How to choose current transformers for connecting meters
 Metering devices for settlements for consumed electricity between the energy organization and consumers must be installed at the border of the network section in terms of balance and operational responsibility between the energy organization and the consumer. The number of meters in the facility must be minimal and justified by the accepted power supply scheme of the facility and the current electricity tariffs for that consumer. Metering devices for tenants located in residential, public and other buildings and isolated in an administrative manner must be installed separately for each independent user (organization, housing management, workshop, shop, workshop, warehouse, etc.).
Metering devices for settlements for consumed electricity between the energy organization and consumers must be installed at the border of the network section in terms of balance and operational responsibility between the energy organization and the consumer. The number of meters in the facility must be minimal and justified by the accepted power supply scheme of the facility and the current electricity tariffs for that consumer. Metering devices for tenants located in residential, public and other buildings and isolated in an administrative manner must be installed separately for each independent user (organization, housing management, workshop, shop, workshop, warehouse, etc.).
Transformation factor current transformers should be chosen according to the calculated connected load, taking into account the operation of the plant in emergency mode.A current transformer is considered overrated in terms of transformation ratio where at 25% rated connected load (in normal mode) the current in the secondary winding will be less than 10% of the rated current of the meter (rated) current of the meter — 5 A).
Depending on the values of the resistance of the users of the secondary circuit Z2, ohms and the secondary load of the current transformer S2, VA, the same current transformer can work in different classes of accuracy. To ensure sufficient accuracy of instrument readings and the operation of protective devices connected to the current transformer, it is necessary that the value of Z2 does not exceed the rated load of the current transformer.
Current transformers have a current ΔI and angular errors δ... The current error, percentage, according to the given ratio, is taken into account in the readings of all devices:
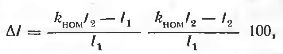
where knom — nominal transformation ratio; I1 and I2 — current of the primary and secondary windings of the transformer, respectively.
The angular error is determined by the angle δ between the current vectors I1 and I2 and is only taken into account in the readings of meters and wattmeters.
Current transformers have the following accuracy classes: 0.2; 0.5; 1; 3; 10, which corresponds to the values of current errors, percent. The accuracy class of current transformers should be 0.5 for commercial meters; for electrical measuring devices — 1; for overcurrent protection relay — 3; for laboratory instruments — 0.2.
Example selection of current transformers for connecting the meter.
Approximate connection current in normal mode — 90 A, in emergency mode — 126 A.
Select current transformers with a transformation factor nt = 150/5 based on the load in emergency mode.
Review. At 25% load, the primary current is I1 = (90 x 25) / 100 = 22.5 A.
Secondary current (at transformation ratio) нt = 150: 5 = 30) will be
Az2 = I1 / nt = 22.5/30 = 0.75 A.
The current transformers are chosen correctly, since Az2 > Azn counter, i.e. 0.75> 0.5.
The cross-section of wires or cables from current transformers to measuring devices should be at least: copper — 2.5, aluminum — 4 mm2. The maximum cross-section of wires and cables that can be connected to the terminals of the meter must not exceed 10 mm2.
When choosing current transformers for billing meters, it is recommended to use data from PUE (table «Selection of current transformers»).Before measuring devices installed at the input, for safe installation, inspection and replacement of measuring devices and current transformers in electrical installations in the presence of two supply lines (inputs) and two distribution nodes that have switching devices for their connection (section switches, ATS, etc.
