How do wires differ from cables?
 The wire is one uninsulated, one or more insulated conductors, over which, depending on the conditions of installation and operation, there may be a non-metallic sheath, winding or braiding with fibrous materials or wire. The conductors may be bare and insulated.
The wire is one uninsulated, one or more insulated conductors, over which, depending on the conditions of installation and operation, there may be a non-metallic sheath, winding or braiding with fibrous materials or wire. The conductors may be bare and insulated.
Bare wires
Bare conductors are those whose conducting cores do not have any protective or insulating coverings. Bare conductors (PSO, PS, A, AC, etc.) are mainly used for overhead power lines… Insulated wires are wires whose wires are covered with rubber or plastic insulation. These wires are braided with cotton yarn or wrapped with rubber, plastic or metal tape over the insulation. Insulated wires are divided into protected and unprotected.
Shielded wires
Insulated wires that have a coating on the electrical insulation designed for sealing and protection from external influences are protected. These include wires APRN, PRVD, APRF, etc. An unprotected insulated wire is a wire that does not have a sheath over the electrical insulation. These are wires APRTO, PRD, APPR, APPV, PPV, etc.
Cords
The cable is a conductor consisting of two or more insulated flexible or highly flexible conductors with a cross-section of up to 1.5 mm2, twisted or laid in parallel, covered, depending on the operating conditions, with a non-metallic sheath or other protective covers.
Cables
 The cable is one or more insulated wires twisted together, enclosed, as a rule, in a common rubber, plastic, metal sheath (NRG, KG, AVVG, etc.). The sheath serves to protect the insulation of the wires from the effects of light, moisture, various chemicals, as well as to protect against mechanical damage.
The cable is one or more insulated wires twisted together, enclosed, as a rule, in a common rubber, plastic, metal sheath (NRG, KG, AVVG, etc.). The sheath serves to protect the insulation of the wires from the effects of light, moisture, various chemicals, as well as to protect against mechanical damage.
Mounting wires
The installation wires are designed for the installation of electrical and lighting networks with a fixed installation outdoors and indoors. They are made with copper and aluminum wires, single and multi-core, with rubber and plastic insulation, unprotected and protected from light mechanical damage. The conductive cores of the wires have standard cross-sections, mm: 0.35; 0.5; 0.75; 1.0; 1.5; 2.5; 4.0; 6.0; 10.0; 16.0 etc.
How to determine the cross-section of a wire, knowing its radius
Depending on the brands, the standard cross-sections of the wires have certain values. If the cross section of the wire is unknown, it is calculated using the following formula:
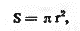
where S is the cross section of the wire, mm2; n is a number equal to 3.14; r — radius of the wire, mm.
The conductor diameter of the current-carrying conductor (without insulation) is measured with a micrometer or caliper… The cross-section of conductors of multi-core wires and cables is determined by the sum of the cross-sections of all conductors.
Varieties of mounting wires
Assembly wires with plastic insulation APV, PV are made without sheath and protective covers, since plastic insulation does not need protection from light, moisture and is resistant to light mechanical loads.
To protect wires with rubber insulation from mechanical damage, the effect of light and moisture, sheaths with a folded seam of AMT aluminum alloy or brass (APRF, PRF, PRFl) or PVC-plastic sheaths (PRVD, etc.) are used.
The insulation of the wires is designed for a certain working voltage, at which they can work safely and for a long time. Therefore, when choosing a brand of wire, it should be borne in mind that the working voltage for which the insulation of the wire is designed must be greater than or equal to the nominal standard value of the voltage of the supply network 380, 220, 127, 42, 12V.
Installation wires must be suitable for the connected load. For the same brand and the same cross-section of the wire, different loads are allowed, which depend on the laying conditions. For example, wires or cables placed in the open cool better than those laid in pipes or hidden under plaster. Rubber-insulated conductors allow a long-term heating temperature of their cores not exceeding 65 ° C, and plastic-insulated conductors -70 ° C
How to decode wire markings
The conductors are marked with letters, then the numbers and the cross-sectional area of the conducting cores are written in numbers. When specifying a conductor, the following structure is assumed. In the center is placed the letter P, denoting a wire, or PP — a flat two- or three-core wire.Before the letters P or PP, the letter A may stand, indicating that the wire is made of aluminum conducting wires; if there is no letter A, then the wires are made of copper.
After the letter P or PP there is a letter characterizing the material from which the insulation of the wires is made: P — rubber, V — polyvinyl chloride and P — polyethylene insulation (APRR, PPV, etc.). The rubber insulation of the wire can be protected with different sheaths: B — made of PVC plastic compound, H — non-flammable chloroprene (nitrite) sheath. The letters B and H are placed after the letters of the insulating material of the wire — APRN, PRI, PRVD.
If the wire has a coating of cotton yarn coated with varnish, then this is indicated by the letter L, and if the yarn is impregnated with an anti-rot compound, then the letter in the brand of the wire is omitted. The letter L is placed at the last place in the designation of the phone brand.
Conductors with flexible current-carrying conductors are marked with the letter G, which is placed after rubber — P or before polyvinyl chloride insulation — B (PRGI, etc.). Single-core and multi-core conductors intended for laying in steel pipes and with a braid impregnated with an anti-rot compound have the letters TO (APRTO, PRTO) at the end of the brand.
The PVC rubber insulating sheath is oil resistant. The flat wires at the base of the separator can be perforated with a hole width of up to 4 mm and a length of up to 20 mm. The distance between the edges of the holes is up to 15 mm. Wires may have labels that make it easier to distinguish the wires during installation.
For cable management devices indoors and outdoors, branching devices from overhead lines to residential buildings and buildings, special conductors are produced with a supporting steel cable that is located inside the conductor, between its insulated cores. Stranded wires are available in 2-, 3- and 4-core and have rubber or PVC insulation. The conducting cores of the AVT wire have insulation of black, blue, brown and other colors. Installation wires are designed for operation at ambient temperatures from -40 to + 50 ° C and relative humidity 95 ± 3% (at + 20 ° C).
How to decipher cable markings
Power cables, as well as the wires, are marked with letters, then the numbers and the cross-sectional area of the current-carrying wires are written in numbers. For electrical wiring, you can use unarmored power cables with rubber and plastic insulation. In order to protect the insulation of the wires from light, moisture, chemicals, as well as mechanical damage, the cables are covered with sheaths of various materials. Metal sheaths made of lead, aluminum and steel are not used as protective sheaths for cables (armor). When insulating cables made of moisture-resistant materials (plastic and rubber), instead of a metal sheath, a plastic or rubber sheath can be made.
Brands of rubber cables — ASRG, SRG, VRG, AVRG, ANRG, NRG; with plastic insulation — AVVG, VVG, APVG, PVG, APsVG, PsVG, APvVG, PVVG.
The first letter in the designation of cable brands, except for the letter A, specifies the material: B — PVC compound, P — polyethylene, Ps — self-extinguishing polyethylene, Pv — vulcanizing polyethylene, N — nitrite, C — lead. The second letter defines the insulating material B — PVC compound, P — rubber. The third letter G means that the cable is not armored.
The power cables of the indicated brands are intended for operation in a stationary state at an ambient temperature of - 50 to + 50 g. With relative humidity up to 98%. The cables are designed for a long-term permissible temperature of their cores up to 70 ° C.
ANRG and NRG brand cables have a non-flammable rubber sheath. To connect portable lamps, mobile electrified machines and portable electrical appliances to the network, flexible cables with rubber insulation of the type KG, KGN, KLG, KPGSN, etc. are used.

