The use of electric water heaters and water heaters in agriculture
Purpose of water heating installations in agriculture
Electric boilers and boilers are used in local and centralized hot water systems. In local systems, they mostly use elementary and less often electrode water heaters with low (16 — 25 kW) power. In centralized systems, hot water is obtained in electric boiler rooms using high-efficiency hot water boilers, as well as electric steam boilers and boilers.
It is most recommended to use hot water supply systems with hot water storage. For this purpose, storage boilers or flow-through boilers are used in combination with well-insulated tanks - hot water accumulators.
Such systems are the most reliable and economical.Storage boilers, included in the hours of "drops" in the daily load schedules, play an important role for consumers - load regulators of power systems, increasing the degree of utilization of transformer substations and electrical networks, reducing voltage deviations in current collectors and improving Power factor… Accumulation systems can significantly increase electricity consumption without increasing the power of transformer substations and transmission capacity of networks.
Devices for heating drinking water for animals are also specific to livestock farms. In winter, the temperature of the water supplied to the farms from boreholes is 4 - 6 °C, and on surface sources - 1.5 - 2 °C. The need to heat water is primarily due to the physiological needs of animals. According to the zootechnical conditions, the optimal temperature of water in drinking troughs for cattle is 12-14 °C and should not fall below 5-7 °C. For fattening pigs — 1 — 3 ОC for laying hens — 10 — 13 ОC.
Animals and birds drink cold water little and reluctantly, this affects their productivity. At the optimal water temperature, milk yield from a cow is 0.5-1 liter per day higher than usual, the need for feed decreases, egg production in chickens increases by 10-15%, etc. In addition, consumption of the excessively cold pod is fraught with colds, especially for young animals, animals and birds. Water heating is also necessary to prevent indoor water pipes and drinking fountains from freezing, especially in unheated rooms and at night.
The method of heating the water for catching depends on the way the animals are raised.With tied content, the auto-singing network is combined in a closed system with a flow-through electric boiler and pump. Make-up water from the water pipes also enters the heater, where it mixes with the heated, also sending the automatic drinking network. The continuous forced circulation of the heated water ensures a constant temperature. Likewise, water is heated in systems for washing cows' udders before milking, for watering plants in protected land, etc.
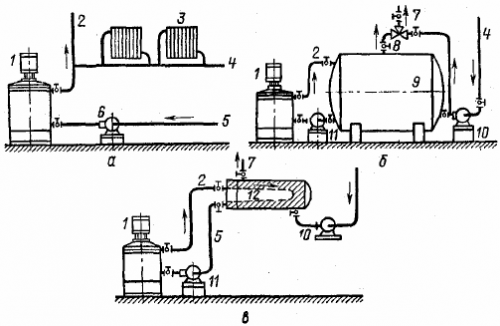
The principles of use of hot water heaters and power electrode heaters are illustrated in Figure 1.
Rice. 1. Schemes of use of electrode boilers and hot water boilers with a voltage of up to 1000 V: a — in the heating system; b — with heat storage capacity; c — with a heat exchanger; 1 — electrode boiler; 2 — main stream; 3 — radiators; 4 — auxiliary network, 5 — return line; 6 — pump (if necessary); 7 — secondary flow and return; 8 — mixing valve; 9 — heat accumulator; 10 — secondary pump; 11 — primary pump; 12 — heat exchanger (boiler).
In hot water supply systems, boilers work in the first circuit of a heat exchanger with a hot water accumulator or a high-speed water-to-water boiler. Operation with a heat exchanger ensures the circulation of non-exchangeable water through the boiler, which significantly reduces the accumulation of scale on the electrodes. Open intake of water from the boilers is possible only if the water is previously softened or if water with a temperature not higher than 60 ° C is used.
Electric boiler unit
Electric boilers are equipped with electric boilers, boilers and other equipment necessary for obtaining steam and hot water and for their delivery to agricultural users.Boiler rooms can be central and local.
Central electric boiler houses are designed for integrated heat supply to a significant number of different consumers, and local ones - for heat supply to a limited number of consumers, usually within one room. Local electric boiler houses are most often specialized: heating or hot water. Hot water or steam generated in electric boilers is delivered to consumers through pipelines (heating networks).
