Principle of operation and fields of application of induction heating
Electrothermal devices that heat electrically conductive materials by injecting inductive currents into them are called induction heaters… Since e. etc. c. induction occurs when the currents that excite the electromagnetic field change, then such devices can only work on alternating current.
The main element of induction heaters is inductor — coil, containing a certain number of turns, which, when alternating current passes through it, creates alternating magnetic field… This is where the (first) conversion of electrical energy into magnetic field energy takes place.
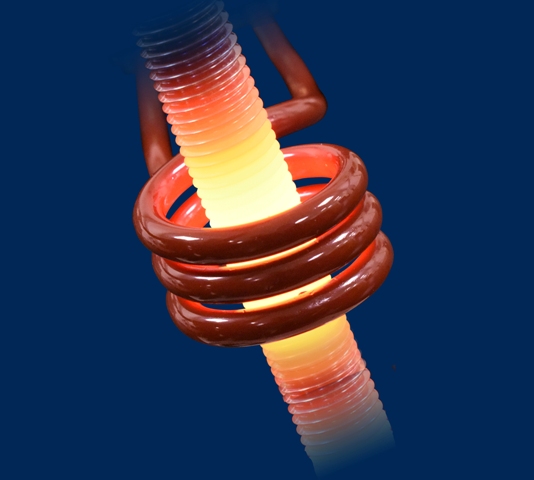
When an electrically conductive body is introduced into an alternating magnetic field, e.g. etc. c. causes the appearance of a «secondary» current. There is a reverse transformation (second) of the magnetic field energy into electrical energy.
Finally, the secondary current induced in the heated body, according to The Joule-Lenz law generates heat: electrical energy is converted into heat.As a result of the third conversion of energy, the heat that provides heating or melting of materials in induction heaters is obtained.
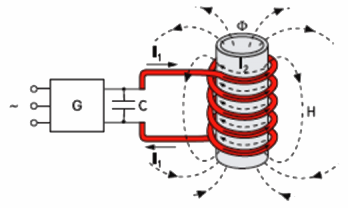
Induction heating circuit
For operation of induction heaters direct contact of the power source with the heated object is not required, only the presence of a magnetic connection between the object and the inductor is required.
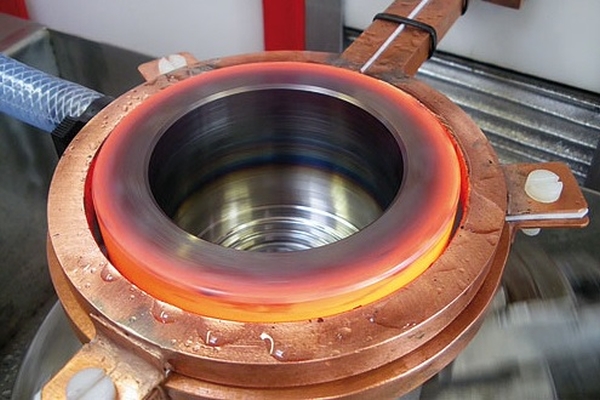
The main and oldest application of induction heaters in industry is their use. such as induction electric furnacesdesigned for melting non-ferrous and ferrous metals and their alloys. Electric induction furnaces ensure high purity of the melt, as they do not introduce any impurities into the molten material.
In addition, induction electric furnaces create uniform heating of the entire mass of molten material without significant local overheating. The latter circumstance is very important when melting multicomponent alloys, the components of which have different melting points. In the presence of local overheating (such as in arc furnaces) in such alloys, lower melting components are intensively consumed and the initial composition of the charge is disturbed.
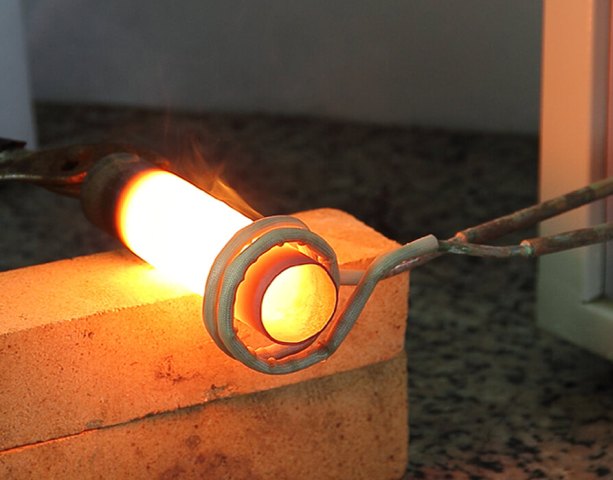

The field of application of induction heaters is not limited to metal melting plants. Often in modern production induction heating used by for surface hardening of parts, in the operations of bending pipes and profiled rolled products from bimetallic products, for welding products with a complex configuration, etc.
When heating electrically conductive materials in a high-frequency electromagnetic field, it plays an important role surface effect... The surface effect becomes more and more apparent as the frequency of the supply current increases.
The ability to quickly heat only the upper layers of the material, which is necessary in surface hardening, is based entirely on the use of this effect.
The thickness of the layer, called «depth of current penetration», depends on the resistance of the material, the frequency of the current and absolute magnetic permeability.
In addition, by choosing such a mode of operation of the induction heater, so as to ensure a high concentration of inductive currents in the surface layers, a significant increase in the efficiency of the heater can be achieved.
The main advantage of the induction surface hardening method is the possibility of a concentrated release of thermal energy in the surface layers of products of arbitrary shape and the possibility of energy transfer without direct contact between the heater and the workpiece. The uniformity of heating of parts with a complex configuration is ensured by inductors of a special shape. Generally the shape of the inductor follows the outline of the part.
 The use of induction heaters, as a rule, improves the quality indicators of technological operations, increases labor productivity and creates conditions for moving production to a higher level with extensive mechanization and process automation.
The use of induction heaters, as a rule, improves the quality indicators of technological operations, increases labor productivity and creates conditions for moving production to a higher level with extensive mechanization and process automation.
Induction heating is also used for such general operation as surfacing… Lamination is the permanent bonding of the weld metal layer to the base metal.
Commonly used is the coating of non-ferrous metals and alloys on steel and cast iron.For surface application, it is necessary and sufficient to melt the filler metal and bring the base metal to a temperature close to the melting point of the filler material. The filler material used for layering can be in any form — in the form of rods, strips, shavings, etc.
The use of induction heating devices in industry is not limited to the considered examples, the scope of their application is extremely wide and increases every year.
Significant advantages in using induction heating methods — efficiency, flexibility of application, high quality of products, increase in labor productivity, etc.
