. Finally, optocouplers are fully compatible with other electronic components.