To calculate heat consumption and select boilers, daily heat load schedules are built. The graphs take into account all consumers supplied with heat from the electric boiler house.
The most suitable are electric boiler houses, with a relatively small power (up to 400-600 kW), which do not require large investments for the reconstruction of power supply systems and the construction of expensive heating networks.
Electric boiler rooms must be equipped with heat storage devices (in the form of hot water or steam), where they can be stored during the night hours of operation of an electric thermal installation. During the day, heat is supplied by taking heat from storage tanks.
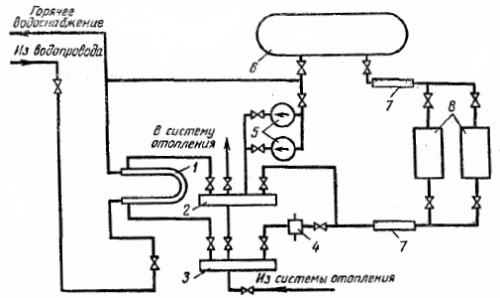
Figure 2 shows a basic diagram of the thermal engineering of a simple electric boiler house with two hot water boilers for heating a livestock farm for 200 — 400 head. Water heated in boilers 8 circulates in a closed system: boiler 8 — heat storage tank, 6 — hot water collector, 2 — heating system — cold water collector, 3 — mud collector, 4 — boiler.
Rice. 2.The basic diagram of the heating technology of the simplest electric boiler house: 1 — high-speed boiler; 2 — hot water collector; 3 — cold water collector; 4 — fender; 5 — circulation pumps; 6 — storage capacity; 7 — insulating insert; 8 — electric boilers (boilers).
Collapsible hot water is obtained in a high-speed boiler 1, where tap water is heated by hot water supplied from collector 2.
Electrical diagram of an electric boiler room
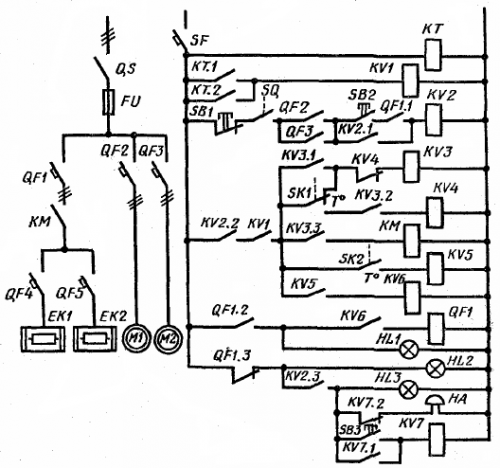
The schematic diagram of the electric boiler house is shown in figure 3.
Rice. 3. Electrical schematic diagram of an electric boiler room
Power is applied to the power circuit via the QS switch. Circulation pumps (primary and reserve) are switched on by automatic switches QF2 and QF3, and boilers by QF4, QF5 and by contactor KM.
Boilers can only be turned on at certain times of the day set by the KT engine time relay, which has two programs. The temperature of the water in the storage tank is monitored by temperature switch SK1. The upper contact SK1 closes when the water temperature is below the norm, the lower contact - when the maximum value is reached. In emergency mode, when the water temperature is 3 — 40 higher than the upper setting of the SKI relay, the SK2 relay is activated.
The locking contact SQ prevents the boilers from starting when the box doors are not closed. The boilers are turned on when one of the contacts of the time relay KT is closed. Before this (by switching on QF2 or QF3) the circulation pump is started, the switches QF4, QF5 and QF1 are switched on.
The SB2 button energizes the coil of the KV2 relay, which, through the intermediate relay KV3, turns on the contactor KM of the boiler supply circuit. When the temperature rises above the minimum, the upper contact SK1 opens, but the KV3 relay is energized through its own contact KV3.1.
When the maximum temperature is reached, the lower contact SK1 closes, the relay KV4 is energized, and through the contact KV3.3, the intermediate relay KV3 removes the voltage from the contactor KM, which turns off the boilers.
In emergency mode, if the circuit does not work, the contact SK2 closes, receives power to the relay KV5, energizes the relay KV6 with its contact, which supplies voltage to the coil of the shunt release of the breaker QF1disconnecting the power supply to the boilers. Contact blocks QF1.3 includes emergency light (HL2) and sound XA.