Electric arc and its characteristics

Electric arc — the passage of electricity through a gas between two electrodes, one of which is a source of electrons (cathode). An electrode is a wire that terminates in any section of an electrical circuit.
Electrons emitted from the cathode in large quantities cause strong ionization of the gas between the electrodes and thus make it possible for a large current to flow between the electrodes.
A characteristic feature of an electric arc, unlike a conventional gas discharge, is that it can burn at low voltage.
The electric arc was discovered by a physicist from St. Petersburg V. V. Petrov in 1802 and found important applications in technology.
An electric arc is a type of discharge characterized by high current density, high temperature, elevated gas pressure, and low voltage drop across the arc gap. In this case, intensive heating of the electrodes (contacts) takes place, on which the so-called are formed. Cathodic and anodic spots. The cathode glow is concentrated in a small bright spot, the incandescent part of the opposite electrode forms the anode spot.
Three areas can be noted in the rainbow, which are very different in the nature of the processes taking place in them. Directly to the negative electrode (cathode) of the arc is the cathode voltage drop region. Next is the plasma arc barrel. Directly to the positive electrode (anode) is the anodic voltage drop region. These regions are shown schematically in Fig. 1.
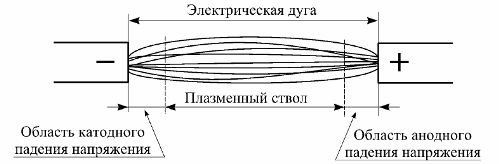
Rice. 1. The structure of the electric arc
The sizes of the cathodic and anodic voltage drop regions in the figure are greatly exaggerated. In reality, their length is very small. For example, the length of the cathodic voltage drop is of the order of the path of free movement of an electron (less than 1 micron). The length of the anode voltage drop region is usually slightly greater than this value.
Under normal conditions, air is a good insulator. So, the voltage required to break an air gap of 1 cm is 30 kV. In order for the air gap to become a conductor, it is necessary to create a certain concentration of charged particles (electrons and ions) in it.
How an electric arc occurs
The electric arc, which is a stream of charged particles, at the initial moment of contact separation occurs as a result of the presence of free electrons in the gas of the arc gap and electrons emitted from the surface of the cathode. The free electrons in the gap between the contacts move at high speed in the direction from the cathode to the anode under the action of the electric field forces.
The field strength at the beginning of the contact gap can reach several thousand kilovolts per centimeter.Under the action of the forces of this field, electrons are drawn from the surface of the cathode and move to the anode, knocking electrons from it, which form an electron cloud. The initial flow of electrons created in this way further forms an intense ionization of the arc gap.
Along with ionization processes, deionization processes occur in parallel and continuously in the arc. The processes of deionization consist in the fact that when two ions of different signs or a positive ion and an electron approach each other, they are attracted and, colliding, are neutralized, in addition, charged particles move from the burning zone of souls with more - high concentration of charges in the environment with a lower concentration of charges. All these factors lead to a decrease in the temperature of the arc, to its cooling and disappearance.

Rice. 2. Electric arc
Arc after ignition
In the stationary combustion mode, the processes of ionization and deionization are in equilibrium. The arc barrel with an equal amount of free positive and negative charges is characterized by a high degree of gas ionization.
A substance whose degree of ionization is close to unity, i.e. in which there are no neutral atoms and molecules is called plasma.
The electric arc is characterized by the following characteristics:
1. A clearly defined boundary between the arc shaft and the environment.
2. The high temperature inside the arc barrel, reaching 6000 — 25000K.
3. High current density and arc tube (100 — 1000 A / mm2).
4. Small values of the anodic and cathodic voltage drop and practically does not depend on the current (10 — 20 V).
Current-voltage characteristic of an electric arc
The main characteristic of a DC arc is the dependence of the arc voltage on the current, which is called the current-voltage (VAC) characteristic.
The arc occurs between the contacts at a certain voltage (Fig. 3), called the ignition voltage Uz and depending on the distance between the contacts, the temperature and pressure of the environment and the speed of the contact separation. Arc extinguishing voltage Ug always less stress U3.
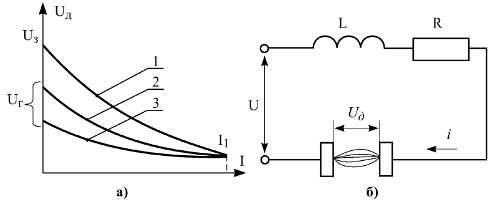
Rice. 3. Current-voltage characteristic of a DC arc (a) and its equivalent circuit (b)
Curve 1 is the static characteristic of the arc, i.e. obtained by slowly varying the current. The characteristic has a falling character. As the current increases, the arc voltage decreases. This means that the resistance of the arc gap decreases faster as the current increases.
If at one speed or another the current in the arc is reduced from I1 to zero and at the same time fix the voltage drop along the arc, then curves 2 and 3 will result. These curves are called dynamic characteristics.
The faster the current is reduced, the lower the dynamic I — V characteristics will be. This is due to the fact that with a decrease in current, such parameters of the arc as the cross section of the barrel, temperature, do not have time to change quickly and acquire values corresponding to a lower value of the current in a steady state.
Arc Gap Voltage Drop:
Ud = Usc + EdId,
where Us = Udo + Ua — voltage drop near the electrode, Ed — longitudinal voltage gradient in the arc, ID — the length of the arc.
It follows from the formula that as the arc length increases, the voltage drop across the arc will increase and the I — V characteristic will be located higher.
They deal with arcing in the design of electrical switching devices. The properties of the electric arc are used in installations for electric arc welding and in arc melting furnaces.
