Inspection and testing of batteries
 In the inspection and testing of storage batteries in electrical substations, the insulation resistance of the battery is measured, its capacity is checked, the density and temperature of the electrolyte in each case is checked, and the voltage of each cell of the battery is checked.
In the inspection and testing of storage batteries in electrical substations, the insulation resistance of the battery is measured, its capacity is checked, the density and temperature of the electrolyte in each case is checked, and the voltage of each cell of the battery is checked.
Measurement of battery insulation resistance
Insulation resistance measurement The accumulator battery is produced by a megohmmeter for a voltage of 500 — 1000 V or by a voltmeter method according to the scheme in fig. 1.
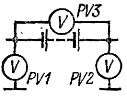
Rice. 1. Measuring the insulation resistance of the storage battery with a voltmeter.
The voltage between the battery poles and the voltage of each pole to ground are measured in series.
Measurements should be made with a single voltmeter accuracy class not lower than 1 with known internal resistance — not less than 50,000 ohms.
Insulation resistance, Ohm,
Rot = (U / (U1 + U2) — 1) NS RHC,
where U — voltage between the poles of the storage battery, V; U1 - voltage between "plus" of the battery and "ground", V, U2 - voltage between "minus" of the battery and "ground", V, Rpr - internal resistance of the voltmeter, Ohm.
The insulation resistance of the battery must be at least:
Nominal voltage, V 24 48 110 220 Insulation resistance, kOhm 14 25 50 100
Checking the capacity of a molded battery
The accumulator battery is charged until (within 1 hour) the cell voltage is equal to 2.6 - 2.75 V and all plates are strongly outgassed.
30 minutes after the end of charging, a control discharge is carried out with a current of 3 or 10 hours for acid and 8 hours for alkaline batteries.
The discharge is carried out to the load resistance or to the charge generator, which is transferred to the motor mode by reducing the excitation current.
During the control discharge, the following are measured hourly: the voltage at the terminals of each cell and the entire battery, the discharge current, the density of the electrolyte in the cells, the temperature of the electrolyte in the control cells.
Discharge is carried out until the voltage at the terminals of the element drops to 1.8 V.
If at least one battery cell voltage is below 1.8 V, discharge must be stopped.
The capacity obtained as a result of the discharge in ampere-hours is brought to a temperature of +25 ° C according to the formula
C25 = Ct / (1 + 0.008 (t — 25)),
where t is the average temperature of the electrolyte during discharge, ° C, Ct is the capacity obtained during discharge, Ah, C25 — capacity reduced to a temperature of + 25 ° C, Ah; 0.008 — temperature coefficient.
The battery capacity obtained as a result of the control discharge, reduced to a temperature of +25 ° C, must correspond to the manufacturer's data.
 Batteries in substation
Batteries in substation
Checking the density and temperature of the electrolyte in each box
The density of the electrolyte at the end of charging should be in the range of 1.2 - 1.21 in cells with surface structure plates (C and SC) and 1.24 in cells with armored plates (SP and SPK), the temperature should not is higher than +40 OS.
The density of the electrolyte at the end of the control discharge of the storage battery must be at least 1.145 in cells C and SK and at least 1.185 in cells SP and SPK.
Checking the voltage of each battery cell
Lagging elements should not exceed 5% of their total number. The voltage of the lagging elements at the end of the discharge should not differ by more than 1 - 1.5% from the average voltage of the remaining elements.
The voltage at the end of the discharge should be at least 1.8 V for Type C (SK) batteries at 3-, 10-hour discharge mode and at least 1.75 V at 0.5, 1, 2- hourly discharge mode.

