Generation and transmission of alternating electric current
An alternating current is a current whose magnitude and direction change periodically. Thanks to alternating current, there is light and heat in our homes today. All industrial enterprises and productions of our time work only thanks to alternating current. Without alternating current, the technological progress of modern civilization would simply be impossible.
To obtain alternating current, electromechanical devices are used, the so-called induction generators… In them, the mechanical energy obtained in one way or another is transferred to the rotor, the rotor rotates, as a result of which the mechanical energy of the rotation of the rotor is converted into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction.
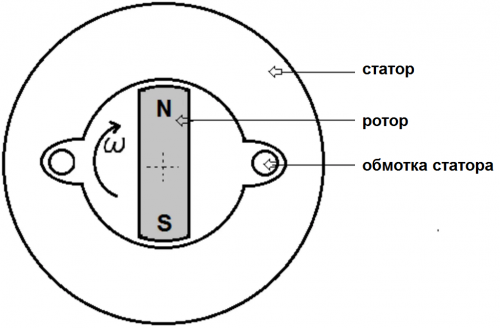
Recall that if you rotate the magnet inside the conducting frame, then there will be an induction in the frame alternating current… The generator works on this principle. Only in an industrial generator, the stator plays the role of a frame, and the role of a magnet is a rotor with a magnetizing coil, actually a rotating electromagnet.
In an industrial generator, the stator is a huge steel structure in the form of a ring with grooves on the inside. A copper three-phase winding is laid in these slots. The magnetic field, as we have already said, is created by the rotor, which is a steel core with a pair (or several pairs, depending on the nominal speed of the rotor) of the poles formed by the current in the rotor winding. A direct current is supplied to the rotor winding from the exciter.
According to the schematic diagram of a two-pole induction alternator, it is easy to understand that the lines of force of the rotor magnetic field cross the turns of the stator winding, while once per revolution the magnetic flux of the rotor changes its direction with respect to the same revolutions of the stator.
Thus, alternating current rather than pulsating direct current is produced in the stator winding. If we talk about a nuclear power plant, then the rotor of the generator receives mechanical rotation from steam, which is supplied under enormous pressure to the blades of a turbine connected to the rotor. Steam in a nuclear power plant is produced from water that is heated by the heat from a nuclear reaction fed to the water through a heat exchanger.
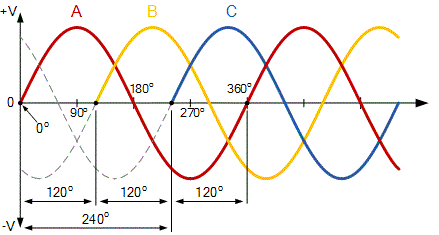
In Russia, the frequency of alternating current in the network is 50 Hz, which means that the rotor of a two-pole generator must make 50 revolutions per second. So, in a nuclear power plant the rotor makes 3000 revolutions per minute, which simply gives the frequency of the generated current as 50 Hz. The direction of the generated current changes according to the sinusoidal (harmonic) law.
The generator winding is divided into three parts, so the alternating current is three-phase.This means that in each of the three parts of the stator winding, the resulting EMF is phase-shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees. The effective value of the generated voltage in the power plant can be from 6.3 to 36.75 kV, depending on the type of generator.
To transmit electrical energy over a long distance, high voltage power lines (PTL)… But if the electricity is transmitted without conversion, at the same voltage that comes from the generator, then the energy losses during transmission will be colossal and practically nothing will reach the end user.
The fact is that energy losses in transmitting wires are proportional to the square of the current value and directly proportional to the resistance of the wires (see The Joule-Lenz law). This means that for more efficient transmission and distribution of electricity, the voltage must first be increased several times in order to reduce the current by the same amount and therefore significantly reduce the transport losses. And only the increased voltage makes sense to transfer to power lines.
Therefore, electricity is first supplied from the power plant to the transformer substation... Here the voltage is increased to 110-750 kV and only then is it fed to the power lines. But the user needs 220 or 380 volts, therefore at the end of the line the high voltage is stepped back down with the help of transformer substations to 6-35 kV.
A transformer is installed at a substation near our house or built into the house. Here the voltage drops again — from 6-35 kV to 220 (380) volts, which are already distributed to consumers.Through the input distribution device, a network of wires and cables diverges into different rooms.