Laboratory ovens
 Since laboratories only have to deal with very small quantities of heated materials or products, laboratory ovens must be small, compact, low power, yet versatile and cover a wide temperature range.
Since laboratories only have to deal with very small quantities of heated materials or products, laboratory ovens must be small, compact, low power, yet versatile and cover a wide temperature range.
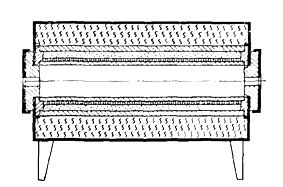
Tube, shaft (crucible) and muffle furnaces are most often used in laboratories. In tube, shaft and muffle furnaces at moderate temperatures, a heating wire or strip is wound on a ceramic tube or muffle (fireclay and corundum for higher temperatures) and everything is placed in a jacket with bulk thermal insulation (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Tubular laboratory furnace
Tubular laboratory furnaces, as a rule, are equipped with two doors, silencing — one. To prevent the heater from moving during expansion due to heating and to prevent short-circuiting of the coil, the muffle and tubes are made with spiral grooves in which the wire is laid. Another way to fix it is to coat the muffle or tube on the heater with a layer of coating (eg fireclay).

Since, in addition, the power of laboratory furnaces is low and the heaters are made of wire or tape with small cross-sections, such furnaces can usually work on nichrome up to 800 — 900 ° C.
For higher temperatures, tube and shaft furnaces are manufactured with an open spiral heater of alloy 0Kh23Yu5A (EI-595) and 0Kh27Yu5A (EI-626), laid in the channels of a tube or shaft, such furnaces can operate up to 1200-1250 ° C .A number of structures of tube, shaft and muffle furnaces at 1200 — 1500 ° C are made with carborundum (Fig. 2) heaters and molybdenum disilicide.
Rice. 2. Laboratory tube furnace with carbide tube heater
Previously widely used laboratory furnaces with platinum heaters are currently not produced, since the temperature range of 1000 — 1300 ° C of such furnaces is currently covered by furnaces with cheaper heaters made of alloys 0X23Yu5A and 0Kh27Yu5A or carburund.
 For higher temperatures, furnaces with coal or graphite heaters were formerly widely used, and even now they are still used.
For higher temperatures, furnaces with coal or graphite heaters were formerly widely used, and even now they are still used.
The most common furnace is the central part of which is a coal tube that serves as a heater. The inner part of the tube is the working space in which the products or materials to be heated are placed.
The ends of the tubes are clamped in powerful shoes of carbon or cast iron, through which voltage is supplied to it from a step-down transformer.Thermal insulation at such high temperatures is either soot, which fills the entire space between the furnace body and the pipe, or ceramic or carbon screens.
Since the carbon tube oxidizes intensively in the air, the furnace body is hermetically sealed and the furnace operates in an atmosphere of hydrogen, nitrogen, or in a vacuum. If the furnace is operated without a protective atmosphere, then the service life of the coal tube is measured in hours.

Furnaces with a coal heater operate at temperatures of about 1500 — 1700 ° C, but with special construction 2000 — 2100 ° C can be obtained.
Since furnaces with a graphite (carbon) heater are inconvenient to operate and cannot be used in cases where carburization of the heated materials is undesirable, furnaces with molybdenum and tungsten heaters with screens, vacuum or hydrogen have also become widely used in laboratory practice used.
See also on this topic: Electrical equipment of a mining electric furnace SSHOD