What is the collector used in DC machines?
Collector It is a system of copper plates isolated from each other and from the armature shaft. Taps from the armature winding are soldered to the plates. The sliding contacts (brushes) are used to connect the collector to the clamps of the machine and to the external circuit.
The collector in electrical machines acts as an AC / DC rectifier (in generators) and the role of automatic switching of the current direction in the rotating armature wires (in motors).
When the magnetic field is crossed by only two wires forming a frame, the collector will be a single ring cut into two parts isolated from each other. Basically, each semicircle is called a collector plate.
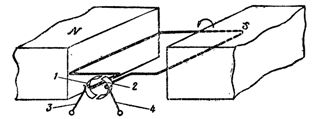
Each start and end of the frame is attached to its own collector plate. Brushes are arranged in such a way that one of them is always connected to a wire that will move to the North Pole and the other to a wire that will move to the South Pole. In fig. 1. shows a general view of a collector electric machine.
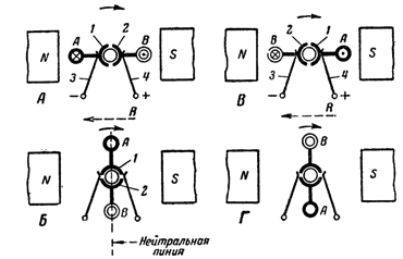
To consider the operation of the manifold, let us refer to Fig.2, in which the frame with wires A and B is shown in section. For clarity, wire A is shown with a thick circle, and wire B with two thin circles.
Brushes are closed to external resistance then e. etc. induced in the wires will induce an electric current in a closed circuit. Therefore, when looking at the operation of the collector, one cannot say no about the induced e. etc. s., and for the induced electric current.

Rice. 1. Electric machine manifold
Rice. 2. Simplified image of the tank
Rice. 3. Rectification of alternating current using a collector
Let the frame rotate clockwise. At the moment when the rotating frame takes the position shown in fig. 3, A, the greatest current will be induced in its wires, because the wires cross the magnetic lines of force running perpendicular to them.
The induced current from wire B connected to collector plate 2 will flow to brush 4 and after passing through the external circuit will return through brush 3 to wire A. In this case the right brush will be positive and the left will be negative.
Further rotation of the bezel (position B) will again induce current in both wires; however, the direction of the current in the wires will be opposite to what they had in position A. Since the collector plates will also rotate with the wires, brush 4 will again supply electric current to the external circuit and the current will return to the frame through brush 3.
It follows that, despite the change in the direction of the current in the rotating wires themselves, due to the switching made by the collector, the direction of the current in the external circuit has not changed.
At the next moment (position D), when the frame again occupies a position on the neutral line, there will be no current in the wires and therefore in the external circuit.
At subsequent moments in time, the considered cycle of movements will be repeated in the same order. In this way, the direction of the induced current in the external circuit due to the collector will remain the same at all times and at the same time the polarity of the brushes will be preserved.
Rice. 4. DC motor collector
The curve in fig. 5. It can be seen from the curve that the current reaches its highest values at the points corresponding to 90 ° and 270 °, that is, when the conductors cross the lines of force directly under the poles. At the points 0 ° (360 °) and 180 °, the current in the external circuit is zero, since the wires, passing through the neutral line, do not cross the power lines.
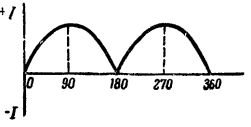
Rice. 5. Curve of the current change in the external circuit for one revolution of the frame after correction by the collector
It is easy to conclude from the curve that although the direction of the current in the external circuit remains unchanged, its value constantly changes from zero to a maximum.
Electricityconstant in direction but variable in magnitude is called pulsating current… For practical purposes, ripple current is very inconvenient. Therefore, in generators, they seek to smooth out ripples and make the current more uniform.
Unlike generators, in DC motors the collector acts as an automatic switch of the current direction in the rotating armature wires.If in the generator the collector serves to correct alternating current into direct current, then in the electric motor the role of the collector is reduced to the distribution of current in the armature windings in such a way that during the entire operation of the electric motor in the wires that are currently under The North Pole, the current flows constantly in what — or in one direction, and in wires located under the South Pole — in the opposite direction.
