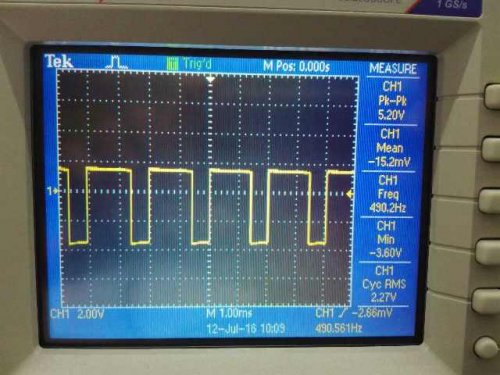
What is a duty cycle
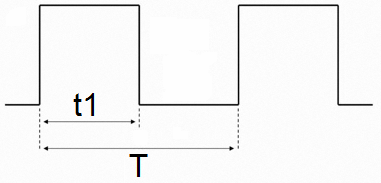
One of the most important quantities in pulse technology is the duty cycle S. The duty cycle S characterizes rectangular pulse, and determines how many times the pulse period T is longer than its duration t1. So, a meander, for example, has a duty cycle equal to 2, since the duration of the pulse in this sequence is equal to half of its period: S = T / t1 = 2.
As you can see, both the numerator and denominator are durations measured in seconds, so the duty cycle is a dimensionless quantity. For reference, recall that a meander is such a pulse sequence where the duration of the positive part of the pulse t1 is equal to the duration of its initial state t0.
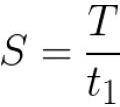
The inverse duty cycle is called the duty cycle D. Thus, theoretically, the duty cycle can range from infinity to 1, while its corresponding duty cycle can range from 0 to 1. Writing the duty cycle is often more convenient than the duty cycle as a fraction.
For example: D = 0.5 — duty cycle of a meander, or duty cycle S = 2 — a more legible record of the same.The duty cycle S = 10 corresponds to the duty cycle D = 0.1 — which means that the duration of the pulse is 10 times smaller than its period (the sum of its positive and initial parts).
 As for speech for pulse width modulation (PWM), then say that when there is a change in pulse width or duration in the driver, it effectively means a change in the constant frequency duty cycle. In this context, the higher the duty cycle, the narrower the pulse, the lower the duty cycle, the wider the pulse.
As for speech for pulse width modulation (PWM), then say that when there is a change in pulse width or duration in the driver, it effectively means a change in the constant frequency duty cycle. In this context, the higher the duty cycle, the narrower the pulse, the lower the duty cycle, the wider the pulse.
Here we can see the etymological connection with the Russian word "well": a large well (actually — a hole between pulses in a sequence) — the pulse itself looks like a narrower, small well — the pulses are wide (but the hole between them is narrow).
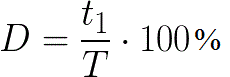
In the English-language literature, the term "duty cycle" is not used, but only the term "duty cycle"-duty cycle is used, which is an analogue of the Russian-language term "duty cycle" (D), only it is usually indicated not as a fraction , and as a percentage. For example, we write D = 0.5, and in English-language literature you can find 50% duty cycle or D = 50% when talking about a meander. Or D = 30% if the duration of the pulse is related to its period from 30 to 100.
Let's look at a simple, practical example. The light turns on for one second every 59 seconds, then turns off for 59 seconds, and so repeats itself indefinitely.
What does it mean? Pulse duration t1 = 1 second, pulse period T = 59 + 1 = 60 seconds. Therefore, what duty cycle does the light turn on?
With duty cycle S = 60/1. The duty cycle is 60.This means that the duty cycle is 1/60, that is, D = 0.01666 or a duty cycle of 1.66%. In this example, it is clearly seen that writing in terms of duty cycle S = 60 is more readable and accurate than writing in terms of duty cycle D = 0.01666 or duty cycle 1.666%.
Finally, there is another useful application of the duty cycle. Pulse counter decoders (type K561IE8) can split the pulse sequence into separate pulses, here again the value of the duty cycle is more appropriate, it can be determined by the capacity of the counter and counted (in proportion to the number of pulses counted by the counter ).
Thus, even for digital technologies, the direct operation of the pulsed duty cycle is often more convenient than the duty cycle typical of the English language literature.