Analog and digital electronics
 Electronics is divided into analog and digital, with the latter replacing analog in almost all positions.
Electronics is divided into analog and digital, with the latter replacing analog in almost all positions.
Analog electronics studies devices that generate and process signals continuously over time.
Digital electronics use time-discrete signals, most often expressed in digital form.
What is a signal? A signal is something that carries information. Light, sound, temperature, speed — all these are physical quantities, the change of which has a certain meaning for us: either as a life process or as a technological process.
A person is capable of perceiving many physical quantities as information. To do this, it has transducers - sensory organs that convert various external signals into impulses (which, by the way, are of an electrical nature) that enter the brain. In this case, all types of signals: light, sound and temperature are converted into impulses of the same nature.
In electronic systems, the functions of the sense organs are performed by sensors (sensors), which convert all physical quantities into electrical signals.For light — photocells, for sound — microphones, for temperature — a thermistor or thermocouple.
Why precisely in electrical signals? The answer is obvious, electrical quantities are universal because any other quantities can be converted to electrical and vice versa; electrical signals are conveniently transmitted and processed.
After receiving information, the human brain, based on the processing of this information, gives control actions to muscles and other mechanisms. Similarly, in electronic systems, electrical signals control electrical, mechanical, thermal and other types of energy through electric motors, electromagnets, electric light sources.
So, the conclusion. What man previously did (or could not) is done by electronic systems: they control, manage, regulate, communicate remotely, etc.
Ways of presenting information
When using electrical signals as a data carrier, two forms are possible:
1) analog — the electrical signal is similar to the original one at any moment in time, i.e. continuously in time. Temperature, pressure, speed change according to a continuous law — sensors convert these values into an electrical signal that changes according to the same law (similar). The values represented in this form can take an infinite number of values within a specified range.
2) a separate — pulse and digital — signal is a series of pulses in which information is encoded. In this case, not all values are coded, but only at certain points in time — signal sampling.
Pulse operation - short-term exposure of the signal alternates with a pause.
Compared to continuous (analog) operation, pulse operation has several advantages:
— large output power values for the same volume of electronic device and higher efficiency;
— increasing noise immunity, accuracy and reliability of electronic devices;
— reduction of the influence of temperatures and dispersion of device parameters, since the work is carried out in two modes: "on" — "off";
— implementation of pulse devices on single-type elements, easily implemented by the method of integral technology (on microcircuits).
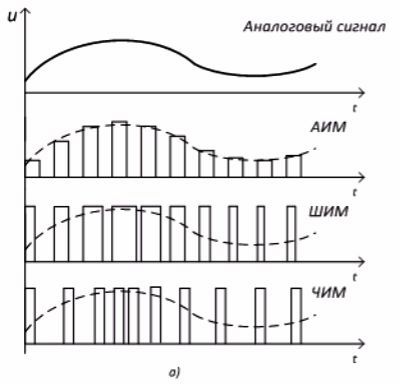
Figure 1a shows the methods of encoding a continuous signal with rectangular pulses—the modulation process.
Pulse-Amplitude Modulation (PAM) — the amplitude of the pulses is proportional to the input signal.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) — the pulse width tpulse is proportional to the input signal, the amplitude and frequency of the pulses are constant.
Pulse-Frequency Modulation (PFM) — the input signal determines the repetition rate of pulses that have a constant duration and amplitude.
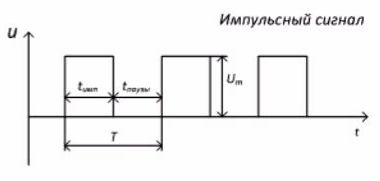
Figure 1 — a) Methods of coding a continuous signal with rectangular pulses, b) Basic parameters of rectangular pulses
The most common pulses are rectangular. Figure 1b shows a periodic sequence of rectangular pulses and their main parameters. The pulses are characterized by the following parameters: Um — pulse amplitude; timp is the pulse duration; tpause — the duration of the pause between pulses; Tp = tp + tp — pulse repetition period; f = 1 / Tp — pulse repetition frequency; QH = Tp / tp — pulse duty cycle.
Along with rectangular pulses in electronic engineering, pulses of sawtooth, exponential, trapezoidal and other shapes are widely used.
Digital mode of operation — information is transmitted in the form of a number that corresponds to a certain set of pulses (digital code), and only the presence or absence of a pulse is essential.
Digital devices most often work with only two signal values - zero «0» (usually low voltage or no pulse) and «1» (usually high voltage level or the presence of a square wave), i.e. the information is presented in a binary number system.
This is due to the convenience of creating, processing, storing and transmitting signals represented in the binary system: the switch is closed — open, the transistor is open — closed, the capacitor is charged — discharged, the magnetic material is magnetized — demagnetized, etc. .
Digital information is represented in two ways:
1) potential — the values «0» and «1» correspond to low and high voltage.
2) impulse — binary variables correspond to the presence or absence of electrical impulses at certain moments of time.