Classification and labeling of power cables
Power cords are conveniently classified according to the rated voltage for which they are designed. The type of insulation and construction characteristics of the cables can also serve as signs of classification.
All power cables can be conditionally divided into two groups according to their nominal operating voltage. The low-voltage group includes cables intended for operation in electrical networks with isolated neutral alternating voltage 1, 3, 6, 10, 20 and 35 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz. The same cables can be used with an earthed neutral in direct current networks. Such cables are produced with impregnated paper, plastic and rubber insulation, and the most promising type of insulation is plastic. Cables with plastic insulation are easier to manufacture, convenient in installation and operation.
The production of plastic-insulated power cables is currently expanding significantly. Rubber insulated power cords are available in limited quantities. Low-voltage cables, depending on the purpose, are produced in single-core, two-core, three-core and four-core versions.Single-core and three-core cables are used in networks with a voltage of 1-35 kV, two- and four-core cables are used in networks with a voltage of up to 1 kV.
The four-wire cable is designed for four-wire networks with variable voltage. The fourth core in it is grounding or neutral, so its cross-section, as a rule, is smaller than the cross-section of the main wires. When laying cables in hazardous areas and in some other cases, the cross-section of the fourth wire is chosen to be equal to the cross-section of the main wires.
The group of high-voltage cables includes cables designed for operation in alternating current networks of 110, 220, 330, 380, 500, 750 kV and more, as well as direct current cables from +100 to +400 kV and more. The majority of high-voltage cables are currently manufactured with oil-impregnated paper insulation - these are oil-filled low- and high-pressure cables. The high dielectric strength of the insulation of these cables is provided by the excess oil pressure in them. Gas-filled cables have also become widespread overseas, in which gas is used, both as an insulating medium and to create excess pressure in the insulation. High voltage cables with plastic insulation are the most promising.
Power cord markings usually include letters indicating the conductor material, insulation, sheath, and type of sheath protection. The marking of the high voltage cable also reflects its design features.
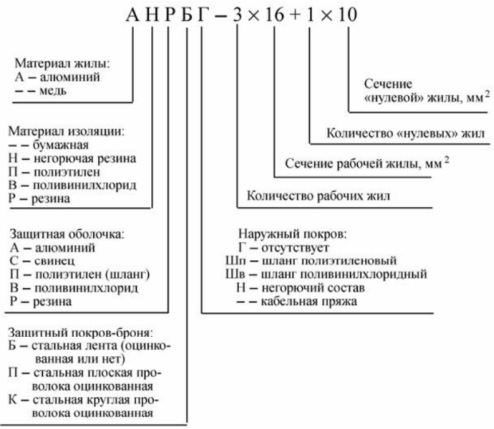
Copper wires are not marked with a special letter in the cable marking, the aluminum wire is marked with the letter A at the beginning of the marking.The next letter of the cable marking indicates the insulation material, and impregnated paper insulation does not have a letter designation, polyethylene insulation is indicated by the letter P, polyvinyl chloride by the letter B, and rubber insulation by the letter P. Then follows the letter corresponding to the type of protective sheath: A — aluminum, C — lead, P — polyethylene hose, B — polyvinyl chloride sheath, R — rubber sheath. The last letters indicate the type of cover.
For example, SG brand cable has a copper core, impregnated paper insulation, lead sheath and no protective covers. The APaShv cable has an aluminum core, polyethylene insulation, an aluminum sheath and a PVC compound hose.
Oil-filled cables contain the letter M in their markings (unlike gas-filled cables, the letter G), as well as a letter denoting the oil pressure characteristic of the cable and related design features. For example, MNS brand cable is an oil-filled low-pressure cable in a lead sheath with a reinforcing and protective cover, or MVDT brand cable is an oil-filled high-pressure cable in a steel conduit.
Symbols for XLPE cables
Basic material
No designation
Copper vein
eg PvP 1×95/16-10
A
Aluminum wire
etc. APvP 1×95/16-10
Insulation material
Pvt
Insulation made of seams
(vulcanized)
polyethylene
ex. PvB 1×95/16-10
Armor
B
Steel belt armor
ex. PvBP 3×95/16-10
Ka
Armor of round aluminum wires e.g. PvKaP 1×95/16-10
Well
Armor made of profiled aluminum wires, e.g. APvPaP 1×95/16-10
Shell
NS
Polyethylene sheath
etc. APvNS 3×150/25-10
Pooh
Polyethylene sheath reinforced with ribs e.g. APvПу3×150/25-10
V
PVC sheath for example. APvV 3×150/25-10
Vng
PVC sheath
reduced flammability
etc. APvVng
G (after the shell designation)
Longitudinal screen sealing with water-swellable strips, for example. APvPG1x150/25-10
2g (after shell designation)
Transverse sealing with an aluminum strip welded to the shell, combined with longitudinal sealing with water-swellable strips, e.g. APvP2g
1×300/35-64/110
Nuclear type
No designation
Round stranded conductor (class 2)
(ready)
Round solid wire (class 1)
ex APvV 1×50 (cool) 16-10

